Korean J Radiol.
2016 Jun;17(3):396-404. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.396.
Liver Shear-Wave Velocity and Serum Fibrosis Markers to Diagnose Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ultrasonography, Baoji Central Hospital, Baoji, Shaanxi 721008, China. guoliangbj@126.com
- 2Department of Ultrasonography, The First Affiliated Hospital of Medical College, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710061, China.
- 3Department of Infectious Disease, Baoji Central Hospital, Baoji, Shaanxi 721008, China.
- KMID: 2451413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.396
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare several noninvasive indices of fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis B, including liver shear-wave velocity (SWV), hyaluronic acid (HA), collagen type IV (CIV), procollagen type III (PCIII), and laminin (LN).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
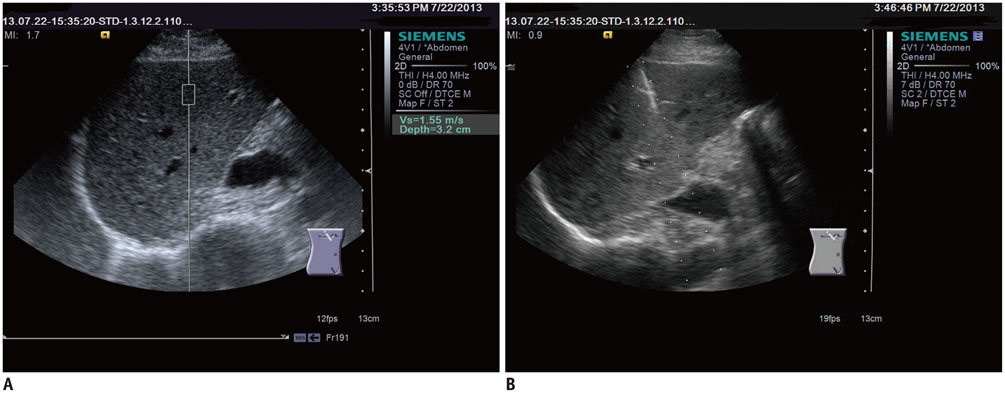
Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) was performed in 157 patients with chronic viral hepatitis B and in 30 healthy volunteers to measure hepatic SWV (m/s) in a prospective study. Serum markers were acquired on the morning of the same day of the ARFI evaluation. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to evaluate and compare the accuracies of SWV and serum markers using METAVIR scoring from liver biopsy as a reference standard.
RESULTS
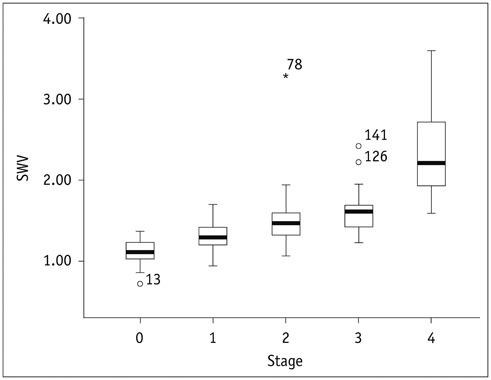
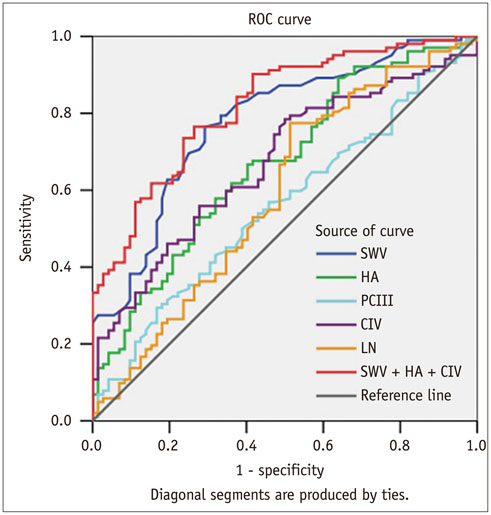
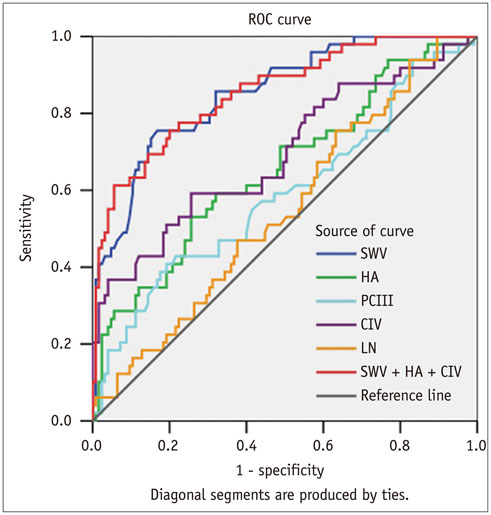
The most accurate test for diagnosing fibrosis F ≥ 1 was SWV with the area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.913, followed by LN (0.744), HA (0.701), CIV (0.690), and PCIII (0.524). The best test for diagnosing F ≥ 2 was SWV (AUC of 0.851), followed by CIV (0.671), HA (0.668), LN (0.562), and PCIII (0.550). The best test for diagnosing F ≥ 3 was SWV (0.854), followed by CIV (0.693), HA (0.675), PCIII (0.591), and LN (0.548). The best test for diagnosing F = 4 was SWV (0.965), followed by CIV (0.804), PCIII (0.752), HA (0.744), and LN (0.662). SWV combined with HA and CIV did not improve diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.931 for F ≥ 1, 0.863 for F ≥ 2, 0.855 for F ≥ 3, 0.960 for F = 4).
CONCLUSION
The performance of SWV in diagnosing liver fibrosis is superior to that of serum markers. However, the combination of SWV, HA, and CIV does not increase the accuracy of diagnosing liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Area Under Curve
Biomarkers/*blood
Case-Control Studies
Collagen Type III/blood
Collagen Type IV/blood
Elasticity Imaging Techniques
Female
Hepatitis B, Chronic/complications/*diagnosis/pathology
Humans
Hyaluronic Acid/blood
Laminin/blood
Liver/diagnostic imaging/pathology/*physiology
Liver Cirrhosis/complications/*diagnosis/pathology
Male
Middle Aged
Prospective Studies
Pulse Wave Analysis
ROC Curve
Severity of Illness Index
Young Adult
Biological Markers
Collagen Type III
Collagen Type IV
Laminin
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Quantitative Measurement of Hepatic Fibrosis with Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: A Comparative Study on Aspartate Aminotransferase to Platelet Ratio Index and Fibrosis-4 Index
Guy Mok Lee, Youe Ree Kim, Jong Hyun Ryu, Tae-Hoon Kim, Eun Young Cho, Young Hwan Lee, Kwon-Ha Yoon
Korean J Radiol. 2017;18(3):444-451. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.3.444.Impact of Liver Fibrosis and Fatty Liver on T1rho Measurements: A Prospective Study
Shuangshuang Xie, Qing Li, Yue Cheng, Yu Zhang, Zhizheng Zhuo, Guiming Zhao, Wen Shen
Korean J Radiol. 2017;18(6):898-905. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.6.898.
Reference
-
1. Ahmad A, Ahmad R. Understanding the mechanism of hepatic fibrosis and potential therapeutic approaches. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:155–167.2. Mormone E, George J, Nieto N. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis and current therapeutic approaches. Chem Biol Interact. 2011; 193:225–231.3. Seki E, Brenner DA. Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015; 22:512–518.4. Manning DS, Afdhal NH. Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1670–1681.5. Jin SY. [Role of liver biopsy in the assessment of hepatic fibrosis--its utility and limitations]. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:138–145.6. Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, Milikowski C, Molina EG, Pyrsopoulos NT, et al. Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:2614–2618.7. Westin J, Lagging LM, Wejstål R, Norkrans G, Dhillon AP. Interobserver study of liver histopathology using the Ishak score in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Liver. 1999; 19:183–187.8. Standish RA, Cholongitas E, Dhillon A, Burroughs AK, Dhillon AP. An appraisal of the histopathological assessment of liver fibrosis. Gut. 2006; 55:569–578.9. Castera L. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Int. 2011; 5:625–634.10. Poynard T, Ngo Y, Perazzo H, Munteanu M, Lebray P, Moussalli J, et al. Prognostic value of liver fibrosis biomarkers: a metaanalysis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7:445–454.11. Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, et al. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005; 41:48–54.12. Lups¸or M, Badea R, Stefănescu H, Grigorescu M, Sparchez Z, Serban A, et al. Analysis of histopathological changes that influence liver stiffness in chronic hepatitis C. Results from a cohort of 324 patients. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2008; 17:155–163.13. Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S, Sotoudeh F, Richter S, Bojunga J, et al. Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology. 2009; 252:595–604.14. Sporea I, Sirli R, Bota S, Fierbint¸eanu-Braticevici C, Petris¸or A, Badea R, et al. Is ARFI elastography reliable for predicting fibrosis severity in chronic HCV hepatitis? World J Radiol. 2011; 3:188–193.15. Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology. 1996; 24:289–293.16. Rifai K, Cornberg J, Mederacke I, Bahr MJ, Wedemeyer H, Malinski P, et al. Clinical feasibility of liver elastography by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI). Dig Liver Dis. 2011; 43:491–497.17. Goertz RS, Amann K, Heide R, Bernatik T, Neurath MF, Strobel D. An abdominal and thyroid status with Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastometry--a feasibility study: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastometry of human organs. Eur J Radiol. 2011; 80:e226–e230.18. Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, Dănilă M, Sendroiu M, et al. Spleen assessment by Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography (ARFI) for prediction of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Med Ultrason. 2010; 12:213–217.19. Zhai L, Madden J, Foo WC, Palmeri ML, Mouraviev V, Polascik TJ, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of human prostates ex vivo. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010; 36:576–588.20. Fahey BJ, Nightingale KR, Nelson RC, Palmeri ML, Trahey GE. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the abdomen: demonstration of feasibility and utility. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005; 31:1185–1198.21. Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Andronescu D, Usvat R, Cretoiu D, Baicus C, Marinoschi G. Acoustic radiation force imaging sonoelastography for noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:5525–5532.22. Zhu CL, Li WT, Li Y, Gao RT. Serum levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 are correlated with liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Dig Dis. 2012; 13:558–563.23. Parsian H, Rahimipour A, Nouri M, Somi MH, Qujeq D. Assessment of liver fibrosis development in chronic hepatitis B patients by serum hyaluronic acid and laminin levels. Acta Clin Croat. 2010; 49:257–265.24. Dong DR, Hao MN, Li C, Peng Z, Liu X, Wang GP, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography, FibroScan®, Forns’ index and their combination in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B, and the impact of inflammatory activity and steatosis on these diagnostic methods. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 11:4174–4182.25. Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M, Sporea I, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Strobel D, et al. Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat. 2012; 19:e212–e219.26. Liu Y, Dong CF, Yang G, Liu J, Yao S, Li HY, et al. Optimal linear combination of ARFI, transient elastography and APRI for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2015; 35:816–825.27. Stibbe KJ, Verveer C, Francke J, Hansen BE, Zondervan PE, Kuipers EJ, et al. Comparison of non-invasive assessment to diagnose liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:962–972.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- RE: Liver Shear-Wave Velocity to Diagnose Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis B
- Non-Invasive Liver Fibrosis Test Using Shear Wave Elastography
- Clinical Implications of Shear Wave Elastography in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Patchy echogenicity of the liver in patients with chronic hepatitis B does not indicate poorer elasticity
- Clinical Application of Non-invasive Diagnosis for Hepatic Fibrosis