J Rheum Dis.
2023 Apr;30(2):116-125. 10.4078/jrd.2023.0005.
Circulating leptin and its correlation with rheumatoid arthritis activity: a meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2541055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2023.0005
Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to investigate the association between the levels of leptin in the circulating of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and the severity of the disease.
Methods
We looked through the databases of Embase, Medline, and the Cochrane Library. We conducted a meta-analysis on the correlations between circulating leptin and the Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) and Creactive protein (CRP) levels in RA patients, as well as a meta-analysis of circulating or circulating leptin levels in RA patients.
Results
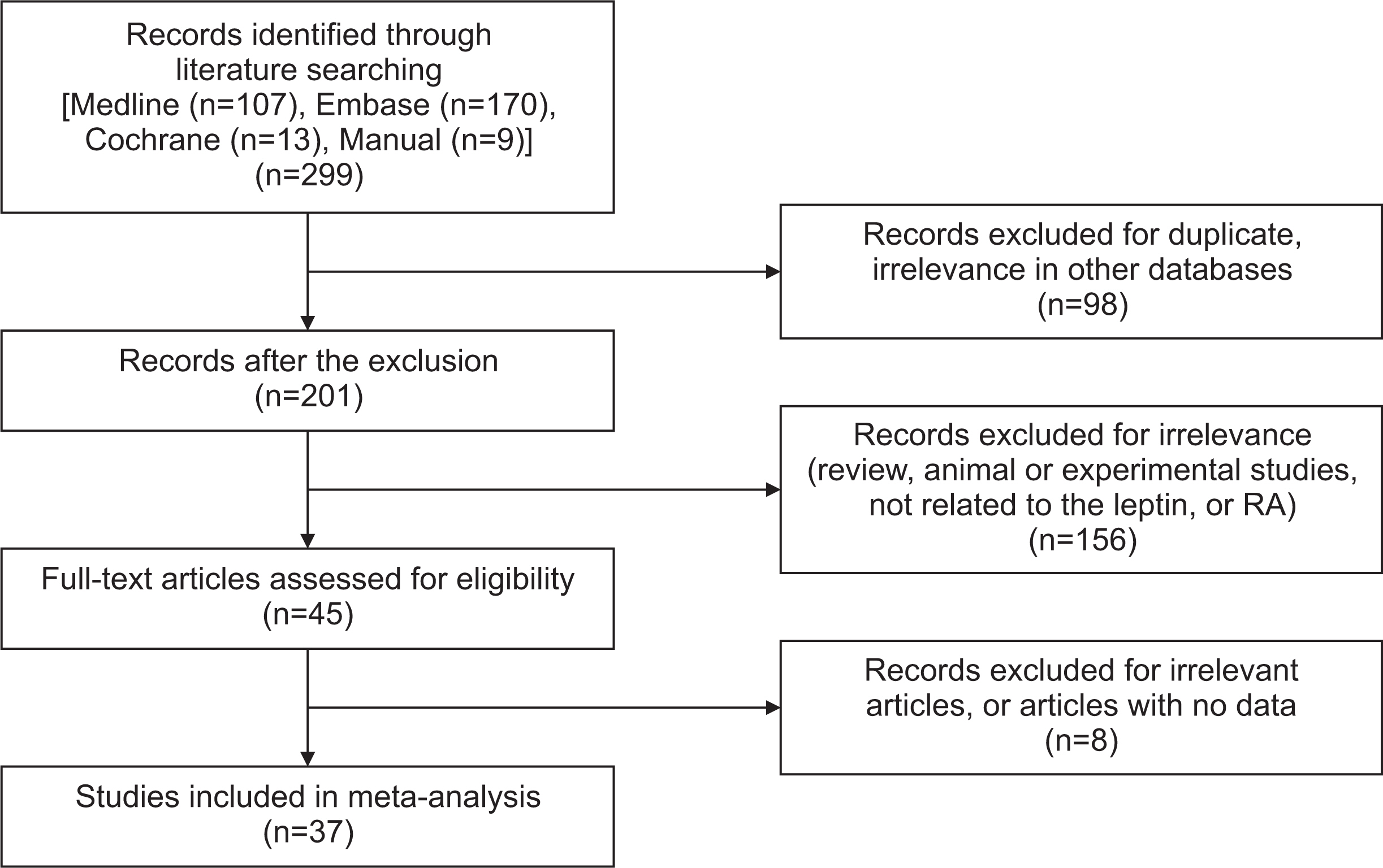
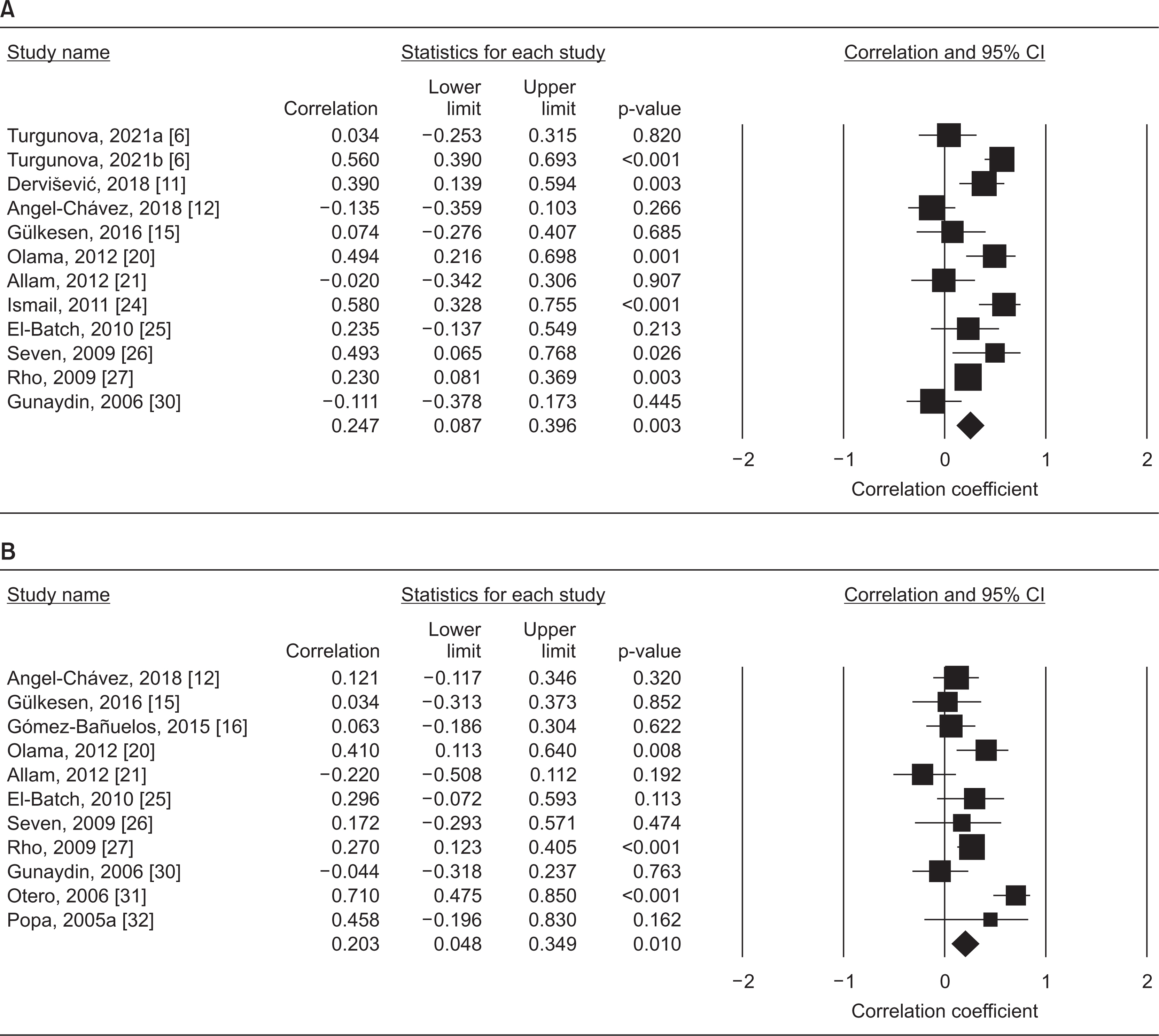
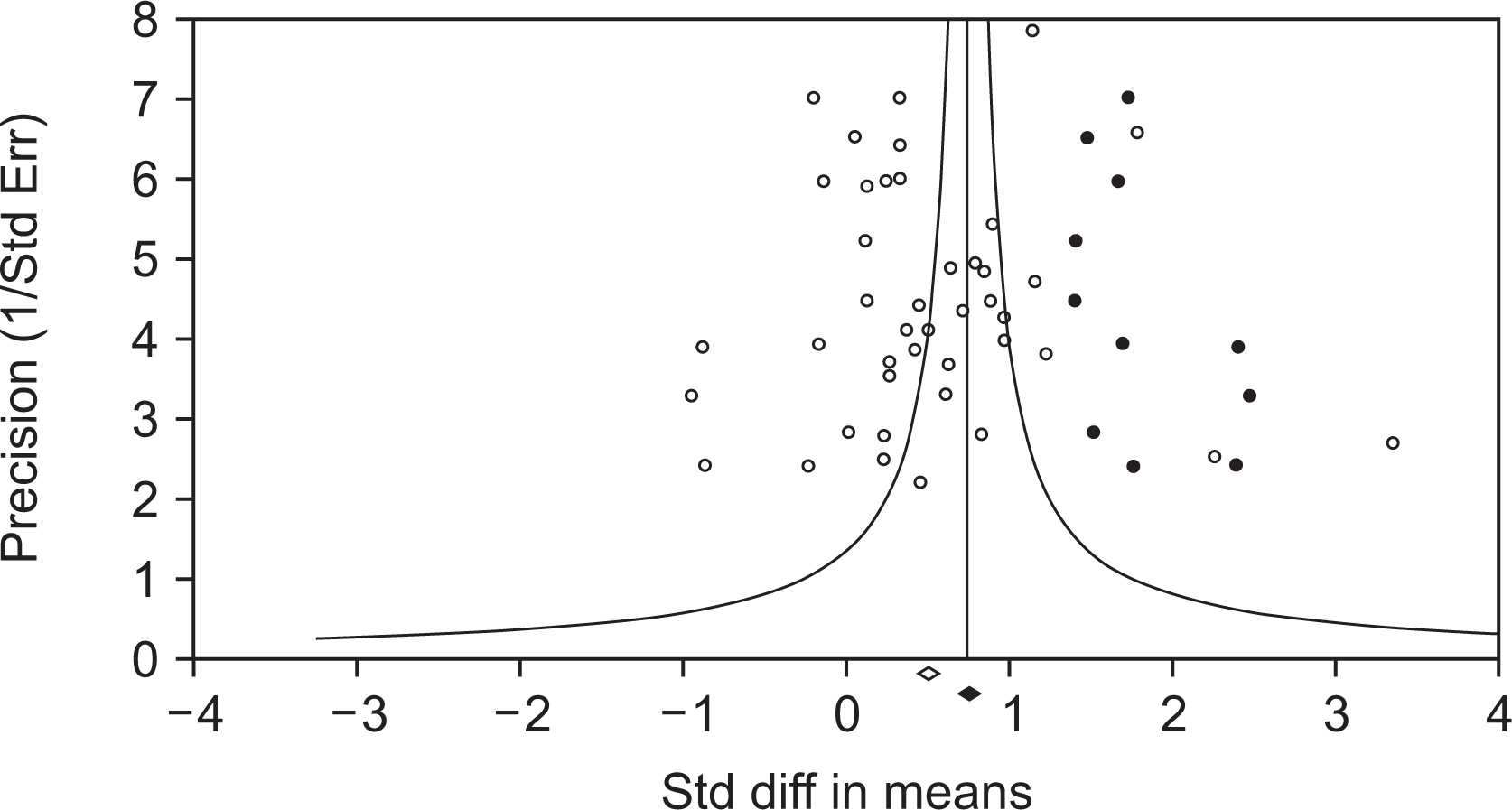
This meta-analysis study analyzed 42 different comparisons from 37 different publications, including a total of 2,350 patients with RA and 1,815 controls. The RA group had substantially higher leptin levels than the control group (standardized mean difference [SMD]=0.507, 95% confidence interval [CI]=0.309~0.704, p<0.001). The finding that RA patients had higher leptin levels was unaffected by sample size. The correlation between circulating leptin levels and DAS28 is statistically significant (correlation coefficient=0.247, 95% CI=0.087~0.396, p=0.003). Leptin levels are also correlated with CRP levels (correlation coefficient=0.203, 95% CI=0.048~0.349, p=0.010).
Conclusion
This comprehensive meta-analysis demonstrates that the circulating leptin levels of RA patients are elevated, and provides compelling evidence of the significant relationship between leptin levels and the activity of RA. The findings of this research suggest that leptin plays a significant role in the pathophysiology of this disease.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Münzberg H, Heymsfield SB. 2019; New insights into the regulation of leptin gene expression. Cell Metab. 29:1013–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.04.005. PMID: 31067443. PMCID: PMC7346278.
Article2. Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN. 1997; Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ. 315:1533–7. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.315.7121.1533. PMID: 9432252. PMCID: PMC2127925.
Article3. Magali Chamorro-Melo Y, Calixto OJ, Bello-Gualtero JM, Bautista-Molano W, Beltran-Ostos A, Romero-Sánchez C. 2022; Evaluation of the adipokine profile (adiponectin, resistin, adipsin, vaspin, and leptin) in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with disease activity. Reumatologia. 60:192–9. DOI: 10.5114/reum.2022.117839. PMID: 35875721. PMCID: PMC9301668.
Article4. Cheleschi S, Tenti S, Bedogni G, Fioravanti A. 2022; Circulating Mir-140 and leptin improve the accuracy of the differential diagnosis between psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Transl Res. 239:18–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.08.001. PMID: 34380068.
Article5. Zhang Y, Johansson L, Andersson-Assarsson J, Taube M, Peltonen M, Svensson PA, et al. 2021; Adiponectin associates with rheumatoid arthritis risk in overweight and obesity independently of other adipokines. J Clin Med. 10:2791. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10132791. PMID: 34201946. PMCID: PMC8267689.
Article6. Turgunova LG, Shalygina AA, Zalkalns JP, Klyuyev DA, Akhmaltdinova LL, Dosmagambetova RS. 2021; Assessment of adipokines, CXCL16 chemokine levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis combined with metabolic syndrome. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 14:1179544120985860. DOI: 10.1177/1179544120985860. PMID: 33613035. PMCID: PMC7868477.
Article7. Chen YM, Chen PK, Chang CK, Lin CC, Chen HH, Lan JL, et al. 2020; Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphism with adipokines and cardiovascular disease risk in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Life (Basel). 10:330. DOI: 10.3390/life10120330. PMID: 33297350. PMCID: PMC7762228.
Article8. Tao SS, Dan YL, Wu GC, Zhang Q, Zhang TP, Fan YG, et al. 2020; Association of leptin gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Chinese population. Biomed Res Int. 2020:3789319. DOI: 10.1155/2020/3789319. PMID: 33083462. PMCID: PMC7559230.9. Chihara K, Hattori N, Ichikawa N, Matsuda T, Saito T. 2020; Re-evaluation of serum leptin and adiponectin concentrations normalized by body fat mass in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 10:15932. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73068-2. PMID: 32985609. PMCID: PMC7522978.
Article10. Hoffman E, Rahat MA, Feld J, Elias M, Rosner I, Kaly L, et al. 2019; Effects of tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, on serum lipid and adipokine levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:4633. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184633. PMID: 31540528. PMCID: PMC6770905.
Article11. Dervišević A, Resić H, Sokolović Š, Babić N, Avdagić N, Začiragić A, et al. 2018; Leptin is associated with disease activity but not with anthropometric indices in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arch Med Sci. 14:1080–6. DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2017.65080. PMID: 30154891. PMCID: PMC6111354.
Article12. Angel-Chávez LI, Ruelas-Cinco E, Hernández-Bello J, Castro E, Vázquez-Villamar M, Parra-Rojas I, et al. 2018; Influence of serum leptin levels and Q223R leptin receptor polymorphism on clinical characteristic of patients with rheumatoid arthritis from Western Mexico. EJIFCC. 29:26–35.13. Rodríguez-Carrio J, Alperi-López M, López P, López-Mejías R, Alonso-Castro S, Abal F, et al. 2017; High triglycerides and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol lipid profile in rheumatoid arthritis: a potential link among inflammation, oxidative status, and dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein. J Clin Lipidol. 11:1043–54.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2017.05.009. PMID: 28662934.14. Najafizadeh SR, Farahmand G, Roudsari AT, Heidari B, Larry M, Nargesi AA, et al. 2016; Absence of a positive correlation between CRP and leptin in rheumatoid arthritis. Heliyon. 2:e00205. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00205. PMID: 27981248. PMCID: PMC5148782.
Article15. Gülkesen A, Akgöl G, Tuncer T, Kal GA, Telo S, Poyraz AK, et al. 2016; Relationship between leptin and neopterin levels and disease activation parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Rheumatol. 31:333–9. DOI: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2016.5893. PMID: 30375574. PMCID: PMC6190973.
Article16. Gómez-Bañuelos E, Navarro-Hernández RE, Corona-Meraz F, Madrigal-Ruíz PM, Martín-Marquez BT, Pizano-Martinez OE, et al. 2015; Serum leptin and serum leptin/serum leptin receptor ratio imbalance in obese rheumatoid arthritis patients positive for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:335. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0850-8. PMID: 26589684. PMCID: PMC4654826.
Article17. Oner SY, Volkan O, Oner C, Mengi A, Direskeneli H, Tasan DA. 2015; Serum leptin levels do not correlate with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Reumatol Port. 40:50–4.18. Abdalla M, Effat D, Sheta M, Hamed WE. 2014; Serum leptin levels in rheumatoid arthritis and relationship with disease activity. Egypt Rheumatol. 36:1–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejr.2013.10.002.
Article19. Toussirot E, Grandclément E, Gaugler B, Michel F, Wendling D, Saas P, et al. 2013; Serum adipokines and adipose tissue distribution in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. A comparative study. Front Immunol. 4:453. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00453. PMID: 24379815. PMCID: PMC3861781.
Article20. Olama SM, Senna MK, Elarman M. 2012; Synovial/serum leptin ratio in rheumatoid arthritis: the association with activity and erosion. Rheumatol Int. 32:683–90. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-010-1698-5. PMID: 21140264.
Article21. Allam A, Radwan A. 2012; The relationship of serum leptin levels with disease activity in Egyptian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Egypt Rheumatol. 34:185–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejr.2012.08.001.
Article22. Kopec-Medrek M, Kotulska A, Widuchowska M, Adamczak M, Więcek A, Kucharz EJ. 2012; Plasma leptin and neuropeptide Y concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab, a TNF-α antagonist. Rheumatol Int. 32:3383–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-011-2182-6. PMID: 22048440. PMCID: PMC3505553.
Article23. Yoshino T, Kusunoki N, Tanaka N, Kaneko K, Kusunoki Y, Endo H, et al. 2011; Elevated serum levels of resistin, leptin, and adiponectin are associated with C-reactive protein and also other clinical conditions in rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med. 50:269–75. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.50.4306. PMID: 21325757.
Article24. Ismail F, Ali HA, Ibrahim HM. 2011; Possible role of leptin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in hypoandrogenicity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Egypt Rheumatol. 33:209–15. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejr.2011.07.006.
Article25. El-Batch MM, Zakaria SS, Farouk G, El Saadany H, Selim M. 2010; Changes in visfatin, adiponectin, leptin and ghrelin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their correlation with disease activity. Turk Biyokim Derg. 35:50–7.26. Seven A, Güzel S, Aslan M, Hamuryudan V. 2009; Serum and synovial fluid leptin levels and markers of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 29:743–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-008-0764-8. PMID: 19009296.27. Rho YH, Solus J, Sokka T, Oeser A, Chung CP, Gebretsadik T, et al. 2009; Adipocytokines are associated with radiographic joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 60:1906–14. DOI: 10.1002/art.24626. PMID: 19565493. PMCID: PMC2894567.
Article28. Canoruç N, Kale E, Turhanoğlu AD, Özmen Ş, Ogün C, Kaplan A. DOI: 10.3906/sag-0801-13.29. Hizmetli S, Kisa M, Gokalp N, Bakici MZ. 2007; Are plasma and synovial fluid leptin levels correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatol Int. 27:335–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-006-0264-7. PMID: 17102942.
Article30. Gunaydin R, Kaya T, Atay A, Olmez N, Hur A, Koseoglu M. 2006; Serum leptin levels in rheumatoid arthritis and relationship with disease activity. South Med J. 99:1078–83. DOI: 10.1097/01.smj.0000240625.27772.79. PMID: 17100028.31. Otero M, Lago R, Gomez R, Lago F, Dieguez C, Gómez-Reino JJ, et al. 2006; Changes in plasma levels of fat-derived hormones adiponectin, leptin, resistin and visfatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1198–201. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2005.046540. PMID: 16414972. PMCID: PMC1798289.
Article32. Popa C, Netea MG, Radstake TR, van Riel PL, Barrera P, van der Meer JW. 2005; Markers of inflammation are negatively correlated with serum leptin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 64:1195–8. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.032243. PMID: 15731289. PMCID: PMC1755600.
Article33. Toussirot E, Nguyen NU, Dumoulin G, Aubin F, Cédoz JP, Wendling D. 2005; Relationship between growth hormone-IGF-I-IGFBP-3 axis and serum leptin levels with bone mass and body composition in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 44:120–5. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh421. PMID: 15466894.
Article34. Härle P, Pongratz G, Weidler C, Büttner R, Schölmerich J, Straub RH. 2004; Possible role of leptin in hypoandrogenicity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:809–16. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.011619. PMID: 15194576. PMCID: PMC1755074.35. Bokarewa M, Bokarew D, Hultgren O, Tarkowski A. 2003; Leptin consumption in the inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 62:952–6. DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.10.952. PMID: 12972473. PMCID: PMC1754314.36. Nishiya K, Nishiyama M, Chang A, Shinto A, Hashimoto K. 2002; [Serum leptin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are correlated with body mass index]. Rinsho Byori. 50:524–7. Japanese.37. Tokarczyk-Knapik A, Nowicki M, Wyroślak J. 2002; [The relation between plasma leptin concentration and body fat mass in patients with rheumatoid arthritis]. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 108:761–7. Polish.38. Salazar-Páramo M, González-Ortiz M, González-López L, Sánchez-Ortiz A, Valera-González IC, Martínez-Abundis E, et al. 2001; Serum leptin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 7:57–9. DOI: 10.1097/00124743-200102000-00016. PMID: 17039093.39. Anders HJ, Rihl M, Heufelder A, Loch O, Schattenkirchner M. 1999; Leptin serum levels are not correlated with disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Metabolism. 48:745–8. DOI: 10.1016/S0026-0495(99)90174-9. PMID: 10381149.
Article40. Cheng J, Luo Y, Li Y, Zhang F, Zhang X, Zhou X, et al. 2022; Sex- and body mass index-specific reference intervals for serum leptin: a population based study in China. Nutr Metab (Lond). 19:54. DOI: 10.1186/s12986-022-00689-x. PMID: 35941672. PMCID: PMC9358897.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Circulating leptin and its correlation with rheumatoid arthritis activity: a meta-analysis
- Circulating Interleukin-37 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Their Correlations With Disease Activity: A Meta-analysis
- YKL-40 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity: A Meta-analysis
- A Study on the Relationship between Mastery and Activity of Daily Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- Association between the Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio, and Platelet-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Rheumatoid Arthritis and their Correlations with the Disease Activity: A Meta-analysis