Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2019 Jul;22(4):358-368. 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.358.
Use of Anti-TNF Alpha Blockers Can Reduce Operation Rate and Lead to Growth Gain in Pediatric Crohn's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mjschj@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2451576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.358
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Pediatric Crohn's disease (CD) is directly related to growth and has a high probability of requiring surgical intervention(s); therefore, more active treatment for CD is required for children. This study investigated the impact of biologics on growth and disease course associated with surgery.
METHODS
This was a retrospective cohort study involving patients diagnosed with CD at the Seoul National University Children's Hospital (Seoul, Korea) between January 2006 and October 2017. The aim was to determine the characteristics of pediatric patients with CD and whether biologics affected growth and the surgical disease course.
RESULTS
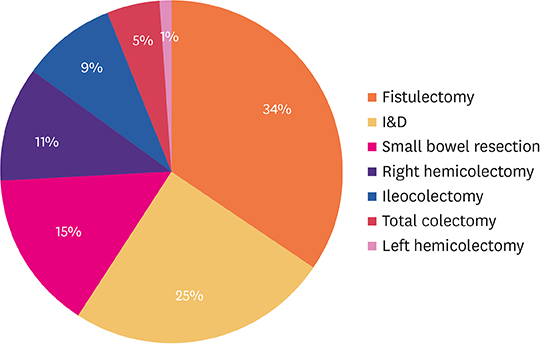
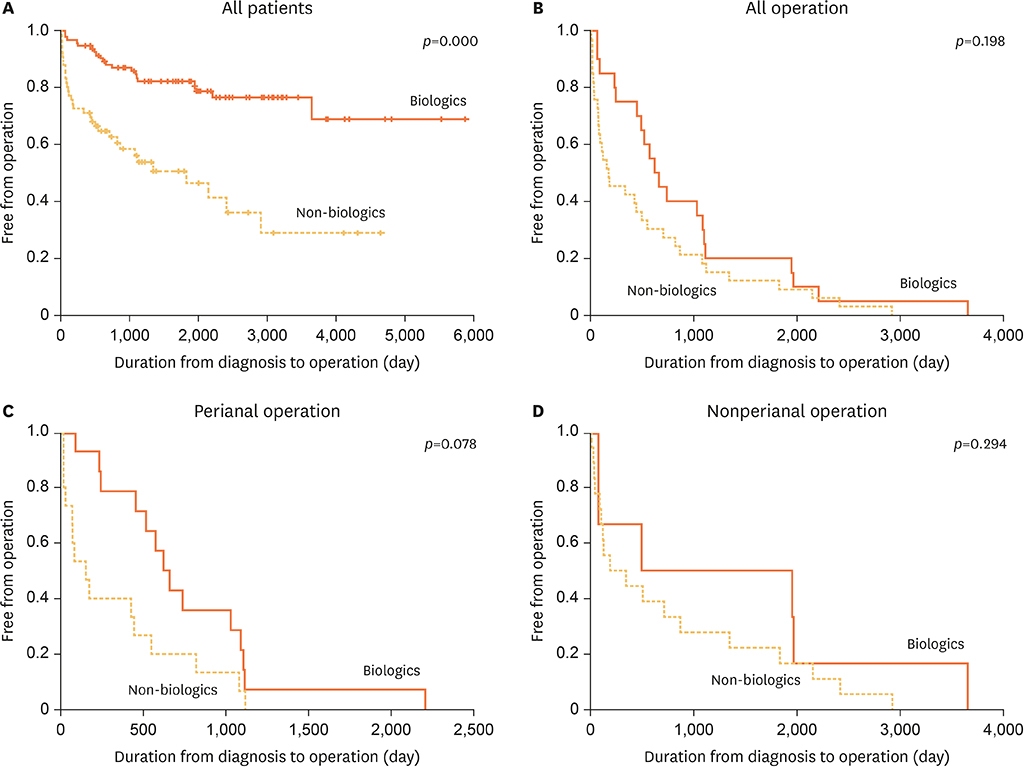
Among patients who underwent surgery for CD, the mean number of operations per patient was 1.89. The mean time from initial diagnosis to surgery was 19.3 months. The most common procedure was fistulectomy (34%), followed by incision and drainage (25%). In all patients, the use of biologics increased the height (p=0.002) and body mass index (BMI) (p=0.005). Among patients who underwent surgery, height (p=0.004) and BMI (p=0.048) were increased in the group using biologics. Patients who used biologics exhibited a low operation rate only within 2 years after diagnosis, with no differences thereafter (p=0.027).
CONCLUSION
Although biologics could not mitigate the operation rate in pediatric patients who underwent surgery for CD, biological therapy delayed disease progression within 2 years of disease onset. Additionally, biologics conferred growth and BMI benefits in this window period. Therefore, it may be helpful to use biologics for optimal growth in pediatric patients with a high probability of undergoing future surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee YJ, Oh SH, Kim KM. The principles of drug therapy of Crohn's disease in child and adolescent. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010; 13:S59–69.
Article2. Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, Wong M, Chow CM, Hui A, et al. Incidence and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease based on results from the Asia-pacific Crohn's and colitis epidemiology study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:158–165.e2.
Article3. Polito JM 2nd, Childs B, Mellits ED, Tokayer AZ, Harris ML, Bayless TM. Crohn's disease: influence of age at diagnosis on site and clinical type of disease. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:580–586.
Article4. Cuffari C, Dubinsky M, Darbari A, Sena L, Baldassano R. Crohn's jejunoileitis: the pediatrician's perspective on diagnosis and management. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005; 11:696–704.
Article5. Lee YA, Chun P, Hwang EH, Mun SW, Lee YJ, Park JH. Clinical features and extraintestinal manifestations of Crohn disease in children. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016; 19:236–242.
Article6. Vernier-Massouille G, Balde M, Salleron J, Turck D, Dupas JL, Mouterde O, et al. Natural history of pediatric Crohn's disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:1106–1113.
Article7. Kim S. Surgery in pediatric Crohn's disease: indications, timing and post-operative management. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2017; 20:14–21.
Article8. Sawczenko A, Ballinger AB, Savage MO, Sanderson IR. Clinical features affecting final adult height in patients with pediatric-onset Crohn's disease. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:124–129.
Article9. Kanof ME, Lake AM, Bayless TM. Decreased height velocity in children and adolescents before the diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988; 95:1523–1527.
Article10. Akobeng AK, Zachos M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody for induction of remission in Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; CD003574.
Article11. Schnitzler F, Fidder H, Ferrante M, Noman M, Arijs I, Van Assche G, et al. Mucosal healing predicts long-term outcome of maintenance therapy with infliximab in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009; 15:1295–1301.
Article12. Rutgeerts P, Diamond RH, Bala M, Olson A, Lichtenstein GR, Bao W, et al. Scheduled maintenance treatment with infliximab is superior to episodic treatment for the healing of mucosal ulceration associated with Crohn's disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:433–442.
Article13. Borrelli O, Bascietto C, Viola F, Bueno de Mesquita M, Barbato M, Mancini V, et al. Infliximab heals intestinal inflammatory lesions and restores growth in children with Crohn's disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2004; 36:342–347.
Article14. Walters TD, Kim MO, Denson LA, Griffiths AM, Dubinsky M, Markowitz J, et al. Increased effectiveness of early therapy with anti-tumor necrosis factor-α vs an immunomodulator in children with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:383–391.
Article15. Lichtenstein GR, Yan S, Bala M, Blank M, Sands BE. Infliximab maintenance treatment reduces hospitalizations, surgeries, and procedures in fistulizing Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2005; 128:862–869.
Article16. Poritz LS, Rowe WA, Koltun WA. Remicade does not abolish the need for surgery in fistulizing Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2002; 45:771–775.
Article17. Hoekman DR, Stibbe JA, Baert FJ, Caenepeel P, Vergauwe P, De Vos M, et al. Long-term outcome of early combined immunosuppression versus conventional management in newly diagnosed Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2018; 12:517–524.
Article18. Ricart E, Panaccione R, Loftus EV, Tremaine WJ, Sandborn WJ. Infliximab for Crohn's disease in clinical practice at the Mayo Clinic: the first 100 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:722–729.
Article19. de Onis M, Garza C, Victora CG, Onyango AW, Frongillo EA, Martines J. The WHO multicentre growth reference study: planning, study design, and methodology. Food Nutr Bull. 2004; 25:S15–26.
Article20. de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ. 2007; 85:660–667.
Article21. Hyams JS, Ferry GD, Mandel FS, Gryboski JD, Kibort PM, Kirschner BS, et al. Development and validation of a pediatric Crohn's disease activity index. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991; 12:439–447.
Article22. Hassan K, Cowan FJ, Jenkins HR. The incidence of childhood inflammatory bowel disease in Wales. Eur J Pediatr. 2000; 159:261–263.
Article23. Henriksen M, Jahnsen J, Lygren I, Aadland E, Schulz T, Vatn MH, et al. Clinical course in Crohn's disease: results of a five-year population-based follow-up study (the IBSEN study). Scand J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:602–610.
Article24. Vasseur F, Gower-Rousseau C, Vernier-Massouille G, Dupas JL, Merle V, Merlin B, et al. Nutritional status and growth in pediatric Crohn's disease: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:1893–1900.
Article25. Ruemmele FM, Veres G, Kolho KL, Griffiths A, Levine A, Escher JC, et al. Consensus guidelines of ECCO/ESPGHAN on the medical management of pediatric Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2014; 8:1179–1207.
Article26. Malik S, Ahmed SF, Wilson ML, Shah N, Loganathan S, Naik S, et al. The effects of anti-TNF-α treatment with adalimumab on growth in children with Crohn's disease (CD). J Crohns Colitis. 2012; 6:337–344.
Article27. Walters TD, Gilman AR, Griffiths AM. Linear growth improves during infliximab therapy in children with chronically active severe Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:424–430.
Article28. Assa A, Hartman C, Weiss B, Broide E, Rosenbach Y, Zevit N, et al. Long-term outcome of tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist's treatment in pediatric Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2013; 7:369–376.
Article29. Walters TD, Griffiths AM. Mechanisms of growth impairment in pediatric Crohn's disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 6:513–523.
Article30. Appau KA, Fazio VW, Shen B, Church JM, Lashner B, Remzi F, et al. Use of infliximab within 3 months of ileocolonic resection is associated with adverse postoperative outcomes in Crohn's patients. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008; 12:1738–1744.
Article31. Sakatani A, Fujiya M, Ito T, Inaba Y, Ueno N, Kashima S, et al. Infliximab extends the duration until the first surgery in patients with Crohn's disease. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:879491.
Article32. Zachos M, Tondeur M, Griffiths AM. Enteral nutritional therapy for induction of remission in Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; CD000542.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Weight Gain and Improvement of Osteoporosis with Anti-TNF Therapy
- Natural Course of Crohn's Disease and Novel Treatment Drugs
- Medical Treatment of Vasculitis; Anti-TNF-alpha Treatment
- Preoperative use of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in Crohn's disease: promises and pitfalls
- The Risk of Tuberculosis in Korean Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Receiving Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Blockers