Electrolyte Blood Press.
2019 Jun;17(1):7-15. 10.5049/EBP.2019.17.1.7.
Delta Neutrophil Index is Useful to Predict Poor Outcomes in Male Patients with Alcoholic Ketoacidosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nephrology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. junning@naver.com
- KMID: 2451516
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2019.17.1.7
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Alcoholic ketoacidosis (AKA) is known as a benign disease, but the related mortality reported in Korea is high. Acidosis and alcohol change the immunity profile, and these changes can be identified early using the delta neutrophil index (DNI). We aimed to evaluate the use of DNI and other standard laboratory parameters as predictors of prognosis in AKA patients.
METHODS
One hundred eighteen males with AKA were evaluated at the Wonju Severance Christian hospital between 2009 and 2014. We performed a retrospective analysis of demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters data. Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) and multivariate Cox regression was used to identify renal survival and mortality.
RESULTS
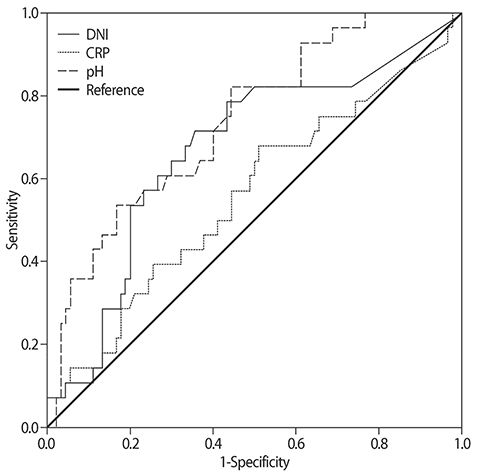
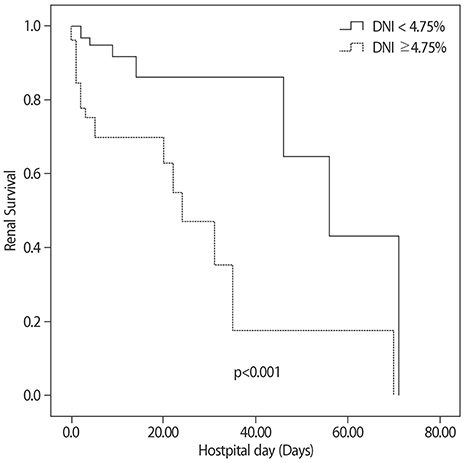
Survival patients had lower initial DNI levels than non-survival patients (4.8±6.4 vs 11.4±12.5, p<0.001). In multivariate-adjusted Cox regression analysis, higher initial increased DNI (HR 1.044, 95% CI 1.003-1.086, p=0.035), and lower initial pH (HR 0.044, 95% CI 0.004-0.452, p=0.008) were risk factors for dialysis during hospitalization. Further, higher initial DNI level (HR 1.037; 95% CI 1.006-1.069; p=0.018), lower initial pH (HR 0.049; 95% CI 0.008-0.312; p=0.001) and lower initial glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (HR 0.981; 95% CI 0.964-0.999; p=0.033) were predictors of mortality. A DNI value of 4.5% was selected as the cut-off value for poor prognosis and Kaplan-Meier plots showed that AKA patients with an initial level DNI ≥4.5% had lower cumulative survival rates than AKA patients with an initial DNI <4.5%.
CONCLUSION
Increased initial serum DNI levels may help to predict renal survival and prognosis in male AKA patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McGuire LC, Cruickshank AM, Munro PT. Alcoholic ketoacidosis. Emerg Med J. 2006; 23:417–420.
Article2. Kraut JA, Kurtz I. Toxic alcohol ingestions: Clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 3:208–225.
Article3. Lee JW, Yang SJ, Jin SC, Joo MD, Choi WI. The prognostic factors for alcoholic ketoacidosis. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2009; 20:86–94.4. Wrenn KD, Slovis CM, Minion GE, Rutkowski R. The syndrome of alcoholic ketoacidosis. Am J Med. 1991; 91:119–128.
Article5. Palmiere C, Augsburger M. The postmortem diagnosis of alcoholic ketoacidosis. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014; 49:271–281.
Article6. Cook RT. Alcohol abuse, alcoholism, and damage to the immune system--a review. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998; 22:1927–1942.
Article7. Seok Y, Choi JR, Kim J, Kim YK, Lee J, Song J, et al. Delta neutrophil index: A promising diagnostic and prognostic marker for sepsis. Shock. 2012; 37:242–246.8. Nahm CH, Choi JW, Lee JW. Delta neutrophil index in automated immature granulocyte counts for assessing disease severity of patients with sepsis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2008; 38:241–246.9. Ahn CW, Kim WH, Lim TH, Cho Ys, Choi KS, Jang BH. The delta neutrophil index (DNI) as a prognostic marker for mortality in adults with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:6621.
Article10. Park BH, Kang YA, Park MS, Jung WJ, Lee SH, Lee SK, et al. Delta neutrophil index as an early marker of disease severity in critically ill patients with sepsis. BMC Infect Dis. 2011; 11:299.
Article11. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: A severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13:818–829.12. Kratz A, Maloum K, O'Malley C, Zini G, Rocco V, Zelmanovic D, et al. Enumeration of nucleated red blood cells with the ADVIA 2120 Hematology System: An International Multicenter Clinical Trial. Lab Hematol. 2006; 12:63–70.
Article13. Harris N, Jou JM, Devoto G, Lotz J, Pappas J, Wranovics D, et al. Performance evaluation of the ADVIA 2120 hematology analyzer: An international multicenter clinical trial. Lab Hematol. 2005; 11:62–70.
Article14. Noor NM, Basavaraju K, Sharpstone D. Alcoholic ketoacidosis: A case report and review of the literature. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2016; 2016:31–33.
Article15. Halperin ML, Hammeke M, Josse RG, Jungas RL. Metabolic acidosis in the alcoholic: A pathophysiologic approach. Metabolism. 1983; 32:308–315.
Article16. Romeo J, Warnberg J, Nova E, Diaz LE, Gomez-Martinez S, Marcos A. Moderate alcohol consumption and the immune system: A review. 98 Supp. Br J Nutr. 2007; 98:Suppl 1. S111–S115.17. Gamble L, Mason CM, Nelson S. The effects of alcohol on immunity and bacterial infection in the lung. Med Mal Infect. 2006; 36:72–77.18. Zhang P, Bagby GJ, Happel KI, Raasch CE, Nelson S. Alcohol abuse, immunosuppression, and pulmonary infection. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008; 1:56–67.
Article19. Laso FJ, Madruga JI, Lopez A, Ciudad J, Alvarez-Mon M, San Miguel J, et al. Abnormalities of peripheral blood T lymphocytes and natural killer cells in alcoholic hepatitis persist after a 3-month withdrawal period. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997; 21:672–676.
Article20. Laso FJ, Madruga JI, San Miguel JF, Ciudad J, Lopez A, Alvarez Mon M, et al. Long lasting immunological effects of ethanol after withdrawal. Cytometry. 1996; 26:275–280.
Article21. Lindroos-Jokinen K, Keltanen T, Vanhala T, Valonen T, Sajantila A. Postmortem measurement of C-reactive protein and interpretation of results in ketoacidosis. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2012; 14:140–146.
Article22. Jain SK, McVie R, Bocchini JA Jr. Hyperketonemia (ketosis), oxidative stress and type 1 diabetes. Pathophysiology. 2006; 13:163–170.
Article23. Kellum JA, Song M, Li J. Science review: extracellular acidosis and the immune response: clinical and physiologic implications. Crit Care. 2004; 8:331–336.24. Lardner A. The effects of extracellular pH on immune function. J Leukoc Biol. 2001; 69:522–530.25. De Marchi S, Cecchin E, Basile A, Bertotti A, Nardini R, Bartoli E. Renal tubular dysfunction in chronic alcohol abuse--effects of abstinence. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:1927–1934.
Article26. Zhou C, Byard RW. Basal renal tubular epithelial cell vacuolization and alcoholic ketoacidosis. J Forensic Sci. 2012; 57:126–128.
Article27. Kellum JA, Song M, Venkataraman R. Effects of hyperchloremic acidosis on arterial pressure and circulating inflammatory molecules in experimental sepsis. Chest. 2004; 125:243–248.
Article28. Kraut JA, Madias NE. Metabolic acidosis: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010; 6:274–285.
Article29. Yu J, Shin Y, Jung HJ, Yun YS, Kim HG, Kim YS, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of acute kidney injury in patients with acute alcohol intoxication. Korean J Nephrol. 2011; 30:26–34.30. Tran DD, Groeneveld AB, van der Meulen J, Nauta JJ, Strack van Schijndel RJ, Thijs LG. Age, chronic disease, sepsis, organ system failure, and mortality in a medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1990; 18:474–479.
Article31. Deitch EA. Multiple organ failure. Pathophysiology and potential future therapy. Ann Surg. 1992; 216:117–134.
Article32. Moss M, Parsons PE, Steinberg KP, Hudson LD, Guidot DM, Burnham EL, et al. Chronic alcohol abuse is associated with an increased incidence of acute respiratory distress syndrome and severity of multiple organ dysfunction in patients with septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:869–877.
Article33. Beal AL, Cerra FB. Multiple organ failure syndrome in the 1990s - Systemic inflammatory response and organ dysfunction. JAMA. 1994; 271:226–233.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessment of Perforation of Acute Appendicitis using the Delta Neutrophil Index Reflecting Peripheral Immature Granulocyte Count
- Usefulness of the delta neutrophil index to lymphocyte ratio to predict prognosis in sepsis patients in the emergency department
- Bilateral Lesion of the Basal Ganglia in Patient with Alcoholic Ketoacidosis : Case Report
- Does delta neutrophil index predict 30-day mortality in patients admitted tointensive care unit via emergency department?
- Delta Neutrophil Index Is Associated with Vasculitis Activity and Risk of Relapse in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis