J Clin Neurol.
2019 Jul;15(3):321-327. 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.321.
Restless Legs Syndrome in Parkinson's Disease Patients: Clinical Features Including Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. neurocho@gmail.com
- 2Ewha Womans University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2451115
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.321
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
We investigated the frequency and clinical features of restless legs syndrome (RLS) in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD).
METHODS
This study included 74 PD patients. RLS was diagnosed in face-to-face assessments of all of the subjects based on diagnostic criteria of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group revised in 2003. We analyzed the clinical features of PD patients with and without RLS and compared the data to idiopathic RLS.
RESULTS
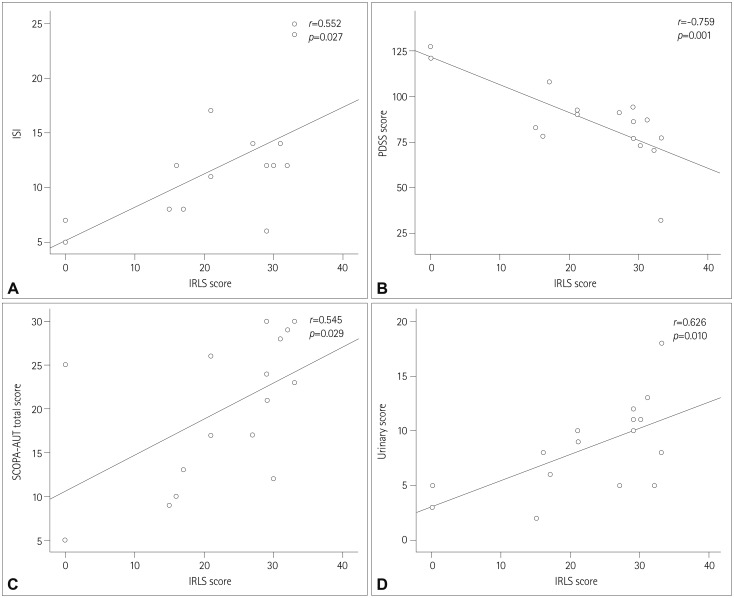
The frequency of RLS in the cohort was 21.6% (n=16). Two (12.5%) of the patients with RLS were not treated with dopaminergic drugs, while 14 (24.1%) of the 58 patients without RLS received treatment with dopaminergic drugs. Anxiety, depression, and quality of life (QoL) were significantly worst in patients with RLS. PD patients with RLS had significantly worse sleep quality (p=0.003) and worse scores on the cardiovascular subscale of the Scales for Outcomes in Parkinson's Disease for Autonomic Symptoms (p=0.031) compared to those without RLS. In the group of PD patients with RLS, RLS preceding PD onset was related to a lower Hoehn and Yahr stage.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that the frequency of RLS in the present patients with PD was higher than that in our previous study of a general population of RLS subjects. Compared to the PD patients without RLS, the present PD patients with RLS suffered from worse sleep quality and QoL, depression, anxiety, and autonomic disturbances, especially those with cardiovascular problems.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ondo WG, Walters AS, Winkelman JW, et al. Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria--history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014; 15:860–873. PMID: 25023924.2. Yeh P, Walters AS, Tsuang JW. Restless legs syndrome: a comprehensive overview on its epidemiology, risk factors, and treatment. Sleep Breath. 2012; 16:987–1007. PMID: 22038683.
Article3. Högl B, Kiechl S, Willeit J, Saletu M, Frauscher B, Seppi K, et al. Restless legs syndrome: a community-based study of prevalence, severity, and risk factors. Neurology. 2005; 64:1920–1924. PMID: 15955944.
Article4. Cho YW, Shin WC, Yun CH, Hong SB, Kim JH, Allen RP, et al. Epidemiology of restless legs syndrome in Korean adults. Sleep. 2008; 31:219–223. PMID: 18274269.
Article5. Yang X, Liu B, Shen H, Li S, Zhao Q, An R, et al. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Sleep Med. 2018; 43:40–46. PMID: 29482811.
Article6. Trenkwalder C, Allen R, Högl B, Paulus W, Winkelmann J. Restless legs syndrome associated with major diseases: a systematic review and new concept. Neurology. 2016; 86:1336–1343. PMID: 26944272.7. Shin HY, Youn J, Yoon WT, Kim JS, Cho JW. Restless legs syndrome in Korean patients with drug-naïve Parkinson's disease: a nation-wide study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013; 19:355–358. PMID: 23047004.
Article8. Pont-Sunyer C, Hotter A, Gaig C, Seppi K, Compta Y, Katzenschlager R, et al. The onset of nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson's disease (the ONSET PD study). Mov Disord. 2015; 30:229–237. PMID: 25449044.9. Oh YS, Kim JS, Park IS, Song IU, Son YM, Park JW, et al. Association between nocturnal/supine hypertension and restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2014; 344:186–189. PMID: 25016570.
Article10. Piao YS, Lian TH, Hu Y, Zuo LJ, Guo P, Yu SY, et al. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson disease: clinical characteristics, abnormal iron metabolism and altered neurotransmitters. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:10547. PMID: 28874701.
Article11. Rana AQ, Siddiqui I, Mosabbir A, Athar A, Syed O, Jesudasan M, et al. Association of pain, Parkinson's disease, and restless legs syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2013; 327:32–34. PMID: 23481589.
Article12. Lee JE, Shin HW, Kim KS, Sohn YH. Factors contributing to the development of restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson disease. Mov Disord. 2009; 24:579–582. PMID: 19097179.
Article13. Chahine LM, Ahmed A, Sun Z. Effects of STN DBS for Parkinson's disease on restless legs syndrome and other sleep-related measures. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011; 17:208–211. PMID: 21216651.
Article14. Rijsman RM, Schoolderman LF, Rundervoort RS, Louter M. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20(Suppl 1):S5–S9. PMID: 24262188.
Article15. Azmin S, Khairul Anuar AM, Nafisah WY, Tan HJ, Raymond AA, Hanita O, et al. Restless legs syndrome and its associated risk factors in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2013; 2013:535613. PMID: 24455416.
Article16. Krishnan PR, Bhatia M, Behari M. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson's disease: a case-controlled study. Mov Disord. 2003; 18:181–185. PMID: 12539212.
Article17. Zhu XY, Liu Y, Zhang XJ, Yang WH, Feng Y, Ondo WG, et al. Clinical characteristics of leg restlessness in Parkinson's disease compared with idiopathic restless legs syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 357:109–114. PMID: 26189051.
Article18. Möller JC, Unger M, Stiasny-Kolster K, Oertel WH. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) and Parkinson's disease (PD)-related disorders or different entities? J Neurol Sci. 2010; 289:135–137. PMID: 19755200.
Article19. Fereshtehnejad SM, Shafieesabet M, Shahidi GA, Delbari A, Lökk J. Restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson's disease: a comparative study on prevalence, clinical characteristics, quality of life and nutritional status. Acta Neurol Scand. 2015; 131:211–218. PMID: 25263328.
Article20. Shneyder N, Adler CH, Hentz JG, Shill H, Caviness JN, Sabbagh MN, et al. Autonomic complaints in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2013; 14:1413–1416. PMID: 24152795.
Article21. Walters AS, Rye DB. Review of the relationship of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements in sleep to hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Sleep. 2009; 32:589–597. PMID: 19480225.
Article22. Gjerstad MD, Tysnes OB, Larsen JP. Increased risk of leg motor restlessness but not RLS in early Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2011; 77:1941–1946. PMID: 22076542.
Article23. Nomura T, Inoue Y, Miyake M, Yasui K, Nakashima K. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of restless legs syndrome in Japanese patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2006; 21:380–384. PMID: 16211604.
Article24. Ondo WG, Vuong KD, Jankovic J. Exploring the relationship between Parkinson disease and restless legs syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2002; 59:421–424. PMID: 11890847.
Article25. Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Miyamoto T, Hirata K. Restless legs syndrome and leg motor restlessness in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2015; 2015:490938. PMID: 26504610.
Article26. Marsh L. Depression and Parkinson's disease: current knowledge. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013; 13:409. PMID: 24190780.
Article27. Kedia S, Moro E, Tagliati M, Lang AE, Kumar R. Emergence of restless legs syndrome during subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2004; 63:2410–2412. PMID: 15623715.
Article28. Klepitskaya O, Liu Y, Sharma S, Sillau SH, Tsai J, Walters AS. Deep brain stimulation improves restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2018; 91:e1013–e1021. PMID: 30111549.
Article29. Liguori C, Mercuri NB, Stefani A, Pierantozzi M. Effective treatment of restless legs syndrome by safinamide in Parkinson's disease patients. Sleep Med. 2018; 41:113–114. PMID: 29268951.
Article30. Wong JC, Li Y, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A, Gao X. Restless legs syndrome: an early clinical feature of Parkinson disease in men. Sleep. 2014; 37:369–372. PMID: 24497665.
Article31. Szatmari S Jr, Bereczki D, Fornadi K, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP, Molnar MZ. Association of restless legs syndrome with incident Parkinson's disease. Sleep. 2017; 40:zsw065.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Introduction for the Questionnaires for Restless Legs Syndrome
- Sleep Disorders in Patients with Parkinson's Disease
- Periodic Limb Movement and Restless legs Syndrome in Neurological Disorders
- A Case of Idiopathic Restless Legs Syndrome in a Child
- Seborrheic Dermatitis Is Related to Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease