World J Mens Health.
2013 Apr;31(1):79-82.
Multiple Intratesticular Cysts
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. joon501@naver.com
- 2Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
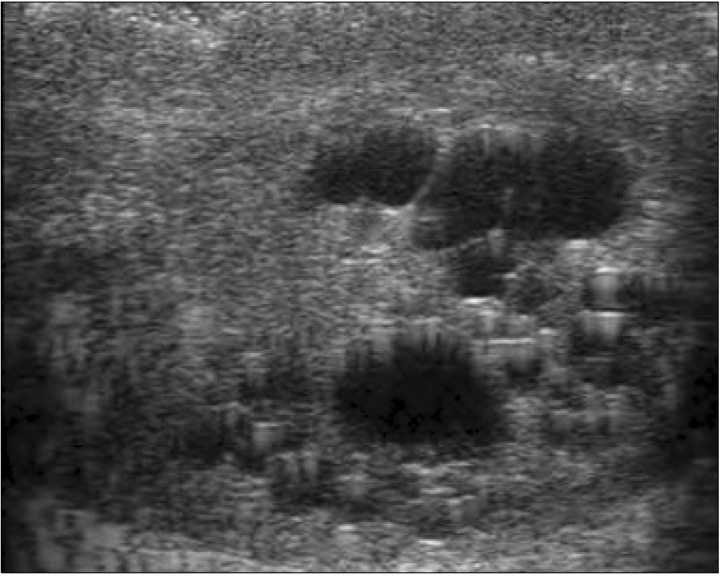
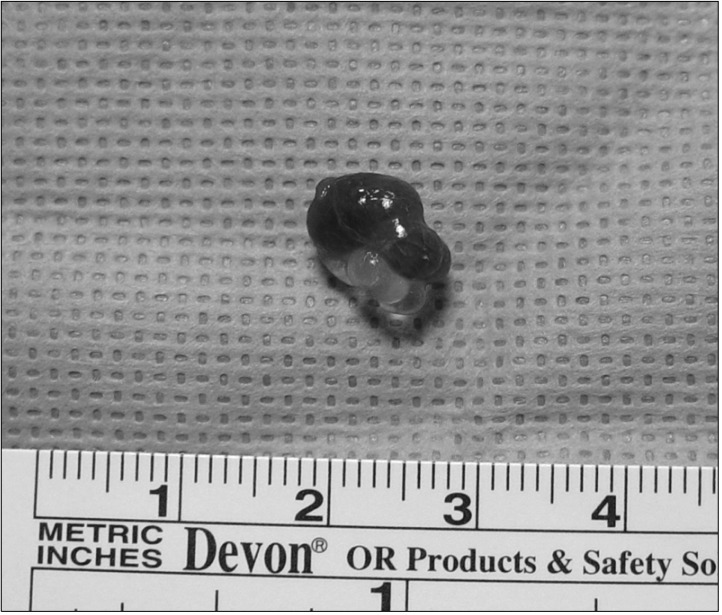
- Intratesticular cysts, once thought to be a rarity, are now being reported with an increasing prevalence as a result of the wider use of scrotal ultrasound scanning. Despite greater understanding of intratesticular cysts, their management remains unclear. Treatment has included enucleation and even radical orchiectomy over fear of the possibility of an associated malignancy. A more conservative approach with serial ultrasound scanning has been advocated if a clear distinction can be made between neoplastic and non-neoplastic testicular cysts. However, in view of the benign nature of such cysts, even repeated ultrasound scanning may not be necessary and may be considered over-treatment. In this study we present clinical and morphological characteristics of multiple cysts in the right testicle in a 62-year-old patient, where a slightly nodular lesion in the right testicle was detected.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hamm B, Fobbe F, Loy V. Testicular cysts: differentiation with US and clinical findings. Radiology. 1988; 168:19–23. PMID: 3289090.
Article2. Khorsandi M, Lobby N, Harkaway RC, Ginsberg PC. Testicular cysts: management and literature review. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1999; 99:537–538. PMID: 10578562.
Article3. Kratzik C, Hainz A, Kuber W, Donner G, Lunglmayr G, Frick J, et al. Surveillance strategy for intratesticular cysts: preliminary report. J Urol. 1990; 143:313–315. PMID: 2405187.
Article4. Höbarth K, Kratzik C. High resolution ultrasonography in the diagnosis of simple intratesticular cysts. Br J Urol. 1992; 70:546–549. PMID: 1467863.5. Leung ML, Gooding GA, Williams RD. High-resolution sonography of scrotal contents in asymptomatic subjects. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984; 143:161–164. PMID: 6610313.
Article6. Gooding GA, Leonhardt W, Stein R. Testicular cysts: US findings. Radiology. 1987; 163:537–538. PMID: 3550884.
Article7. Dmochowski RR, Rudy DC, Weitzner S, Corriere JN Jr. Simple cyst of the testis. J Urol. 1989; 142:1078–1081. PMID: 2677412.
Article8. Rifkin M, Cochlin DL. Imaging of the Scrotum & Penis. 2002. 1st ed. New York: Martin Dunitz;p. 33–94.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Various Intratesticular Hypoechoic Lesions on Scrotal Sonography
- Comparison of Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasonography in the Detection of Intratesticular Blood Flow of Normal Infants
- A case of intratesticular simple cyst
- Intratesticular Simple Cyst: Report of a Case
- Intratesticular Varicocele Associated with Ipsilateral Extratesticular Varicocele