J Adv Prosthodont.
2019 Apr;11(2):128-137. 10.4047/jap.2019.11.2.128.
Physical characteristics of ceramic/glass-polymer based CAD/CAM materials: Effect of finishing and polishing techniques
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey.
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey. ferhanegilmez@gmail.com
- KMID: 2444147
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2019.11.2.128
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to compare the effect of different finishing and polishing techniques on water absorption, water solubility, and microhardness of ceramic or glass-polymer based computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials following thermocycling.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
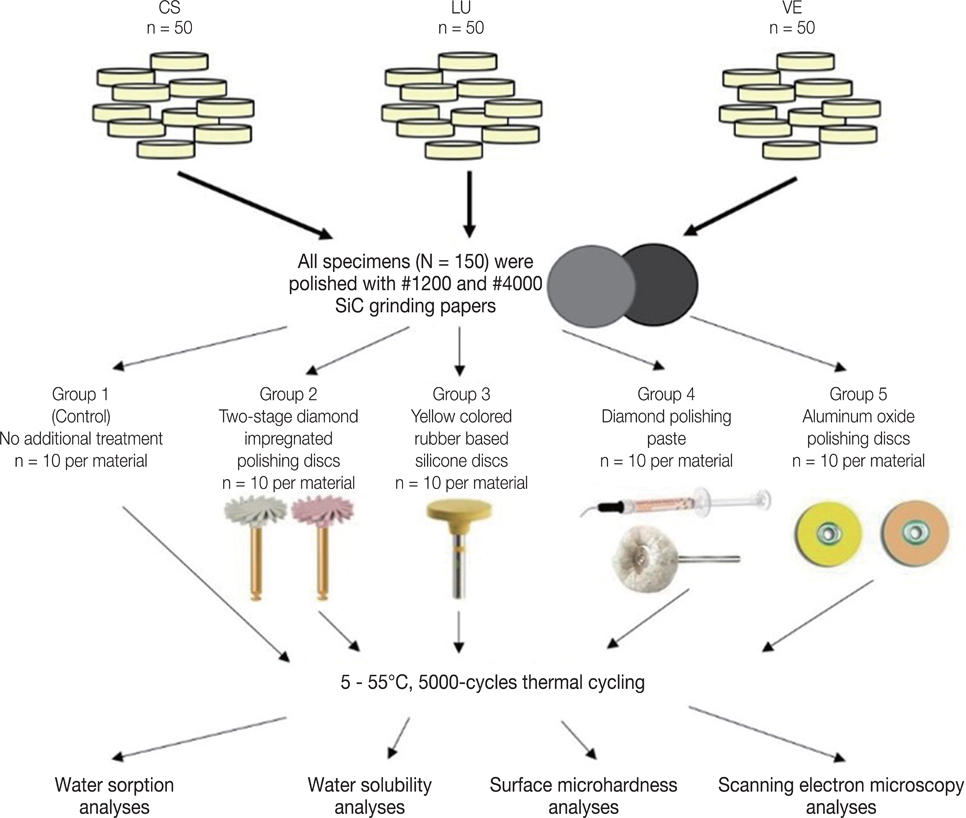
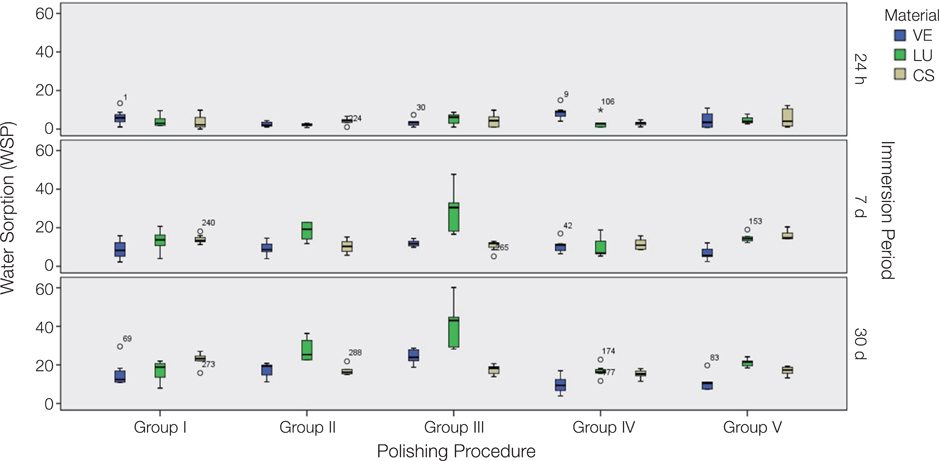
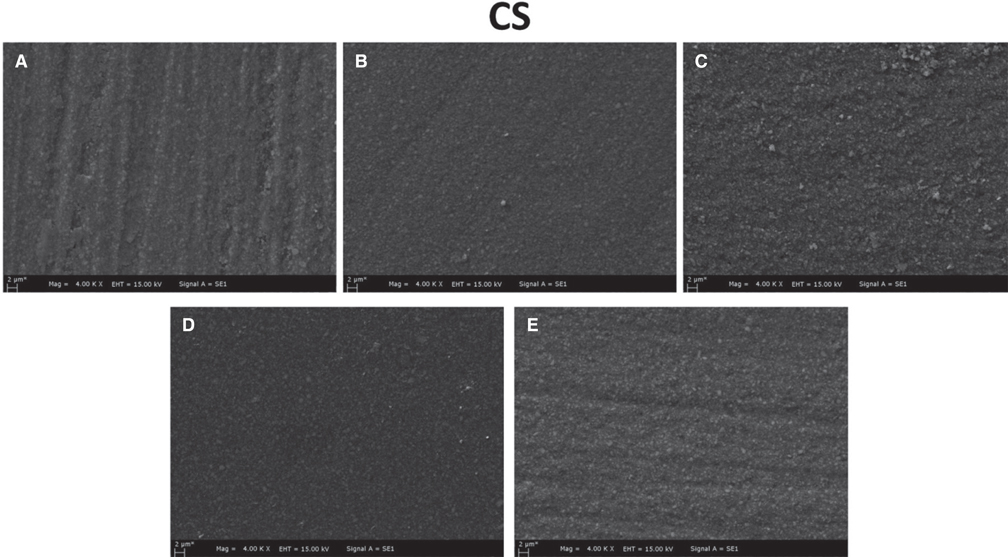
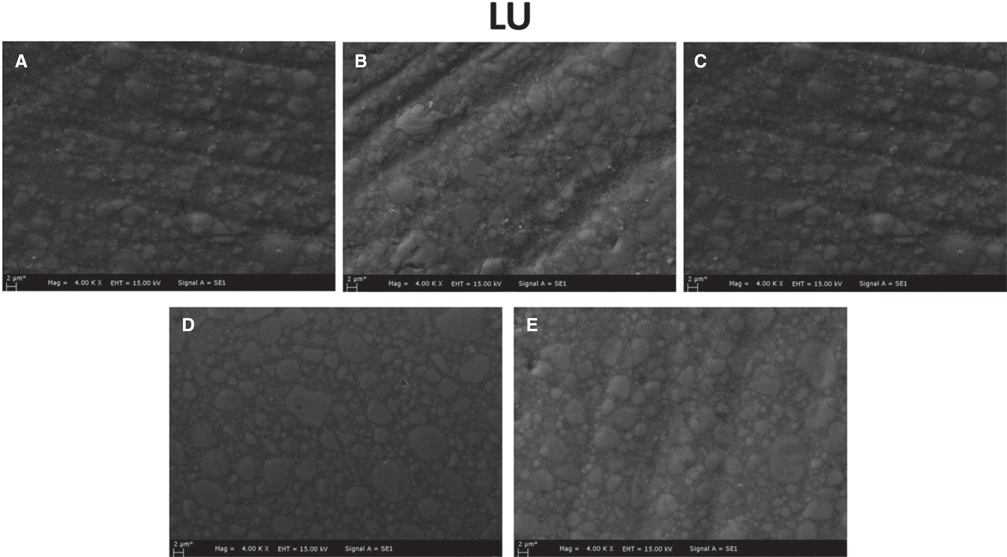
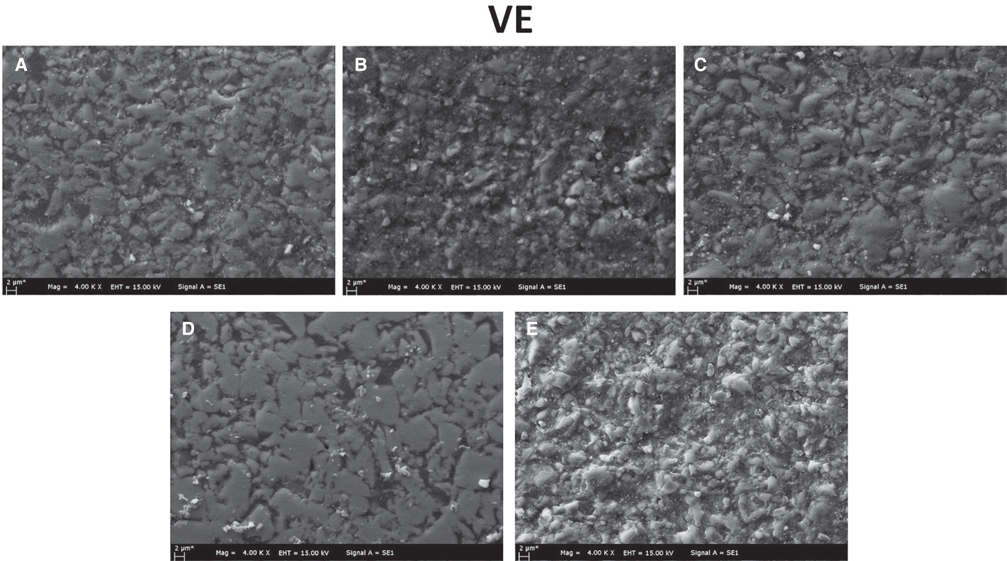
150 disc-shaped specimens were prepared from three different hybrid materials and divided into five subgroups according to the applied surface polishing techniques. All specimens were subjected up to #4000 grit SiC paper grinding. No additional polishing has been done to the control group (Group I). Other polishing procedures were as follows: Group II: two-stage diamond impregnated polishing discs; Group III: yellow colored rubber based silicone discs; Group IV: diamond polishing paste; and Group V: Aluminum oxide polishing discs. Subsequently, 5000-cycles of thermocycling were applied. The analyses were conducted after 24 hours, 7 days, and 30 days of water immersion. Water absorption and water solubility results were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Tukey post-hoc tests. Besides, microhardness data were compared by Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests (P<.05).
RESULTS
Surface polishing procedures had significant effects on water absorption and solubility and surface microhardness of resin ceramics (P<.05). Group IV exhibited the lowest water absorption and the highest microhardness values (P<.05). Immersion periods had no effect on the microhardness of hybrid ceramic materials (P>.05).
CONCLUSION
Surface finishing and polishing procedures might negatively affect physical properties of hybrid ceramic materials. Nevertheless, immersion periods do not affect the microhardness of the materials. Final polishing by using diamond polishing paste can be recommended for all CAD/CAM materials.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stawarczyk B, Awad D, Ilie N. Blue-Light transmittance of esthetic monolithic CAD/CAM materials with respect to their composition, thickness, and curing conditions. Oper Dent. 2016; 41:531–540.
Article2. Fasbinder DJ, Neiva GF. Surface evaluation of polishing techniques for new resilient CAD/CAM restorative materials. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2016; 28:56–66.
Article3. Vichi A, Fonzar RF, Goracci C, Carrabba M, Ferrari M. Effect of finishing and polishing on roughness and gloss of lithium disilicate and lithium silicate zirconia reinforced glass ceramic for CAD/CAM systems. Oper Dent. 2018; 43:90–100.
Article4. Acar B, Egilmez F. Effects of various polishing techniques and thermal cycling on the surface roughness and color change of polymer-based CAD/CAM materials. Am J Dent. 2018; 31:91–96.5. Alshali RZ, Salim NA, Satterthwaite JD, Silikas N. Long-term sorption and solubility of bulk-fill and conventional resincomposites in water and artificial saliva. J Dent. 2015; 43:1511–1518.
Article6. Tekçe N, Pala K, Demirci M, Tuncer S. Changes in surface characteristics of two different resin composites after 1 year water storage: An SEM and AFM study. Scanning. 2016; 38:694–700.
Article7. Egilmez F, Ergun G, Cekic-Nagas I, Vallittu PK, Lassila LVJ. Does artificial aging affect mechanical properties of CAD/CAM composite materials. J Prosthodont Res. 2018; 62:65–74.
Article8. Hampe R, Lümkemann N, Sener B, Stawarczyk B. The effect of artificial aging on Martens hardness and indentation modulus of different dental CAD/CAM restorative materials. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018; 86:191–198.
Article9. El Gezawi M, Kaisarly D, Al-Saleh H, ArRejaie A, Al-Harbi F, Kunzelmann KH. Degradation potential of bulk versus incrementally applied and indirect composites: color, microhardness, and surface deterioration. Oper Dent. 2016; 41:e195–e208.
Article10. Toledano M, Osorio R, Osorio E, Fuentes V, Prati C, Garcia-Godoy F. Sorption and solubility of resin-based restorative dental materials. J Dent. 2003; 31:43–50.
Article11. Poplawski T, Loba K, Pawlowska E, Szczepanska J, Blasiak J. Genotoxicity of urethane dimethacrylate, a tooth restoration component. Toxicol in vitro. 2010; 24:854–862.
Article12. Ruse ND, Sadoun MJ. Resin-composite blocks for dental CAD/CAM applications. J Dent Res. 2014; 93:1232–1234.
Article13. ISO 4049. Dentistry - Polymer-based restorative materials. Geneva; Switzerland: International Standards Organization (ISO);2009. Available at: https://www.iso.org/standard/42898.html.14. Gajewski VE, Pfeifer CS, Fróes-Salgado NR, Boaro LC, Braga RR. Monomers used in resin composites: degree of conversion, mechanical properties and water sorption/solubility. Braz Dent J. 2012; 23:508–514.
Article15. Belli R, Geinzer E, Muschweck A, Petschelt A, Lohbauer U. Mechanical fatigue degradation of ceramics versus resin composites for dental restorations. Dent Mater. 2014; 30:424–432.
Article16. Vasudeva G. Monomer systems for dental composites and their future: a review. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2009; 37:389–398.17. Fleming GJ, Awan M, Cooper PR, Sloan AJ. The potential of a resin-composite to be cured to a 4mm depth. Dent Mater. 2008; 24:522–529.
Article18. Liebermann A, Wimmer T, Schmidlin PR, Scherer H, Löffler P, Roos M, Stawarczyk B. Physicomechanical characterization of polyetheretherketone and current esthetic dental CAD/CAM polymers after aging in different storage media. J Prosthet Dent. 2016; 115:321–328.
Article19. Rodrigues SA Jr, Ferracane JL, Della Bona A. Flexural strength and Weibull analysis of a microhybrid and a nanofill composite evaluated by 3- and 4-point bending tests. Dent Mater. 2008; 24:426–431.20. Takeshige F, Kawakami Y, Hayashi M, Ebisu S. Fatigue behavior of resin composites in aqueous environments. Dent Mater. 2007; 23:893–899.
Article21. American Dental Association. Reports of councils and bureaus revised American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association specification no 27 for resin-based filling materials. 1988. p. 8–9.22. Watanabe T, Miyazaki M, Takamizawa T, Kurokawa H, Rikuta A, Ando S. Influence of polishing duration on surface roughness of resin composites. J Oral Sci. 2005; 47:21–25.
Article23. Venturini D, Cenci MS, Demarco FF, Camacho GB, Powers JM. Effect of polishing techniques and time on surface roughness, hardness and microleakage of resin composite restorations. Oper Dent. 2006; 31:11–17.
Article24. Aytac F, Karaarslan ES, Agaccioglu M, Tastan E, Buldur M, Kuyucu E. Effects of novel finishing and polishing systems on surface roughness and morphology of nanocomposites. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2016; 28:247–261.
Article25. Egilmez F, Ergun G, Cekic-Nagas I, Vallittu PK, Lassila LV. Short and long term effects of additional post curing and polishing systems on the color change of dental nano-composites. Dent Mater J. 2013; 32:107–114.
Article26. Bottino MC, Valandro LF, Kantorski KZ, Bressiani JC, Bottino MA. Polishing methods of an alumina-reinforced feldspar ceramic. Braz Dent J. 2006; 17:285–289.
Article27. Rinastiti M, Özcan M, Siswomihardjo W, Busscher HJ. Effects of surface conditioning on repair bond strengths of non-aged and aged microhybrid, nanohybrid, and nanofilled composite resins. Clin Oral Investig. 2011; 15:625–633.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of surface finishing treatments on the color stability of CAD/CAM materials
- The effects of different polishing techniques on the staining resistance of CAD/CAM resin-ceramics
- Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of the Leucite-Reinforced Glass-Ceramics for Dental CAD/CAM
- Evaluation of marginal fit of 2 CAD-CAM anatomic contour zirconia crown systems and lithium disilicate glass-ceramic crown
- Marginal fit of the digident CAD/CAM zirconia ceramic crowns