Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 May;73(5):260-268. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.5.260.
Renal and Urinary Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kidney@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2447595
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.5.260
Abstract
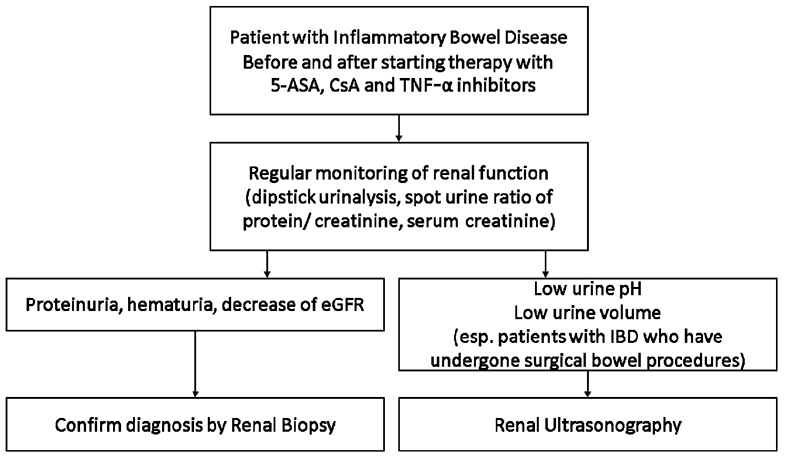
- The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is increasing rapidly and extra-intestinal manifestations in IBD are also increasing. The prevalence of renal and urinary involvement in IBD ranges from 4-23%. Nephrolithiasis is the most common urinary complication in IBD patients. Parenchymal renal disease is rare but has been well documented and presents most commonly as glomerulonephritis or tubulointerstitial nephritis. The overall morbidity of IBD-related renal manifestations is significant. Therefore, a high index of clinical suspicion and optimal monitoring of the renal function are needed for the early diagnosis and prevention of IBD-related renal manifestations and complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Rawsthorne P, Yu N. The prevalence of extraintestinal diseases in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1116–1122.
Article2. Mendoza JL, Lana R, Taxonera C, Alba C, Izquierdo S, Díaz-Rubio M. Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease: differences between Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Med Clin (Barc). 2005; 125:297–300.3. Greuter T, Vavricka SR. Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease - epidemiology, genetics, and pathogenesis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 13:307–317.
Article4. Pardi DS, Tremaine WJ, Sandborn WJ, McCarthy JT. Renal and urologic complications of inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998; 93:504–514.
Article5. Yang SK, Yun S, Kim JH, et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in the Songpa-Kangdong district, Seoul, Korea, 1986-2005: a KASID study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:542–549.
Article6. Ng SC, Tang W, Leong RW, et al. Environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based case-control study in Asia-Pacific. Gut. 2015; 64:1063–1071.7. Corica D, Romano C. Renal involvement in inflammatory bowel diseases. J Crohns Colitis. 2016; 10:226–235.
Article8. Das KM. Relationship of extraintestinal involvements in inflammatory bowel disease: new insights into autoimmune pathogenesis. Dig Dis Sci. 1999; 44:1–13.9. Rothfuss KS, Stange EF, Herrlinger KR. Extraintestinal manifestations and complications in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:4819–4831.
Article10. Sato H, Umemura K, Yamamoto T, Sato H. Interstitial nephritis associated with ulcerative colitis in monozygotic twins. BMJ Case Rep. 2017; 2017:bcr2016218346.
Article11. Danese S, Semeraro S, Papa A, et al. Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:7227–7236.
Article12. Oikonomou K, Kapsoritakis A, Eleftheriadis T, Stefanidis I, Potamianos S. Renal manifestations and complications of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:1034–1045.
Article13. Ambruzs JM, Walker PD, Larsen CP. The histopathologic spectrum of kidney biopsies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 9:265–270.
Article14. Shield DE, Lytton B, Weiss RM, Schiff M Jr. Urologic complications of inflammatory bowel disease. J Urol. 1976; 115:701–706.
Article15. Andersson H, Bosaeus I, Fasth S, Hellberg R, Hultén L. Cholelithiasis and urolithiasis in Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987; 22:253–256.
Article16. Parks JH, Worcester EM, O'Connor RC, Coe FL. Urine stone risk factors in nephrolithiasis patients with and without bowel disease. Kidney Int. 2003; 63:255–265.
Article17. Kane S. Urogenital complications of Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:12 Suppl. S640–S643.
Article18. Gkentzis A, Kimuli M, Cartledge J, Traxer O, Biyani CS. Urolithiasis in inflammatory bowel disease and bariatric surgery. World J Nephrol. 2016; 5:538–546.
Article19. Fisang C, Anding R, Müller SC, Latz S, Laube N. Urolithiasis--an interdisciplinary diagnostic, therapeutic and secondary preventive challenge. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015; 112:83–91.20. Primas C, Novacek G, Schweiger K, et al. Renal insufficiency in IBD--prevalence and possible pathogenetic aspects. J Crohns Colitis. 2013; 7:e630–e634.21. Ambruzs JM, Larsen CP. Renal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2018; 44:699–714.
Article22. Allison MJ, Cook HM, Milne DB, Gallagher S, Clayman RV. Oxalate degradation by gastrointestinal bacteria from humans. J Nutr. 1986; 116:455–460.
Article23. McConnell N, Campbell S, Gillanders I, Rolton H, Danesh B. Risk factors for developing renal stones in inflammatory bowel disease. BJU Int. 2002; 89:835–841.
Article24. Cury DB, Moss AC, Schor N. Nephrolithiasis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in the community. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2013; 6:139–142.
Article25. Varda BK, McNabb-Baltar J, Sood A, et al. Urolithiasis and urinary tract infection among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review of US emergency department visits between 2006 and 2009. Urology. 2015; 85:764–770.
Article26. Hubert D, Beaufils M, Meyrier A. Immunoglobulin A glomerular nephropathy associated with inflammatory colitis. Apropos of 2 cases. Presse Med. 1984; 13:1083–1085.27. Trimarchi HM, Iotti A, Iotti R, Freixas EA, Peters R. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy and ulcerative colitis. A focus on their pathogenesis. Am J Nephrol. 2001; 21:400–405.28. Takemura T, Okada M, Yagi K, Kuwajima H, Yanagida H. An adolescent with IgA nephropathy and Crohn disease: pathogenetic implications. Pediatr Nephrol. 2002; 17:863–866.
Article29. Forshaw MJ, Guirguis O, Hennigan TW. IgA nephropathy in association with Crohn's disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2005; 20:463–465.
Article30. Onime A, Agaba EI, Sun Y, et al. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy complicating ulcerative colitis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2006; 38:349–353.
Article31. Lee JM, Lee KM, Kim HW, et al. Crohn's disease in association with IgA nephropathy. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 52:115–119.32. Moayyedi P, Fletcher S, Harnden P, Axon AT, Brownjohn A. Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis associated with ulcerative colitis: case reports of two patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995; 10:1923–1924.33. Fornaciari G, Maccari S, Borgatti PP, et al. Nephrotic syndrome from 5-ASA for ulcerative colitis? Complicated by carcinoma of the colon and sclerosing cholangitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997; 24:37–39.34. Firwana BM, Hasan R, Chalhoub W, et al. Nephrotic syndrome after treatment of Crohn's disease with mesalamine: case report and literature review. Avicenna J Med. 2012; 2:9–11.
Article35. Casella G, Perego D, Baldini V, Monti C, Crippa S, Buda CA. A rare association between ulcerative colitis (UC), celiac disease (CD), membranous glomerulonephritis, leg venous thrombosis, and heterozygosity for factor V Leiden. J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37:761–762.
Article36. Warling O, Bovy C, Coïmbra C, Noterdaeme T, Delwaide J, Louis E. Overlap syndrome consisting of PSC-AIH with concomitant presence of a membranous glomerulonephritis and ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:4811–4816.
Article37. Shaer AJ, Stewart LR, Cheek DE, Hurray D, Self SE. IgA antiglomerular basement membrane nephritis associated with Crohn's disease: a case report and review of glomerulonephritis in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 41:1097–1109.
Article38. Plaisier E, Borradori L, Hellmark T, et al. Anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis and bullous pemphigoid caused by distinct anti-alpha 3(IV)NC1 and anti-BP180 antibodies in a patient with Crohn's disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 40:649–654.39. Marques da Costa P, Correia L, Correia LA. The complexity of renal involvment in IBD-C3 glomerulopathy in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018; 24:e4–e5.
Article40. Pouria S, Barratt J. Secondary IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2008; 28:27–37.
Article41. Wang J, Anders RA, Wu Q, et al. Dysregulated LIGHT expression on T cells mediates intestinal inflammation and contributes to IgA nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:826–835.
Article42. Efstratiadis G, Mainas A, Leontsini M. Renal amyloidosis complicating Crohn's disease. Case report and review of the literature. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996; 22:308–310.43. Ebert EC, Nagar M. Gastrointestinal manifestations of amyloidosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:776–787.
Article44. Wester AL, Vatn MH, Fausa O. Secondary amyloidosis in inflammatory bowel disease: a study of 18 patients admitted to Rikshospitalet University Hospital, Oslo, from 1962 to 1998. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2001; 7:295–300.
Article45. Tosca Cuquerella J, Bosca-Watts MM, Anton Ausejo R, Tejedor Alonso S, Mora De Miguel F, Minguez Perez M. Amyloidosis in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2016; 10:1245–1253.
Article46. Cabezuelo JB, Egea JP, Ramos F, Torrella E, Muray S, Alcázar C. Infliximab in the treatment of amyloidosis secondary to Crohn's disease. Nefrologia. 2012; 32:385–388.47. Iñarrairaegui Bastarrica M, Arín Letamendia A, Zozaya Urmeneta JM, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and amyloidosis. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 27:260–263.48. Park YK, Han DS, Eun CS. Systemic amyloidosis with Crohn's disease treated with infliximab. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:431–432.
Article49. Pukitis A, Zake T, Groma V, Ostrovskis E, Skuja S, Pokrotnieks J. Effect of infliximab induction therapy on secondary systemic amyloidosis associated with Crohn's disease: case report and review of the literature. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2013; 22:333–336.50. Blackmur JP, Chapman FA, Bellamy CO, et al. Anti-TNF-α therapy for renal amyloid as a complication of Crohn's disease. QJM. 2014; 107:57–59.
Article51. Itano S, Nagayama I, Yamaguchi Y, et al. A case of drug-induced granulomatous interstitial nephritis during the long course of Crohn's disease. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2013; 55:167–171.52. Tadic M, Grgurevic I, Scukanec-Spoljar M, et al. Acute interstitial nephritis due to mesalazine. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005; 10:103–105.53. Margetts PJ, Churchill DN, Alexopoulou I. Interstitial nephritis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with mesalamine. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001; 32:176–178.
Article54. Agharazii M, Marcotte J, Boucher D, Noël R, Lebel M. Chronic interstitial nephritis due to 5-aminosalicylic acid. Am J Nephrol. 1999; 19:373–376.
Article55. De Broe ME, Stolear JC, Nouwen EJ, Elseviers MM. 5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease: is there a link? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997; 12:1839–1841.56. Witte T, Olbricht CJ, Koch KM. Interstitial nephritis associated with 5-aminosalicylic acid. Nephron. 1994; 67:481–482.57. Manenti L, De Rosa A, Buzio C. Mesalazine-associated interstitial nephritis: twice in the same patient. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997; 12:2031.
Article58. Bailly E, Von Tokarski F, Beau-Salinas F, et al. Interstitial nephritis secondary to vedolizumab treatment in Crohn disease and safe rechallenge using steroids: a case report. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018; 71:142–145.
Article59. Izzedine H, Simon J, Piette AM, et al. Primary chronic interstitial nephritis in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:1436–1440.
Article60. Marcus SB, Brown JB, Melin-Aldana H, Strople JA. Tubulointerstitial nephritis: an extraintestinal manifestation of Crohn disease in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 46:338–341.
Article61. Waters AM, Zachos M, Herzenberg AM, Harvey E, Rosenblum ND. Tubulointerstitial nephritis as an extraintestinal manifestation of Crohn's disease. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008; 4:693–697.
Article62. Tokuyama H, Wakino S, Konishi K, Hashiguchi A, Hayashi K, Itoh H. Acute interstitial nephritis associated with ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2010; 14:483–486.
Article63. Shahrani Muhammad HS, Peters C, Casserly LF, Dorman AM, Watts M. Relapsing tubulointerstitial nephritis in an adolescent with inflammatory bowel disease without aminosalicylate exposure. Clin Nephrol. 2010; 73:250–252.64. Tovbin D, Kachko L, Hilzenrat N. Severe interstitial nephritis in a patient with renal amyloidosis and exacerbation of Crohn's disease. Clin Nephrol. 2000; 53:147–151.65. Colvin RB, Traum AZ, Taheri D, Jafari M, Dolatkhah S. Granulomatous interstitial nephritis as a manifestation of Crohn disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014; 138:125–127.
Article66. Timmermans SA, Christiaans MH, Abdul-Hamid MA, Stifft F, Damoiseaux JG, van Paassen P. Granulomatous interstitial nephritis and Crohn's disease. Clin Kidney J. 2016; 9:556–559.
Article67. Lewis B, Mukewar S, Lopez R, Brzezinski A, Hall P, Shen B. Frequency and risk factors of renal insufficiency in inflammatory bowel disease inpatients. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1846–1851.
Article68. Gisbert JP, González-Lama Y, Maté J. 5-Aminosalicylates and renal function in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:629–638.69. Elseviers MM, D'Haens G, Lerebours E, et al. Renal impairment in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: association with aminosalicylate therapy? Clin Nephrol. 2004; 61:83–89.
Article70. Heap GA, So K, Weedon M, et al. Clinical features and HLA association of 5-aminosalicylate (5-ASA)-induced nephrotoxicity in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016; 10:149–158.
Article71. Corrigan G, Stevens PE. Review article: interstitial nephritis associated with the use of mesalazine in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 14:1–6.
Article72. World MJ, Stevens PE, Ashton MA, Rainford DJ. Mesalazine-associated interstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996; 11:614–621.
Article73. Calviño J, Romero R, Pintos E, et al. Mesalazine-associated tubulo-interstitial nephritis in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Nephrol. 1998; 49:265–267.74. Oikonomou KA, Kapsoritakis AN, Stefanidis I, Potamianos SP. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity in inflammatory bowel disease. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011; 119:c89–c96.
Article75. Ciarcia R, Damiano S, Florio A, et al. The protective effect of apocynin on cyclosporine a-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2015; 116:1848–1856.
Article76. Burdmann EA, Andoh TF, Yu L, Bennett WM. Cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol. 2003; 23:465–476.
Article77. Sereno J, Rodrigues-Santos P, Vala H, et al. Transition from cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction to nephrotoxicity in an in vivo rat model. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15:8979–8997.
Article78. Baumgart DC, Pintoffl JP, Sturm A, Wiedenmann B, Dignass AU. Tacrolimus is safe and effective in patients with severe steroid-refractory or steroid-dependent inflammatory bowel disease--a long-term follow-up. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1048–1056.
Article79. den Broeder AA, Assmann KJ, van Riel PL, Wetzels JF. Nephrotic syndrome as a complication of anti-TNFalpha in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Neth J Med. 2003; 61:137–141.80. Chin G, Luxton G, Harvey JM. Infliximab and nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005; 20:2824–2826.
Article81. Saint Marcoux B, De Bandt M. CRI (Club Rhumatismes et Inflammation). Vasculitides induced by TNFalpha antagonists: a study in 39 patients in France. Joint Bone Spine. 2006; 73:710–713.82. Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Muñoz S, et al. Autoimmune diseases induced by TNF-targeted therapies: analysis of 233 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007; 86:242–251.83. Kim Y, Matsushita K, Sang Y, et al. Association of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T and natriuretic peptide with incident ESRD: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015; 65:550–558.
Article84. Waugh J, Hooper R, Lamb E, et al. Spot protein-creatinine ratio and spot albumin-creatinine ratio in the assessment of pre-eclampsia: a diagnostic accuracy study with decision-analytic model-based economic evaluation and acceptability analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2017; 21:1–90.
Article85. Inker LA, Astor BC, Fox CH, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 63:713–735.
Article86. Pearle MS, Goldfarb DS, Assimos DG, et al. Medical management of kidney stones: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2014; 192:316–324.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dermatologic Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Pediatric Age
- A Pediatric Case of Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Renal Amyloidosis
- Pathogenesis and clinical perspectives of extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel diseases
- Abdominal Pain over 6 Months