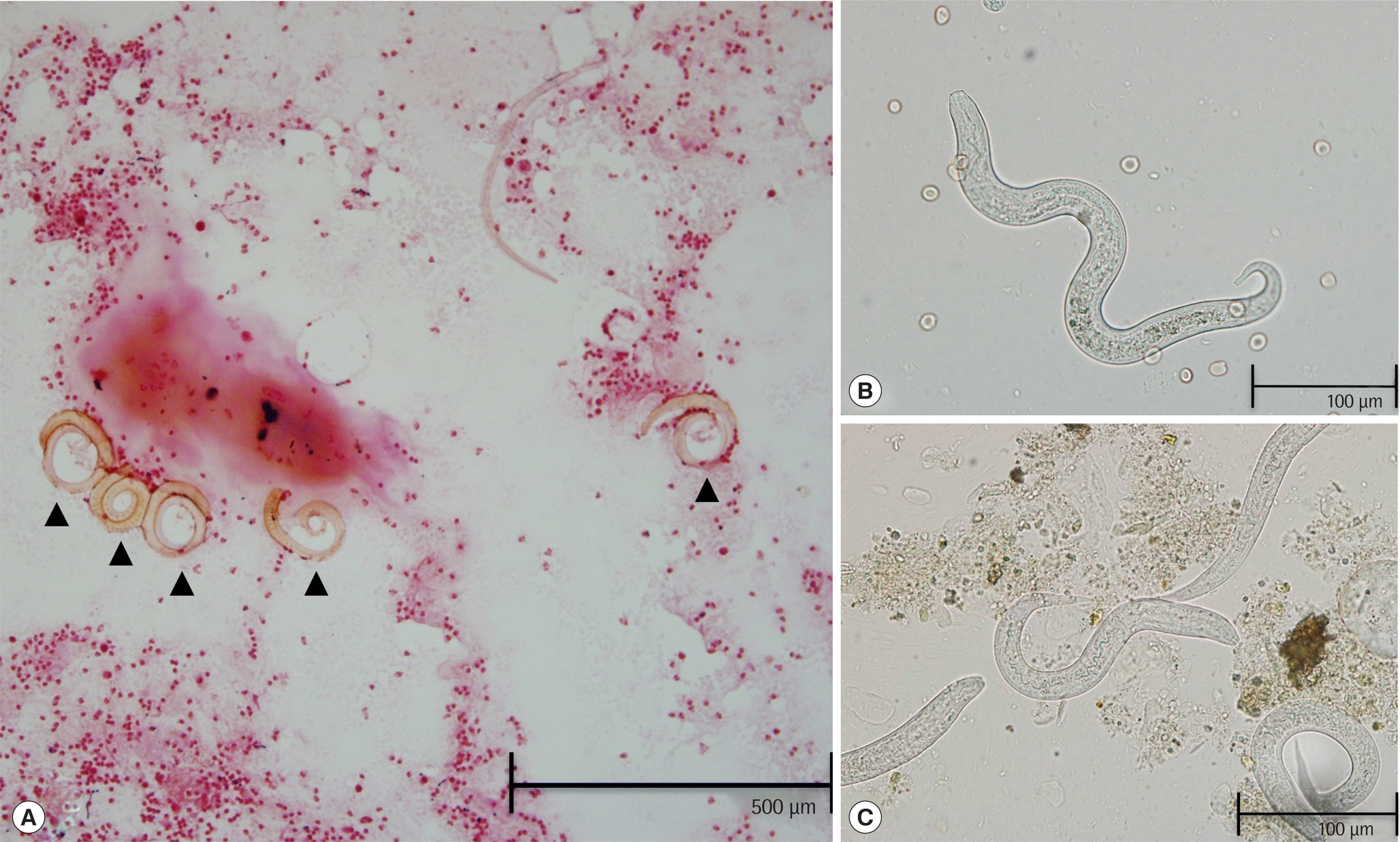
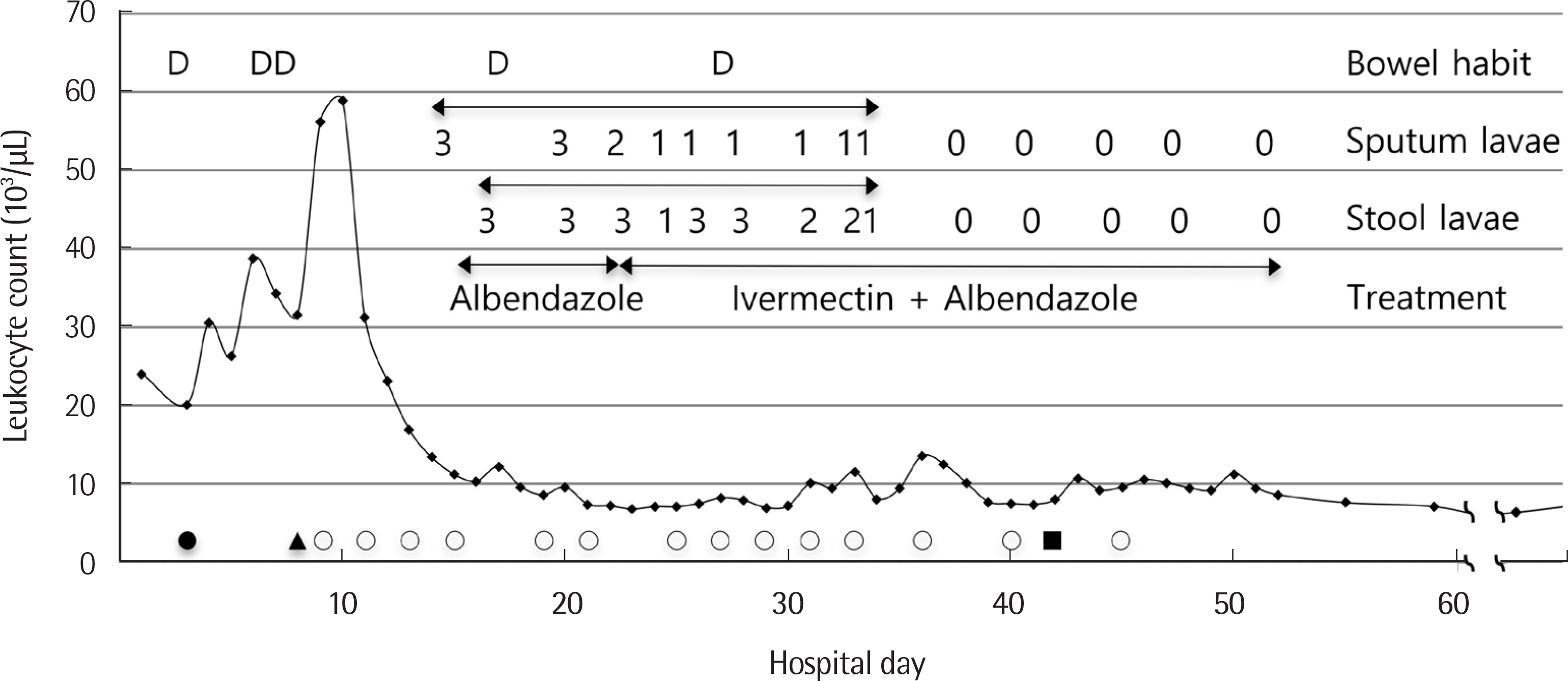
Lab Med Online.
2019 Jul;9(3):171-176. 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.171.
A Case of Chronic Strongyloidiasis with Recurrent Hyperinfection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. mnkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Oncology, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2450843
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.171
Abstract
- Strongyloides stercoralis is an intestinal nematode that often causes chronic diarrhea and may develop severe complicated form of hyperinfection or disseminated infection in immunocompromised patients. Here, we report a case of recurrent strongyloidiasis presenting with pulmonary and meningeal involvement. A 55-year-old male diagnosed with pancreatic cancer 4 months ago was admitted due to chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss for 2-3 months. He had been treated with albendazole for chronic recurrent strongyloidiasis 13 years ago and again 2 years ago. He developed sepsis of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli on Days 3 and 7, respectively, and then meningitis of E. coli on Day 42. Strongyloidiasis was diagnosed by detection of abundant filariform larvae in sputum specimens on Day 15. He was treated for disseminated strongyloidiasis with albendazole and ivermectin for five weeks until clearance of larvae was confirmed in sputum and stool specimens. Laboratory diagnosis is important to guide appropriate treatment and to prevent chronic and recurrent strongyloidiasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sheorey H. Biggs B. Ryan N. Nematodes. Jorgensen JH, editor. editors.Manual of clinical microbiology. 11th ed.Washington, DC: ASM Press;2015. p. 2456–8.2. Kassalik M and Mönkemüller K. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7:766–8.3. Pradhan G, Behera P, Panigrahi MK, Bhuniya S, Mohapatra PR, Turuk J, et al. Pulmonary strongyloidiasis masquerading as exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016; 79:307–11.
Article4. Siddiqui AA and Berk SL. Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 33:1040–7.5. Keiser PB and Nutman TB. Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004; 17:208–17.6. Segarra-Newnham M. Manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Ann Pharmacother. 2007; 41:1992–2001.
Article7. Yoon DH, Yang SJ, Kim JS, Hong ST, Chai JY, Lee SH, et al. A case of fatal malabsorption syndrome caused by strongyloidiasis complicated with isosporiasis and human cytomegalovirus infection. Korean J Parasitol. 1992; 30:53–8.
Article8. Hong YH, Kim JW, Rheem IS, Kim JS, Kim SB, Chai JY, et al. Observation of the free-living adults of Strongyloides stercoralis from a human stool in Korea. Infect Chemother. 2009; 41:105–8.
Article9. Kim YJ, Ahn MJ, Park KC, Lee HY, Kim KH, Byeon KM, et al. Pulmonary strongyloidiasis with alveolar hemorrhage in a patient receiving chemotherapy. Korean J Med. 2009; 76:502–5.10. Kim J, Joo HS, Kim DH, Lim H, Kang YH, Kim MS. A case of gastric strongyloidiasis in a Korean patient. Korean J Parasitol. 2003; 41:63–7.
Article11. Schar F, Trostdorf U, Giardina F, Khieu V, Muth S, Marti H, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: global distribution and risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013; 7:e2288.
Article12. Cho SH, Jung BS, Lee SE. National survey of intestinal parasitic infections in Korea, 8th Report. 2013. https://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/info/Cdc-KrInfo0301.jsp?menuIds=HOME006-MNU3003-MNU2950-MNU2951&cid=24152. [Updated on Jan 2014].13. Lee SK, Shin BM, Chung NS, Chai JY, Lee SH. Second report on intestinal parasites among the patients of Seoul Paik Hospital (1984–1992). Korean J Parasitol. 1994; 32:27–33.
Article14. Chai JY, Park JH, Guk SM, Kim HJ, Kim WH, Kim JL, et al. Status of intestinal parasite infections among 4,137 residents from provinces nationwide and metropolitan areas in the Republic of Korea (2004). Infect Chemother. 2006; 38:198–203.15. Kim HS, Kim YE, Yun EY, Ju JH, Ma JE, Lee GD, et al. A case of fatal hyperinfective strongyloidiasis with acute respiratory failure and intestinal perforation in lung cancer patient. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2010; 68:29–33.
Article16. Cho JY, Kwon JG, Ha KH, Oh JY, Jin MI, Heo SW, et al. A case of steroid-induced hyperinfective strongyloidiasis with bacterial meningitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012; 60:330–4.
Article17. Rah YM, Yun SA, Yoon HJ, Lee SY. Strongyloides hyperinfection in an elderly patient treated for stomach cancer. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2014; 18:41–5.18. Mejia R and Nutman TB. Screening, prevention, and treatment for hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated infections caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012; 25:458–63.19. Gill GV and Bell DR. Strongyloides stercoralis infection in former far east prisoners of war. Br Med J. 1979; 2:572.20. Buonfrate D, Requena-Mendez A, Angheben A, Munoz J, Gobbi F, Van Den Ende J, et al. Severe strongyloidiasis: a systematic review of case reports. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:78.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary Strongyloidiasis Masquerading as Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- A Case of Severe Strongyloidiasis in a Patient with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Receiving Long-Term Steroid Therapy
- A Case of Strongyloides Stercoralis Infection of Stomach in Association with Meningitis
- A Case of Fatal Strongyloidiasis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Molecular Characterization of the Isolate
- Strongyloides Hyperinfection in an Elderly Patient Treated for Stomach Cancer