Imaging Sci Dent.
2019 Jun;49(2):103-113. 10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.103.
Correlations between anatomical variations of the nasal cavity and ethmoidal sinuses on cone-beam computed tomography scans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Dental Implant Research Center, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Dental School, Hamadan University of Medical Science, Hamadan, Iran.
- 2Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran.
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Dental School, Zanjan University of Medical Science, Zanjan, Iran. Bahar_Hekmat70@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2450176
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
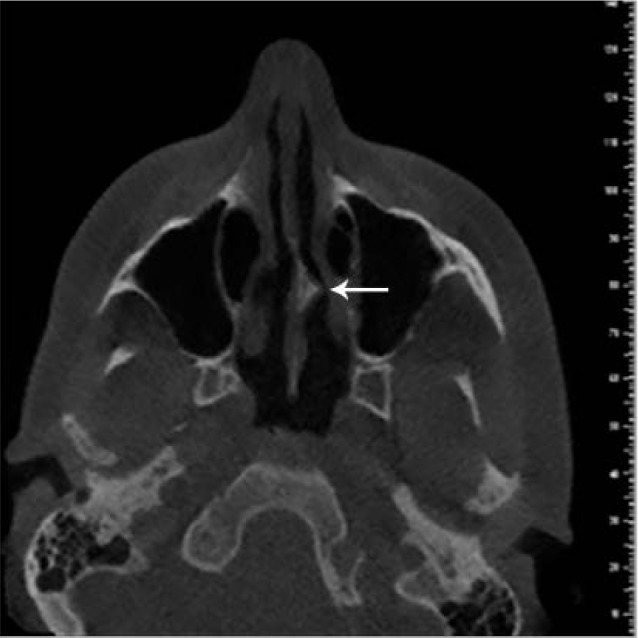
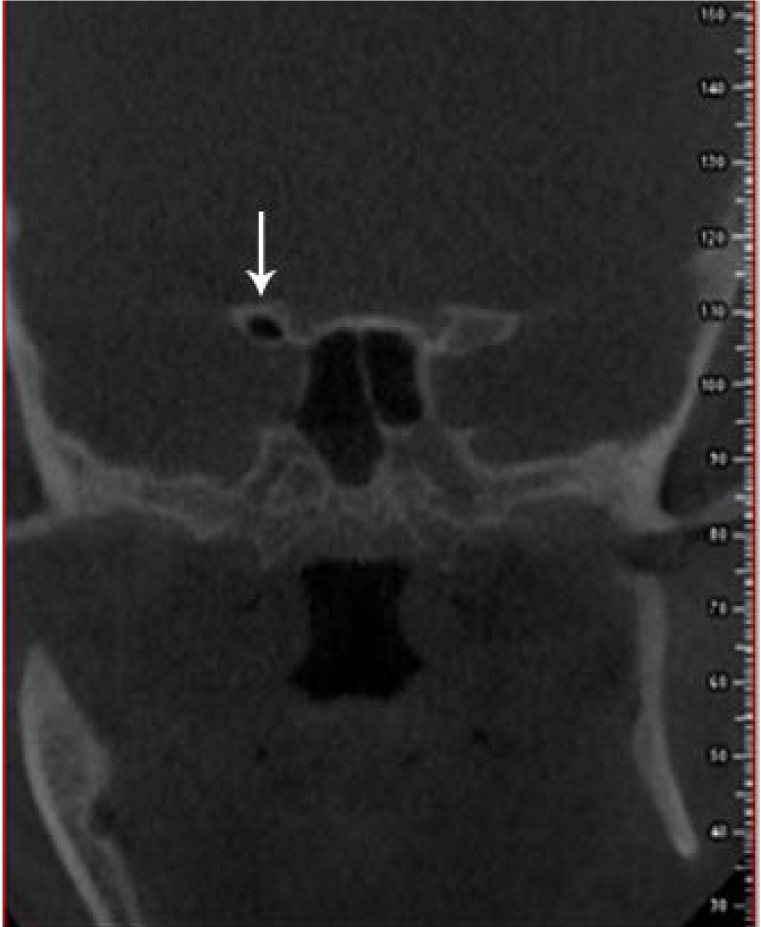
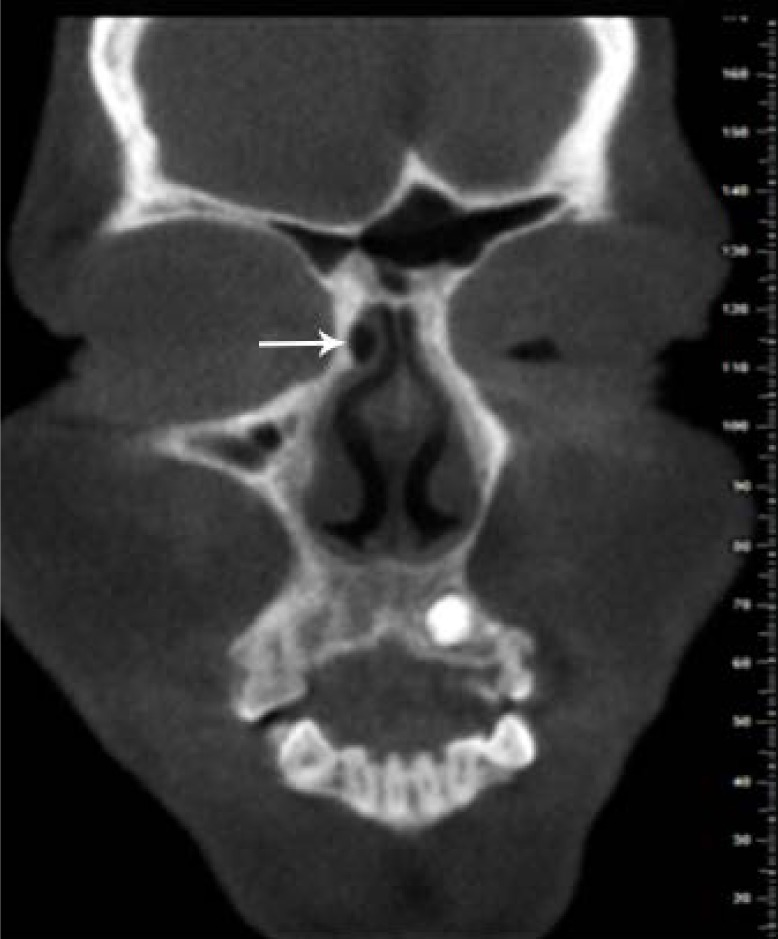
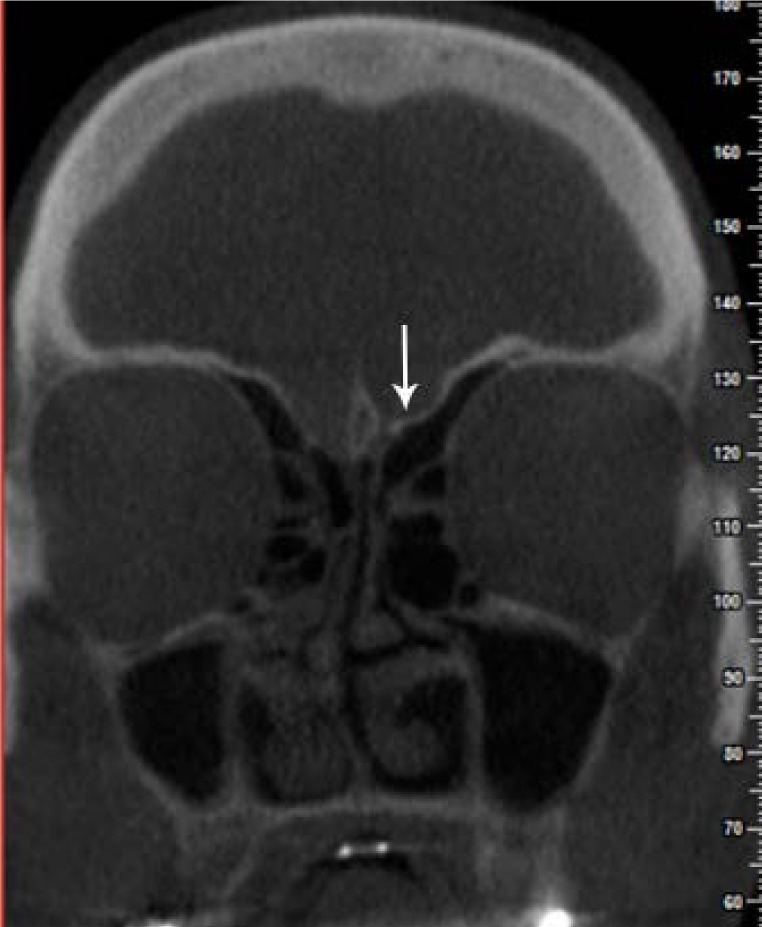
Anatomical variations of the external nasal wall are highly important, since they play a role in obstruction or drainage of the ostiomeatal complex and ventilation and can consequently elevate the risk of pathological sinus conditions. This study aimed to assess anatomical variations of the nasal cavity and ethmoidal sinuses and their correlations on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This cross-sectional study evaluated CBCT scans of 250 patients, including 107 males and 143 females, to determine the prevalence of anatomical variations of the nasal cavity and ethmoidal sinuses. All images were taken using a New Tom 3G scanner. Data were analyzed using the chi-square test, Kruskal-Wallis test, and the Mann-Whitney test.
RESULTS
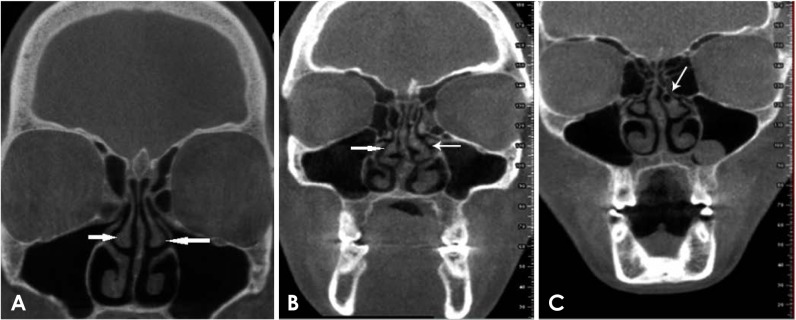
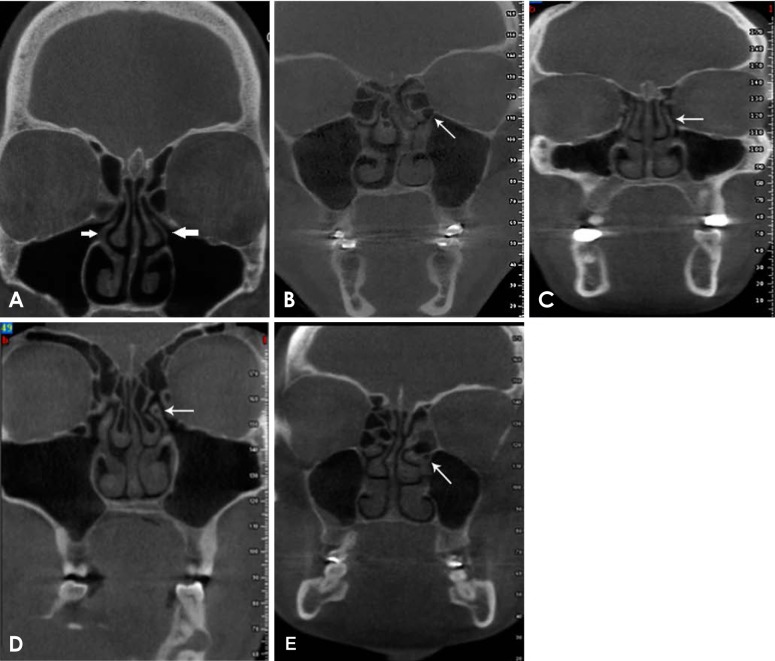
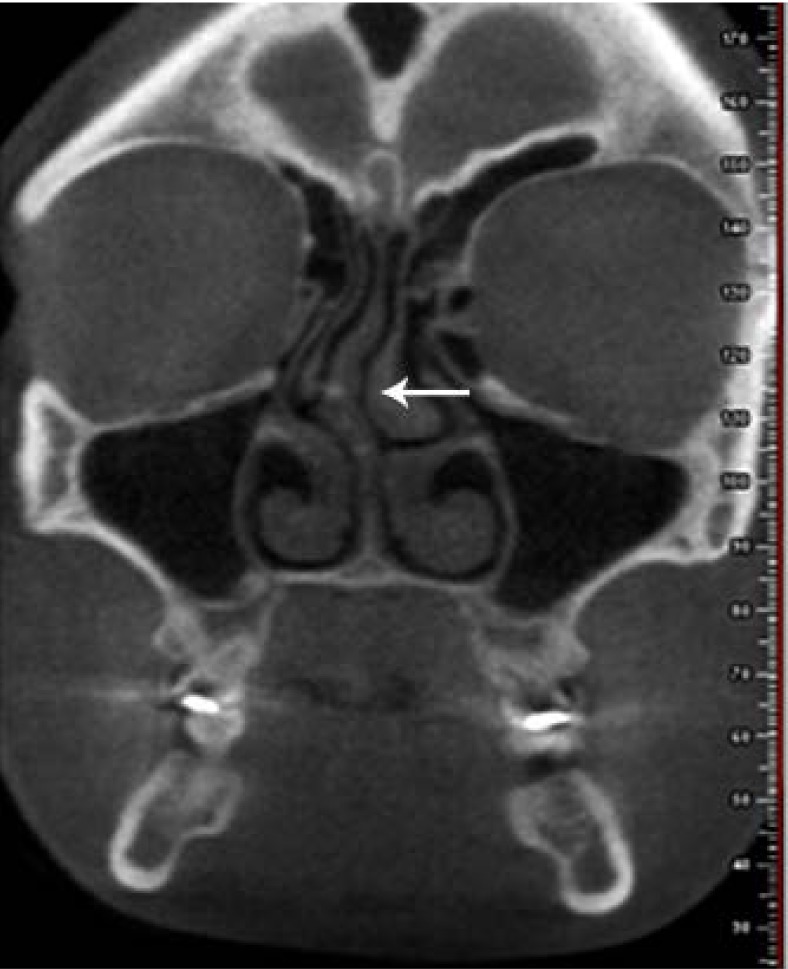
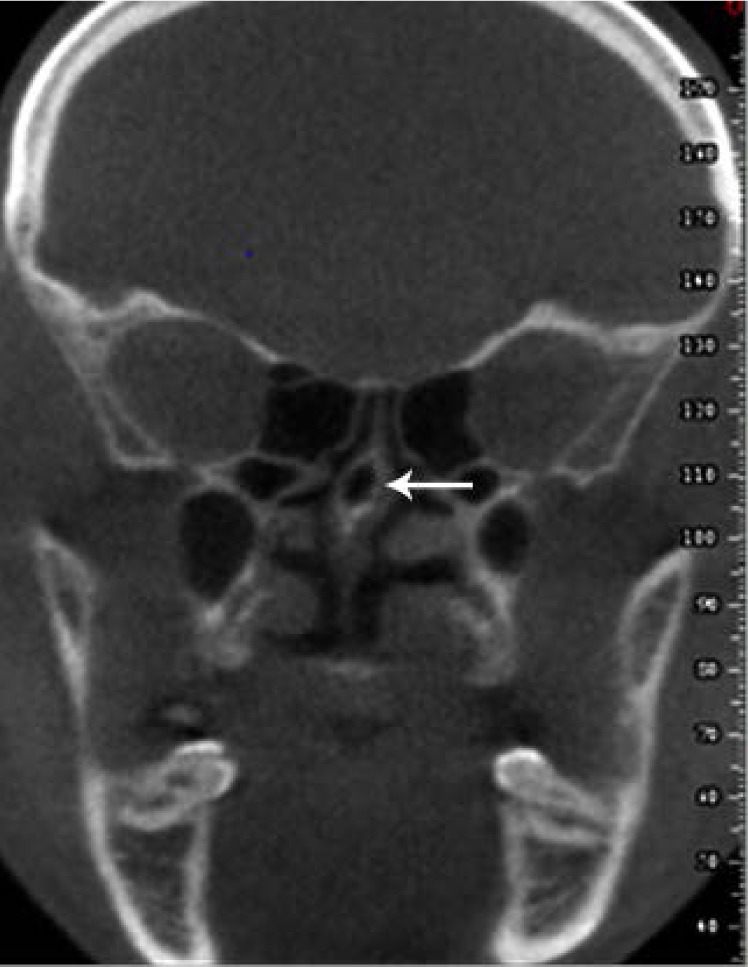
The most common anatomical variations were found to be nasal septal deviation (90.4%), agger nasi air cell (53.6%), superior orbital cell (47.6%), pneumatized nasal septum (40%), and Onodi air cell (37.2%). Correlations were found between nasal septal deviation and the presence of a pneumatized nasal septum, nasal spur, and Haller cell. No significant associations were noted between the age or sex of patients and the presence of anatomical variations (P>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Radiologists and surgeons must pay close attention to the anatomical variations of the sinonasal region in the preoperative assessment to prevent perioperative complications.
MeSH Terms
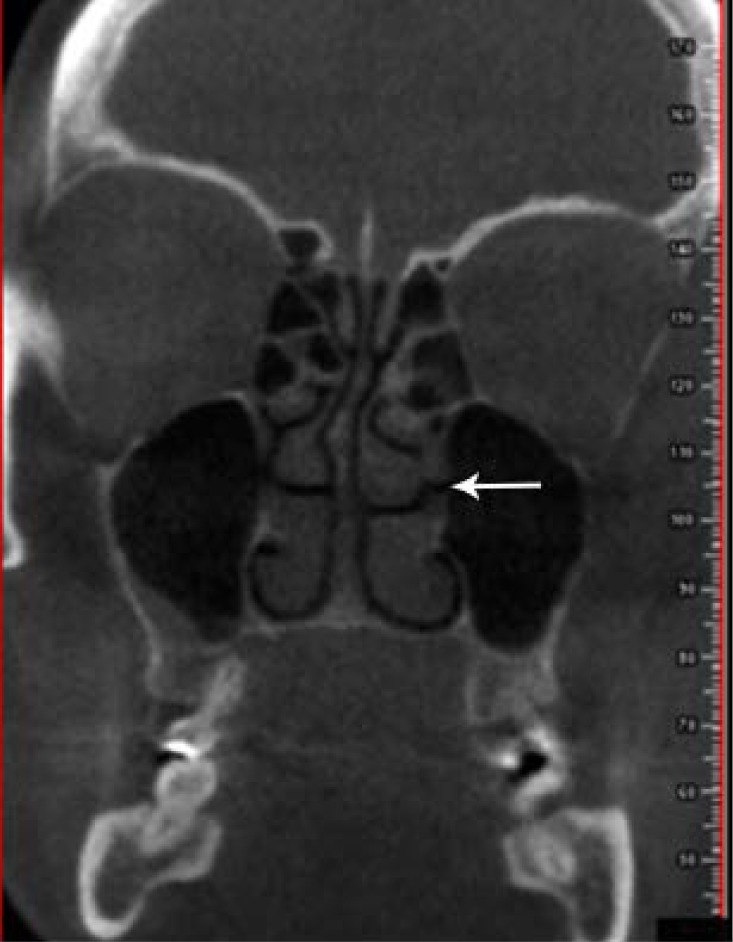
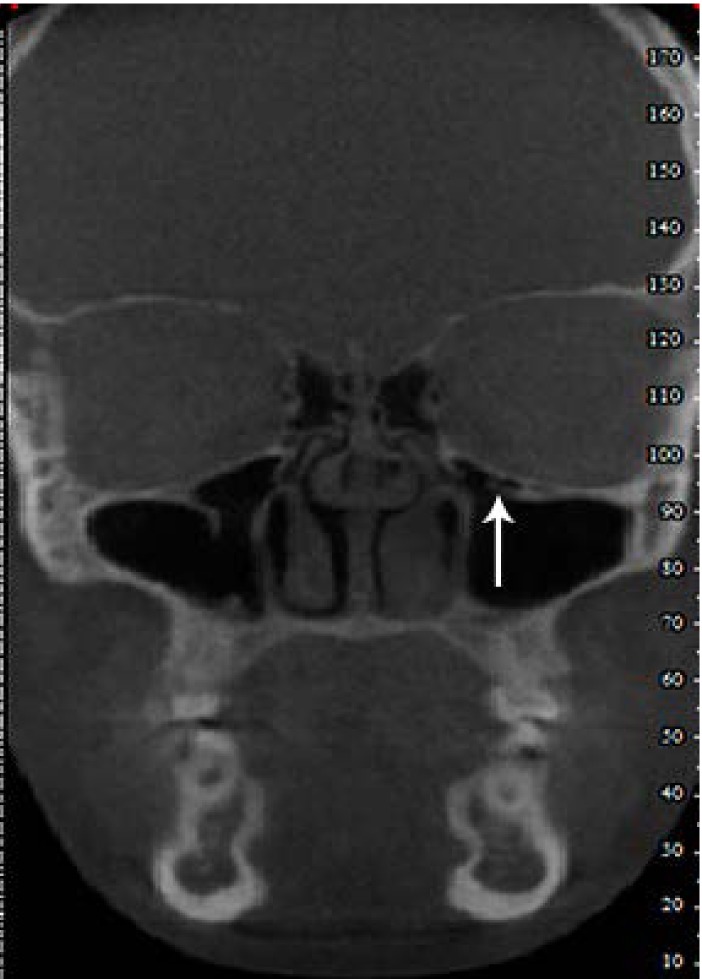
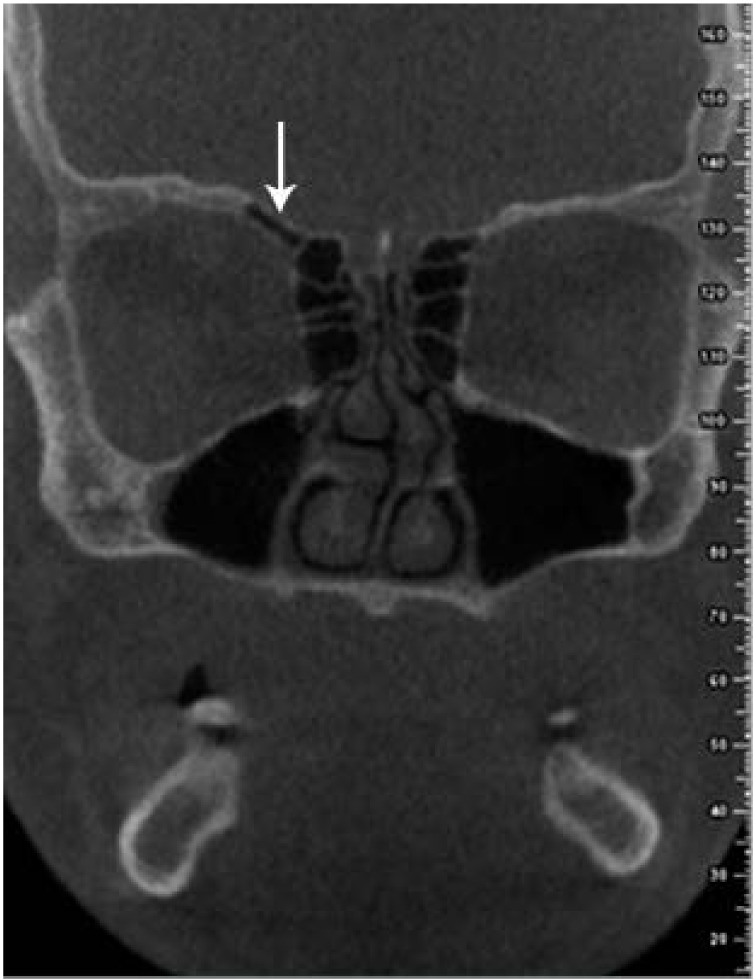
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Investigation of the prevalence and main features of skull-base anomalies and characteristics of the sphenoid sinus using cone-beam computed tomography
Aslıhan Akbulut, Oğuzhan Demirel, Kaan Orhan
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;48(4):207-218. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.4.207.
Reference
-
1. Koo SK, Kim JD, Moon JS, Jung SH, Lee SH. The incidence of concha bullosa, unusual anatomic variation and its relationship to nasal septal deviation: a retrospective radiologic study. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017; 44:561–570. PMID: 28173975.
Article2. Parks ET. Cone beam computed tomography for the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Dent Clin North Am. 2014; 58:627–651. PMID: 24993926.
Article3. Al-Abri R, Bhargava D, Al-Bassam W, Al-Badaai Y, Sawhney S. Clinically significant anatomical variants of the paranasal sinuses. Oman Med J. 2014; 29:110–113. PMID: 24715937.
Article4. Tao Z, Zhang J, Yang Q, Xiao B, Kong Y. Differences of anatomic variations in ostiomeatal complex between two sides of the deviated septum. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2001; 36:132–134. PMID: 12761982.5. Khojastepour L, Mirhadi S, Mesbahi SA. Anatomical variations of ostiomeatal complex in CBCT of patients seeking rhinoplasty. J Dent (Shiraz). 2015; 16:42–48. PMID: 25759857.6. Güldner C, Ningo A, Voigt J, Diogo I, Heinrichs J, Weber R, et al. Potential of dosage reduction in cone-beam-computed tomography (CBCT) for radiological diagnostics of the paranasal sinuses. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 270:1307–1315. PMID: 22986413.
Article7. Roman RA, Hedeşiu M, Gersak M, Fidan F, Băciuţ G, Băciuţ M. Assessing the prevalence of paranasal sinuses anatomical variants in patients with sinusitis using cone beam computer tomography. Clujul Med. 2016; 89:419–421.
Article8. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 7th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier;2014.9. Shokri A, Khajeh S. In vitro comparison of the effect of different slice thicknesses on the accuracy of linear measurements on cone beam computed tomography images in implant sites. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26:157–160. PMID: 25569395.
Article10. Shokri A, Miresmaeili A, Farhadian N, Falah-Kooshki S, Amini P, Mollaie N. Effect of changing the head position on accuracy of transverse measurements of the maxillofacial region made on cone beam computed tomography and conventional posterior-anterior cephalograms. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2017; 46:20160180. PMID: 28306330.
Article11. de Miranda CM, de Miranda Maranhão CP, Arraes FM, Padilha IG, de Farias LD, de Araujo Jatobá MS. Anatomical variations of paranasal sinuses at multislice computed tomography: what to look for. Radiol Bras. 2011; 44:256–262.12. Som PM, Curtin HD. Head and neck imaging. 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier;2011.13. Dasar U, Gokce E. Evaluation of variations in sinonasal region with computed tomography. World J Radiol. 2016; 8:98–108. PMID: 26834948.
Article14. Bremke M, Leppek R, Werner JA. Digital volume tomography in ENT medicine. HNO. 2010; 58:823–832. PMID: 20544169.15. Kurzweg T, Dalchow CV, Bremke M, Majdani O, Kureck I, Knecht R, et al. The value of digital volume tomography in assessing the position of cochlear implant arrays in temporal bone specimens. Ear Hear. 2010; 31:413–419. PMID: 20440115.
Article16. Aramani A, Karadi RN, Kumar S. A study of anatomical variations of osteomeatal complex in chronic rhinosinusitis patients-CT findings. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:KC01–KC04.17. Mamatha H, Shamasundar NM, Bharathi MB, Prasanna LC. Variations of ostiomeatal complex and its applied anatomy: a CT scan study. Indian J Sci Technol. 2010; 3:904–907.
Article18. Adeel M, Rajput MS, Akhter S, Ikram M, Arain A, Khattak YJ. Anatomical variations of nose and para-nasal sinuses; CT scan review. J Pak Med Assoc. 2013; 63:317–319. PMID: 23914628.19. Lerdlum S, Vachiranubhap B. Prevalence of anatomic variation demonstrated on screening sinus computed tomography and clinical correlation. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005; 88(Suppl 4):S110–S115.20. Stallman JS, Lobo JN, Som PM. The incidence of concha bullosa and its relationship to nasal septal deviation and paranasal sinus disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:1613–1618. PMID: 15502150.21. Earwaker J. Anatomic variants in sinonasal CT. Radiographics. 1993; 13:381–415. PMID: 8460226.
Article22. Mathew R, Omami G, Hand A, Fellows D, Lurie A. Cone beam CT analysis of Haller cells: prevalence and clinical significance. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2013; 42:20130055. PMID: 23975112.
Article23. Fadda GL, Rosso S, Aversa S, Petrelli A, Ondolo C, Succo G. Multiparametric statistical correlations between paranasal sinus anatomic variations and chronic rhinosinusitis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2012; 32:244–251. PMID: 23093814.24. Albuquerque CB, Zambrana NR, Zambrana JR, Ribeiro RA, Salgado DM, Costa C. Evaluation of prevalence of Haller cells and their relationship with maxilofacial changes. Clin Lab Res Dent. 2018; 54:1–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Agreement between cone-beam computed tomography and functional endoscopic sinus surgery for detection of pathologies and anatomical variations of the paranasal sinuses in chronic rhinosinusitis patients: A prospective study
- Middle meatal nasal recesses of the maxillary sinuses and dangerously modified nasal anatomy
- Anatomical variations of the ethmoid sinuses and their association with health or pathology of the ethmoid and maxillary sinuses in a Southern Chinese population: An analysis using cone-beam computed tomography
- Accessory mental foramen: A rare anatomical variation detected by cone-beam computed tomography
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report