Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2019 May;12(2):212-216. 10.21053/ceo.2018.00808.
Clinical Characteristics and Management of Saccular Cysts: A Single Institute Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Institute of Logopedics and Phoniatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ewellcastle@gmail.com
- KMID: 2447431
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2018.00808
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
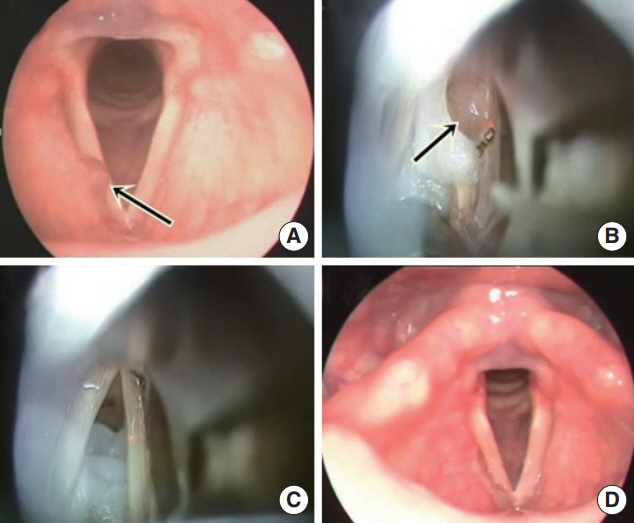
A saccular cyst is defined as a dilated saccule of the larynx, filled with mucus, and is located between the false vocal cords and the thyroid cartilage. Although this uncommon laryngeal condition is benign in nature, it could lead to dyspnea, stridor, and airway obstruction, depending on its size and location. Furthermore, some saccular cysts have been associated with laryngeal carcinoma. This study aimed to characterize this rather uncommon laryngeal condition to aid in determining the proper management of this pathology.
METHODS
Medical records were retrospectively reviewed of all patients with saccular cysts diagnosed and treated between 2006 and 2017 at a tertiary otolaryngologic care center.
RESULTS
Seven patients with saccular cysts were identified (male:female=2:5; mean age, 34.1 years); two were pediatric patients. Surgical intervention was performed in all patients by laryngo-microsurgery using CO2 laser. There was no recurrence after the initial surgical treatment.
CONCLUSION
Saccular cysts can be managed endoscopically using CO2 laser, without requiring an external approach. Therefore, an endoscopic approach should be actively considered for an optimal treatment outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holinger LD, Barnes DR, Smid LJ, Holinger PH. Laryngocele and saccular cysts. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1978; Sep-Oct. 87(5 Pt 1):675–85.
Article2. Young VN, Smith LJ. Saccular cysts: a current review of characteristics and management. Laryngoscope. 2012; Mar. 122(3):595–9.3. Niparko JK, Moran ML, Baker SR. Laryngeal saccular cyst: an unusual clinical presentation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1987; Dec. 97(6):576–9.
Article4. Harrison DF. Saccular mucocele and laryngeal cancer. Arch Otolaryngol. 1977; Apr. 103(4):232–4.
Article5. Micheau C, Luboinski B, Lanchi P, Cachin Y. Relationship between laryngoceles and laryngeal carcinomas. Laryngoscope. 1978; Apr. 88(4):680–8.
Article6. Mitroi M, Capitanescu A, Popescu FC, Popescu C, Mogoanta CA, Mitroi G, et al. Laryngocele associated with laryngeal carcinoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011; 52(1):183–5.7. Thabet MH, Kotob H. Lateral saccular cysts of the larynx: aetiology, diagnosis and management. J Laryngol Otol. 2001; Apr. 115(4):293–7.
Article8. Xiao Y, Wang J, Ma L, Han D. The clinical characteristics of congenital laryngeal saccular cysts. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016; 136(2):168–71.
Article9. Cohen O, Tzelnick S, Galitz YS, Shoffel-Havakuk H, Hain M, Halperin D, et al. Potential causative factors for saccular disorders: association with smoking and other laryngeal pathologies. J Voice. 2017; Sep. 31(5):621–7.
Article10. Hogikyan ND, Bastian RW. Endoscopic CO2 laser excision of large or recurrent laryngeal saccular cysts in adults. Laryngoscope. 1997; Feb. 107(2):260–5.11. Parkes WJ, Propst EJ. Advances in the diagnosis, management, and treatment of neonates with laryngeal disorders. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016; Aug. 21(4):270–6.
Article12. Civantos FJ, Holinger LD. Laryngoceles and saccular cysts in infants and children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992; Mar. 118(3):296–300.
Article13. Holzki J, Carroll RG. History of anatomical studies of the pediatric larynx. Paediatr Anaesth. 2016; Feb. 26(2):223–5.
Article14. Kaur A, Kini U, Alva SK. Cysts of the larynx: a clinicopathologic study of nine cases. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998; Jul. 50(3):250–6.15. DeSanto LW, Devine KD, Weiland LH. Cysts of the larynx: classification. Laryngoscope. 1970; Jan. 80(1):145–76.16. Kinnunen I, Klemi P, Grenman R. Saccular laryngeal cysts: three case studies and review of the literature. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2000; Mar-Apr. 62(2):109–11.17. Rubin JS, Silver CE. Surgical approach to submucosal lesions of the supraglottic larynx: the supero-lateral thyrotomy. J Laryngol Otol. 1992; May. 106(5):416–9.
Article18. Kumar S, Garg S, Sahni JK. Radiofrequency ablation of laryngeal saccular cyst in infants: a series of six cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; May. 76(5):667–9.
Article19. Zheng X, Bielamowicz S, Luo H, Mittal R. A computational study of the effect of false vocal folds on glottal flow and vocal fold vibration during phonation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009; Mar. 37(3):625–42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics and Management of Intrathoracic Bronchogenic Cysts: A Single Center Experience
- Incidental Saccular Aneurysms on Head MR Angiography: 5 Years' Experience at a Single Large-Volume Center
- Multiple Intratesticular Cysts
- Ameloblastoma Arising in Odontogenic Cysts: Report of 5 Cases and its Histologic Characteristics
- Management of Simple Hepatic Cyst: Is It Time to Change Our Paradigm to Early Non-Surgical Intervention?