Endocrinol Metab.
2019 Jun;34(2):140-149. 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.140.
Association between Circulating Irisin and C-Reactive Protein Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Nutritional Health Research Center, Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran. abbasnezhad.a@ajums.ac.ir
- 2Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, Nutritional Health Research Center, Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran.
- 3Razi Herbal Medicines Research Center, Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran.
- KMID: 2450514
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.140
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although previous studies have demonstrated that irisin plays an anti-inflammatory role in the body, conflicting results have been reported regarding the correlation between serum levels of irisin and C-reactive protein (CRP). The present meta-analysis was conducted to further investigate the correlation between irisin and CRP levels.
METHODS
We systematically searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, SCOPUS, and Ovid to retrieve studies assessing the correlation between irisin and CRP levels. Meta-analyses were performed using a random-effects model, and the I 2 index was used to evaluate heterogeneity.
RESULTS
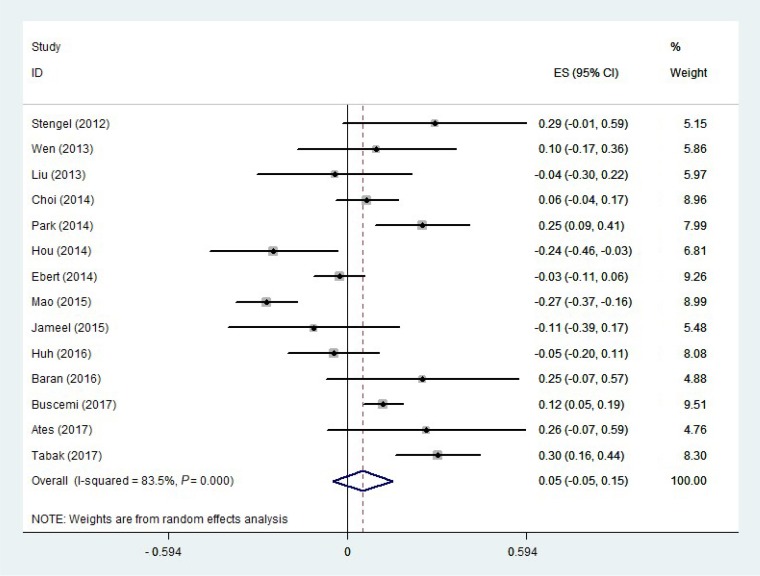
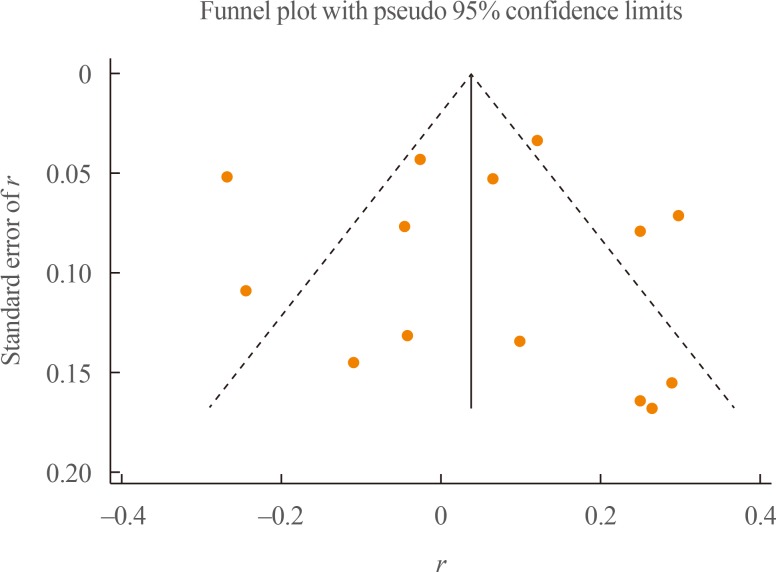
Of the 428 studies that were initially found, 14 studies with 2,530 participants met the inclusion criteria for the meta-analysis. The pooled effect size was calculated as 0.052 (95% confidence interval, −0.047 to 0.152; P=0.302). Subgroup analyses identified s ignificant, positive, but weak correlations between CRP and irisin levels in cohort studies, studies conducted among healthy participants, studies in which the male-to-female ratio was less than 1, in overweight or obese subjects, and in studies with a sample size of at least 100 participants.
CONCLUSION
The present meta-analysis found no overall significant correlation between irisin and CRP levels, although a significant positive correlation was found in overweight or obese subjects. Well-designed studies are needed to verify the results of the present meta-analysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012; 481:463–468. PMID: 22237023.
Article2. Chen JQ, Huang YY, Gusdon AM, Qu S. Irisin: a new molecular marker and target in metabolic disorder. Lipids Health Dis. 2015; 14:2. PMID: 25588692.
Article3. Mazur-Bialy AI, Pochec E, Zarawski M. Anti-inflammatory properties of irisin, mediator of physical activity, are connected with TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18:E701. PMID: 28346354.
Article4. Raschke S, Eckardt K, Bjorklund Holven K, Jensen J, Eckel J. Identification and validation of novel contraction-regulated myokines released from primary human skeletal muscle cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e62008. PMID: 23637948.
Article5. Xiang L, Xiang G, Yue L, Zhang J, Zhao L. Circulating irisin levels are positively associated with endothelium-dependent vasodilation in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients without clinical angiopathy. Atherosclerosis. 2014; 235:328–333. PMID: 24911636.
Article6. Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD, Efstathiadou ZA, Makras P, Perakakis N, Kountouras J, et al. Irisin in metabolic diseases. Endocrine. 2018; 59:260–274. PMID: 29170905.
Article7. Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008; 9:46–56. PMID: 18073775.
Article8. Calder PC. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006; 83(6 Suppl):1505S–1519S. PMID: 16841861.
Article9. Li W, Luo X, Liu Z, Chen Y, Li Z. Prognostic value of C-reactive protein levels in patients with bone neoplasms: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0195769. PMID: 29668751.
Article10. Du Clos TW, Mold C. C-reactive protein: an activator of innate immunity and a modulator of adaptive immunity. Immunol Res. 2004; 30:261–277. PMID: 15531769.
Article11. Kasapis C, Thompson PD. The effects of physical activity on serum C-reactive protein and inflammatory markers: a systematic review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:1563–1569. PMID: 15893167.12. Hou N, Han F, Sun X. The relationship between circulating irisin levels and endothelial function in lean and obese subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2015; 83:339–343. PMID: 25382211.
Article13. Buscemi S, Corleo D, Vasto S, Buscemi C, Massenti MF, Nuzzo D, et al. Factors associated with circulating concentrations of irisin in the general population cohort of the ABCD study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018; 42:398–404. PMID: 29027533.
Article14. Jameel F, Thota RN, Wood LG, Plunkett B, Garg ML. Sex-dependent association between circulating irisin levels and insulin resistance in healthy adults. J Nutr Intermed Metab. 2015; 2:86–92.
Article15. Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [Internet]. Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute;c2019. cited 2019 Mar 28. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.16. Liu JJ, Wong MD, Toy WC, Tan CS, Liu S, Ng XW, et al. Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2013; 27:365–369. PMID: 23619195.
Article17. Ebert T, Focke D, Petroff D, Wurst U, Richter J, Bachmann A, et al. Serum levels of the myokine irisin in relation to metabolic and renal function. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014; 170:501–506. PMID: 24399249.
Article18. Choi ES, Kim MK, Song MK, Kim JM, Kim ES, Chung WJ, et al. Association between serum irisin levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in health screen examinees. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e110680. PMID: 25343462.
Article19. Mao Y, Xu W, Xie Z, Dong Q. Association of irisin and CRP levels with the radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016; 20:86–89. PMID: 26625129.
Article20. Stengel A, Hofmann T, Goebel-Stengel M, Elbelt U, Kobelt P, Klapp BF. Circulating levels of irisin in patients with anorexia nervosa and different stages of obesity: correlation with body mass index. Peptides. 2013; 39:125–130. PMID: 23219488.21. Wen MS, Wang CY, Lin SL, Hung KC. Decrease in irisin in patients with chronic kidney disease. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e64025. PMID: 23667695.
Article22. Park KH, Zaichenko L, Peter P, Davis CR, Crowell JA, Mantzoros CS. Diet quality is associated with circulating C-reactive protein but not irisin levels in humans. Metabolism. 2014; 63:233–241. PMID: 24315778.
Article23. Ates I, Arikan MF, Erdogan K, Kaplan M, Yuksel M, Topcuoglu C, et al. Factors associated with increased irisin levels in the type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Regul. 2017; 51:1–7. PMID: 28222023.
Article24. Huh JH, Ahn SV, Choi JH, Koh SB, Chung CH. High serum irisin level as an independent predictor of diabetes mellitus: a longitudinal population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3742. PMID: 27281072.25. Tabak O, Simsek G, Erdenen F, Sozer V, Hasoglu T, Gelisgen R, et al. The relationship between circulating irisin, retinol binding protein-4, adiponectin and inflammatory mediators in patients with metabolic syndrome. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 61:515–523. PMID: 28977161.
Article26. Baran A, Mysliwiec H, Kiluk P, Swiderska M, Flisiak I. Serum irisin levels in patients with psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017; 28:304–308. PMID: 27786588.
Article27. Perakakis N, Triantafyllou GA, Fernandez-Real JM, Huh JY, Park KH, Seufert J, et al. Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017; 13:324–337. PMID: 28211512.
Article28. Ebert T, Kralisch S, Wurst U, Scholz M, Stumvoll M, Kovacs P, et al. Association of metabolic parameters and rs726344 in FNDC5 with serum irisin concentrations. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016; 40:260–265. PMID: 26285604.
Article29. Mazur-Bialy AI, Bilski J, Pochec E, Brzozowski T. New insight into the direct anti-inflammatory activity of a myokine irisin against proinflammatory activation of adipocytes. Implication for exercise in obesity. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017; 68:243–251. PMID: 28614774.30. Hurlimann J, Thorbecke GJ, Hochwald GM. The liver as the site of C-reactive protein formation. J Exp Med. 1966; 123:365–378. PMID: 4379352.
Article31. Ballou SP, Lozanski G. Induction of inflammatory cytokine release from cultured human monocytes by C-reactive protein. Cytokine. 1992; 4:361–368. PMID: 1420997.
Article32. Chi M, Tridandapani S, Zhong W, Coggeshall KM, Mortensen RF. C-reactive protein induces signaling through Fc gamma RIIa on HL-60 granulocytes. J Immunol. 2002; 168:1413–1418. PMID: 11801683.33. Tilg H, Vannier E, Vachino G, Dinarello CA, Mier JW. Antiinflammatory properties of hepatic acute phase proteins: preferential induction of interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist over IL-1 beta synthesis by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1993; 178:1629–1636. PMID: 7693853.
Article34. Chen N, Li Q, Liu J, Jia S. Irisin, an exercise-induced myokine as a metabolic regulator: an updated narrative review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016; 32:51–59. PMID: 25952527.
Article35. Biniaminov N, Bandt S, Roth A, Haertel S, Neumann R, Bub A. Irisin, physical activity and fitness status in healthy humans: no association under resting conditions in a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0189254. PMID: 29381744.
Article36. Sokolove J, Lepus CM. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: latest findings and interpretations. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013; 5:77–94. PMID: 23641259.
Article37. Pedersen BK, Akerstrom TC, Nielsen AR, Fischer CP. Role of myokines in exercise and metabolism. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007; 103:1093–1098. PMID: 17347387.
Article38. Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Zacho M, Asp S, Pedersen BK. Evidence that interleukin-6 is produced in human skeletal muscle during prolonged running. J Physiol. 1998; 508(Pt 3):949–953. PMID: 9518745.
Article39. Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW. C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999; 19:972–978. PMID: 10195925.40. Jackson AS, Stanforth PR, Gagnon J, Rankinen T, Leon AS, Rao DC, et al. The effect of sex, age and race on estimating percentage body fat from body mass index: the Heritage Family Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002; 26:789–796. PMID: 12037649.
Article41. MacKenzie KE, Wiltshire EJ, Pena AS, Gent R, Hirte C, Piotto L, et al. Hs-CRP is associated with weight, BMI, and female sex but not with endothelial function in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009; 10:44–51. PMID: 18798827.
Article42. Anastasilakis AD, Polyzos SA, Saridakis ZG, Kynigopoulos G, Skouvaklidou EC, Molyvas D, et al. Circulating irisin in healthy, young individuals: day-night rhythm, effects of food intake and exercise, and associations with gender, physical activity, diet, and body composition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:3247–3255. PMID: 24915120.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Is Associated with Serum Chemerin and Irisin but Not with Apolipoprotein M Levels
- Circulating leptin and its correlation with rheumatoid arthritis activity: a meta-analysis
- Associations between circulating interleukin-18 levels and adult-onset Still’s disease: a meta-analysis
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and hypertension risk after adjusting for publication bias