Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Apr;73(4):230-234. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.4.230.
Concomitant Liver and Brain Abscesses Caused by Parvimonas Micra
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea. p100100@dau.ac.kr
- 2Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2443637
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.4.230
Abstract
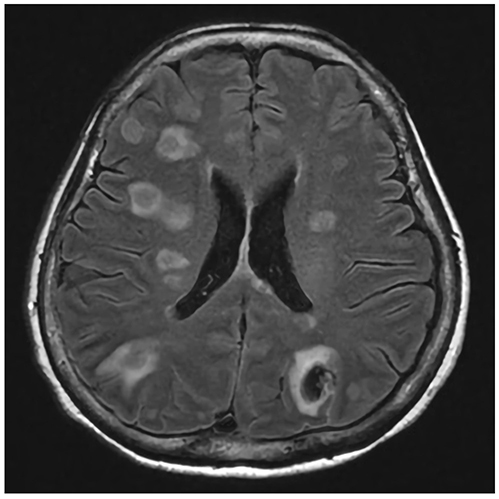
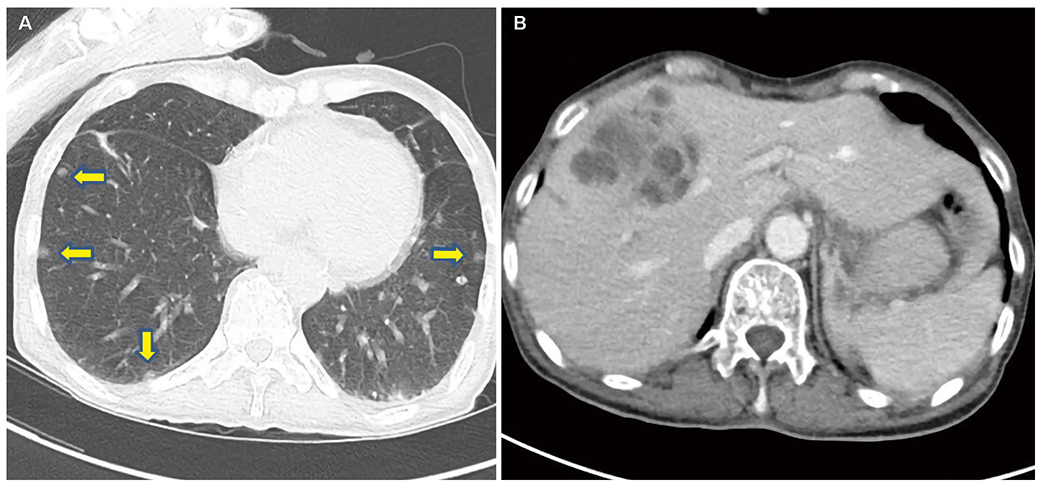
- Anaerobic infections have been reported to be responsible for 3-10% of pyogenic liver abscesses in Korea, and reported anaerobes include Fusobacterium, Bacillus fragilis, and Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Parvimonas micra is an anaerobic, Gram-positive, non-spore-forming bacterial species and a constituent of normal flora on skin, vagina, gastrointestinal tract, and oral cavity that can cause opportunistic infections. However, it has only rarely been reported to be a cause of liver abscess; only one such case has been reported in Korea. We experienced a case of concomitant liver and brain abscesses caused by Parvimonas micra in a non-immunodeficient 65-year-old female patient without diabetes or periodontal disease. Parvimonas micra infection was confirmed by blood culture using VITEK® 2 cards and by bacterial 16s ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. We conclude that we should not overlook anaerobes as a cause of liver abscess.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung DR, Lee SS, Lee HR, et al. Emerging invasive liver abscess caused by K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae in Korea. J Infect. 2007; 54:578–583.
Article2. Kim JK, Chung DR, Wie SH, Yoo JH, Park SW. Korean Study Group for Liver Abscess. Risk factor analysis of invasive liver abscess caused by the K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 28:109–111.
Article3. Ha J, Choi SP, Lee WH, et al. A clinical study on pyogenic liver abscesses: the changes in the clinical features during the recent 12 years. Korean J Med. 2008; 74:37–50.4. Branum GD, Tyson GS, Branum MA, Meyers WC. Hepatic abscess. Changes in etiology, diagnosis, and management. Ann Surg. 1990; 212:655–662.
Article5. Seeto RK, Rockey DC. Pyogenic liver abscess. Changes in etiology, management, and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996; 75:99–113.
Article6. Sabbaj J, Sutter VL, Finegold SM. Anaerobic pyogenic liver abscess. Ann Intern Med. 1972; 77:627–638.
Article7. Kim YH, Yoon HJ, Park CW, et al. A case of liver abscess caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum in a patient with recurrent periodontal diseases. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:42–46.8. Lee EH, Degener JE, Welling GW, Veloo AC. Evaluation of the vitek 2 ANC card for identification of clinical isolates of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:1745–1749.
Article9. Woo PC, Lau SK, Teng JL, Tse H, Yuen KY. Then and now: use of 16s rDNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification and discovery of novel bacteria in clinical microbiology laboratories. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008; 14:908–934.
Article10. Murdoch DA, Shah HN. Reclassification of peptostreptococcus magnus (prevot 1933) holdeman and moore 1972 as finegoldia magna comb. nov. and peptostreptococcus micros (prevot 1933) smith 1957 as micromonas micros comb. nov. Anaerobe. 1999; 5:555–559.
Article11. Cobo F, Rodríguez-Granger J, Sampedro A, Aliaga-Martínez L, Navarro-Marí JM. Pleural effusion due to Parvimonas micra. A case report and a literature review of 30 cases. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2017; 30:285–292.12. Gendron R, Grenier D, Maheu-Robert L. The oral cavity as a reservoir of bacterial pathogens for focal infections. Microbes Infect. 2000; 2:897–906.
Article13. Dana AN, Bauman WA. Bacteriology of pressure ulcers in individuals with spinal cord injury: what we know and what we should know. J Spinal Cord Med. 2015; 38:147–160.
Article14. Lee Y, Park Y, Kim MS, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns for recent clinical isolates of anaerobic bacteria in South Korea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:3993–3997.
Article15. Kim DS, Kim HJ, Park KS, et al. A case of diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by Klebsiella liver abscess and brain abscess. Korean J Med. 2011; 81:652–656.16. Wagner KW, Schön R, Schumacher M, Schmelzeisen R, Schulze D. Case report: brain and liver abscesses caused by oral infection with Streptococcus intermedius. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 102:e21–e23.
Article17. Saeed S, Zafar U, Johnson LB. Fusobacterium causing concomitant brain and liver abscesses. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2005; 13:265–267.
Article18. Chen D, Dong M, Zhao K, Sun F, Wang H, Liu Z. Unusual synchronous liver and brain abscesses infected by rare Aerococcus viridians in a patient with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations on FDG PET/CT: a case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e9048.19. Hsiao SY, Chang WN, Lin WC, et al. The experiences of non-operative treatment in patients with bacterial brain abscess. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011; 17:615–620.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Brain Abscess due to Parvimonas micra in a Healthy Child without Dental Disease
- A Case of Brain Abscess due to Parvimonas micra
- A Case of Infectious Spondylodiscitis due to Parvimonas Micra
- Parvimonas micra-Induced Paraspinal Abscess and Pyogenic Spondylitis Following Dental Extraction: A Case Report with a Brief Literature Review
- Concomitant use of corticosteroid and antimicrobials for liver abscesses in patients with chronic granulomatous disease