World J Mens Health.
2019 May;37(2):226-233. 10.5534/wjmh.180062.
Metabolic Syndrome Is an Independent Risk Factor for Acquired Premature Ejaculation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. hyunjs@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2443238
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.180062
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine the role of metabolic syndrome (MetS) as a risk factor for acquired premature ejaculation (PE) after considering the various risk factors, such as lower urinary tract symptoms, erectile dysfunction, hypogonadism, and prostatitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2012 to January 2017, records of 1,029 men were analyzed. We performed multivariate analysis to identify risk factors for PE, including the covariate of age, marital status, International Prostate Symptom Score, International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) score, National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) score, serum testosterone levels, and all components of MetS. Acquired PE was defined as self-reported intravaginal ejaculation latency time ≤3 minutes, and MetS was diagnosed using the modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria.
RESULTS
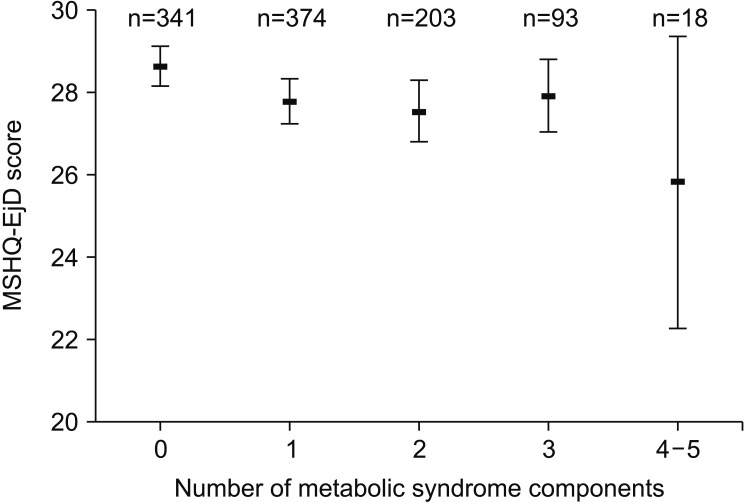
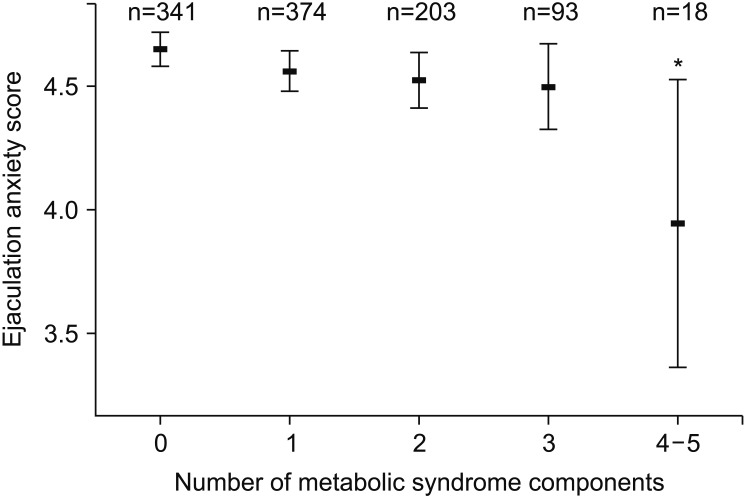
Of 1,029 men, 74 subjects (7.2%) had acquired PE and 111 (10.8%) had MetS. Multivariate analysis showed that the IIEF overall satisfaction score (odds ratio [OR]=0.67, p<0.001), NIH-CPSI pain score (OR=1.07, p=0.035), NIH-CPSI voiding score (OR=1.17, p=0.032), and presence of MetS (OR=2.20, p=0.022) were significantly correlated with the prevalence of acquired PE. In addition, the Male Sexual Health Questionnaire for Ejaculatory Dysfunction scores and ejaculation anxiety scores progressively decreased as the number of components of MetS increased.
CONCLUSIONS
MetS may be an independent predisposing factor for the development of acquired PE. Effective prevention and treatment of MetS could also be important for the prevention and treatment of acquired PE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Academies and Institutes
Adult
Anxiety
Causality
Cholesterol
Education
Ejaculation
Erectile Dysfunction
Humans
Hypogonadism
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Male
Marital Status
Multivariate Analysis
Obesity
Premature Ejaculation*
Prevalence
Prostate
Prostatitis
Reproductive Health
Risk Factors*
Testosterone
Cholesterol
Testosterone
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Lifestyle Modification Strategy for Patients with Premature Ejaculation as Metabolic Syndrome
Yu Seob Shin, Hong Seok Shin, Jong Kwan Park
World J Mens Health. 2019;37(3):372-373. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.190011.
Reference
-
1. McMahon CG, Lee G, Park JK, Adaikan PG. Premature ejaculation and erectile dysfunction prevalence and attitudes in the Asia-Pacific region. J Sex Med. 2012; 9:454–465. PMID: 22023395.
Article2. Lee SW, Lee JH, Sung HH, Park HJ, Park JK, Choi SK, et al. The prevalence of premature ejaculation and its clinical characteristics in Korean men according to different definitions. Int J Impot Res. 2013; 25:12–17. PMID: 22931761.
Article3. Serefoglu EC, McMahon CG, Waldinger MD, Althof SE, Shindel A, Adaikan G, et al. An evidence-based unified definition of lifelong and acquired premature ejaculation: report of the second International Society for Sexual Medicine ad hoc committee for the definition of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2014; 11:1423–1441. PMID: 24848805.
Article4. Wein AJ, Coyne KS, Tubaro A, Sexton CC, Kopp ZS, Aiyer LP. The impact of lower urinary tract symptoms on male sexual health: EpiLUTS. BJU Int. 2009; 103(Suppl 3):33–41.
Article5. Laumann EO, Nicolosi A, Glasser DB, Paik A, Gingell C, Moreira E, et al. ; GSSAB Investigators' Group. Sexual problems among women and men aged 40-80 y: prevalence and correlates identified in the Global Study of Sexual Attitudes and Behaviors. Int J Impot Res. 2005; 17:39–57. PMID: 15215881.6. Gonen M, Kalkan M, Cenker A, Ozkardes H. Prevalence of premature ejaculation in Turkish men with chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Androl. 2005; 26:601–603. PMID: 16088036.
Article7. Corona G, Jannini EA, Mannucci E, Fisher AD, Lotti F, Petrone L, et al. Different testosterone levels are associated with ejaculatory dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:1991–1998. PMID: 18399946.
Article8. Sullivan ME, Thompson CS, Dashwood MR, Khan MA, Jeremy JY, Morgan RJ, et al. Nitric oxide and penile erection: is erectile dysfunction another manifestation of vascular disease? Cardiovasc Res. 1999; 43:658–665. PMID: 10690337.
Article9. Vallance P, Chan N. Endothelial function and nitric oxide: clinical relevance. Heart. 2001; 85:342–350. PMID: 11179281.10. Wheatcroft SB, Williams IL, Shah AM, Kearney MT. Pathophysiological implications of insulin resistance on vascular endothelial function. Diabet Med. 2003; 20:255–268. PMID: 12675638.
Article11. Heidler S, Temml C, Broessner C, Mock K, Rauchenwald M, Madersbacher S, et al. Is the metabolic syndrome an independent risk factor for erectile dysfunction? J Urol. 2007; 177:651–654. PMID: 17222651.12. Skilton MR, Moulin P, Terra JL, Bonnet F. Associations between anxiety, depression, and the metabolic syndrome. Biol Psychiatry. 2007; 62:1251–1257. PMID: 17553465.
Article13. Pan A, Keum N, Okereke OI, Sun Q, Kivimaki M, Rubin RR, et al. Bidirectional association between depression and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1171–1180. PMID: 22517938.14. Waldinger MD, Berendsen HH, Blok BF, Olivier B, Holstege G. Premature ejaculation and serotonergic antidepressants-induced delayed ejaculation: the involvement of the serotonergic system. Behav Brain Res. 1998; 92:111–118. PMID: 9638953.
Article15. Rosmond R, Bouchard C, Björntorp P. Increased abdominal obesity in subjects with a mutation in the 5-HT(2A) receptor gene promoter. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002; 967:571–575. PMID: 12079891.
Article16. Muldoon MF, Mackey RH, Williams KV, Korytkowski MT, Flory JD, Manuck SB. Low central nervous system serotonergic responsivity is associated with the metabolic syndrome and physical inactivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:266–271. PMID: 14715860.
Article17. Bolat D, Kocabas GU, Gunlusoy B, Aydogdu O, Aydin ME. The relationship between acquired premature ejaculation and metabolic syndrome: a prospective, comparative study. Int J Impot Res. 2017; 29:105–109. PMID: 28179637.
Article18. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute scientific statement. Circulation. 2005; 112:2735–2752. PMID: 16157765.19. World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications Australia;2000. p. 11–12.20. McMahon CG, Althof SE, Waldinger MD, Porst H, Dean J, Sharlip ID, et al. An evidence-based definition of lifelong premature ejaculation: report of the International Society for Sexual Medicine (ISSM) ad hoc committee for the definition of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:1590–1606. PMID: 18466262.
Article21. Takeuchi T, Nakao M, Nomura K, Yano E. Association of metabolic syndrome with depression and anxiety in Japanese men. Diabetes Metab. 2009; 35:32–36. PMID: 19046916.
Article22. Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A. Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:2169–2180. PMID: 17498510.
Article23. El-Nashaar A, Shamloul R. Antibiotic treatment can delay ejaculation in patients with premature ejaculation and chronic bacterial prostatitis. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:491–496. PMID: 17367444.24. McMahon CG, Stuckey BG, Andersen M, Purvis K, Koppiker N, Haughie S, et al. Efficacy of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) in men with premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2005; 2:368–375. PMID: 16422868.
Article25. Lee WK, Lee SH, Cho ST, Lee YS, Oh CY, Yoo C, et al. Comparison between on-demand dosing of dapoxetine alone and dapoxetine plus mirodenafil in patients with lifelong premature ejaculation: prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J Sex Med. 2013; 10:2832–2841. PMID: 23937271.
Article26. Nicolosi A, Laumann EO, Glasser DB, Moreira ED Jr, Paik A, Gingell C. Global Study of Sexual Attitudes and Behaviors Investigators' Group. Sexual behavior and sexual dysfunctions after age 40: the global study of sexual attitudes and behaviors. Urology. 2004; 64:991–997. PMID: 15533492.
Article27. Porst H, Montorsi F, Rosen RC, Gaynor L, Grupe S, Alexander J. The Premature Ejaculation Prevalence and Attitudes (PEPA) survey: prevalence, comorbidities, and professional help-seeking. Eur Urol. 2007; 51:816–824. discussion 824. PMID: 16934919.
Article28. Corona G, Rastrelli G, Maggi M. Treatment of premature ejaculation and comorbid endocrine and metabolic disorders. In : Jannini EA, McMahon CG, Waldinger MD, editors. Premature ejaculation: from etiology to diagnosis and treatment. Milano: Springer;2013. p. 289–303.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Premature Ejaculation and Endocrine Disorders: A Literature Review
- Clomipramine in the Treatment of Premature Ejaculation
- Sertraline Treatment in Premature Ejaculation: A Double Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study
- Psychological Personality Test in Premature Ejaculation Patients
- The Efficacy and Safety of Paroxetine on the Treatment of Premature Ejaculation