Ann Dermatol.
2019 Aug;31(4):446-449. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.4.446.
Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome by Adalimumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Soon Chun Hyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Soon Chun Hyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. freesia0210@naver.com
- KMID: 2451484
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.4.446
Abstract
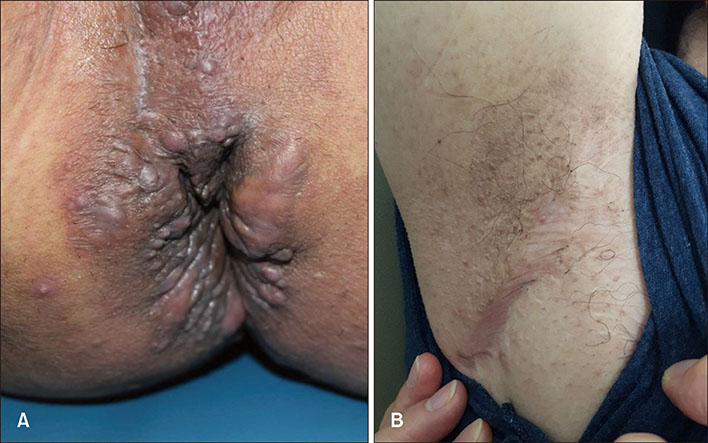
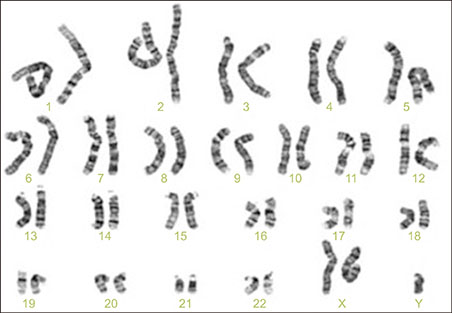
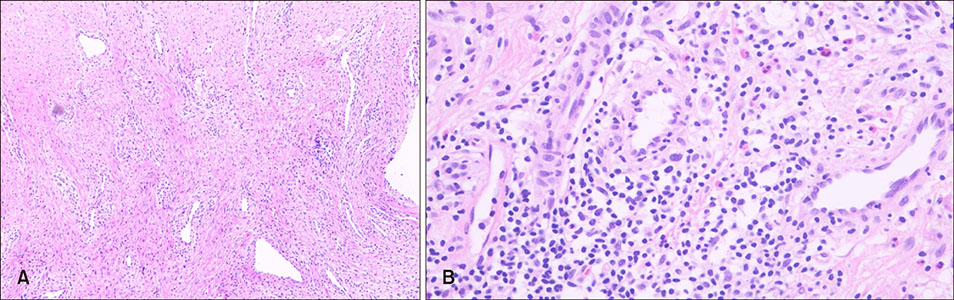
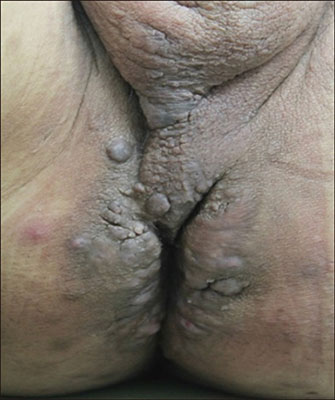
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, inflammatory and painful skin disease with recurrent nodules and tracts involving the intertriginous regions. It is known that the patient with HS shows an increased risk of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome and autoimmune diseases. Klinefelter syndrome (KS) is a sex chromosomal disorder occurring in males due to an abnormality of sexual differentiation, characterized by 47, XXY karyotype. Also, KS is related with somatic comorbidities such as metabolic syndrome, autoimmune and rheumatologic disorders as HS is. We report a HS patient with KS who shows a big improvement while on tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thorlacius L, Theut Riis P, Jemec GBE. Severe hidradenitis suppurativa responding to treatment with secukinumab: a case report. Br J Dermatol. 2018; 179:182–185.
Article2. Lim ZV, Oon HH. Management of hidradenitis suppurativa in patients with metabolic comorbidities. Ann Dermatol. 2016; 28:147–151.
Article3. Boer J. Does obesity cause a distinct phenotype of hidradenitis suppurativa? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018; 32:e195–e196.
Article4. Baillargeon J, Al Snih S, Raji MA, Urban RJ, Sharma G, Sheffield-Moore M, et al. Hypogonadism and the risk of rheumatic autoimmune disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2016; 35:2983–2987.
Article5. Oktenli C, Yesilova Z, Kocar IH, Musabak U, Ozata M, Inal A, et al. Study of autoimmunity in Klinefelter's syndrome and idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J Clin Immunol. 2002; 22:137–143.6. Jiang-Feng M, Hong-Li X, Xue-Yan W, Min N, Shuang-Yu L, Hong-Ding X, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetes in patients with Klinefelter syndrome: a longitudinal observational study. Fertil Steril. 2012; 98:1331–1335.
Article7. Maarouf M, Clark AK, Lee DE, Shi VY. Targeted treatments for hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of the current literature and ongoing clinical trials. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018; 29:441–449.
Article8. Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, Patruno C, Balato N, Fabbrocini G, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017; 10:105–115.
Article9. Høst C, Skakkebæk A, Groth KA, Bojesen A. The role of hypogonadism in Klinefelter syndrome. Asian J Androl. 2014; 16:185–191.
Article10. Kobak S, Yalçin M, Karadeniz M, Oncel G. Coexistence of ankylosing spondylitis and Klinefelter's syndrome. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2013; 2013:543953.
Article11. Belling K, Russo F, Jensen AB, Dalgaard MD, Westergaard D, Rajpert-De Meyts E, et al. Klinefelter syndrome comorbidities linked to increased X chromosome gene dosage and altered protein interactome activity. Hum Mol Genet. 2017; 26:1219–1229.
Article12. Seminog OO, Seminog AB, Yeates D, Goldacre MJ. Associations between Klinefelter's syndrome and autoimmune diseases: English national record linkage studies. Autoimmunity. 2015; 48:125–128.
Article13. Bobjer J, Katrinaki M, Tsatsanis C, Lundberg Giwercman Y, Giwercman A. Negative association between testosterone concentration and inflammatory markers in young men: a nested cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e61466.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Skin Infection Caused by Serratia marcescens in an Immunocompetent Patient with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Management of severe hidradenitis suppurativa with biologic therapy and wide excision
- Sqamous Cell Carcinoma Arising from Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Patients with Metabolic Comorbidities