Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2018 Jun;17(2):50-56. 10.12779/dnd.2018.17.2.50.
Brain Perfusion Correlates of Apathy in Alzheimer's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Ewha Brain Institute, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. siuy@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Department of Neurology, Veterans Hospital, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2442808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2018.17.2.50
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Apathy is one of the most common neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). It may have adverse impacts on the progression of AD. However, its neurobiological underpinnings remain unclear. The objective of this study was to investigate differences in regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) between AD patients with apathy and those without apathy.
METHODS
Sixty-six apathetic AD patients and 66 AD patients without apathy completed Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) and underwent technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scans. Voxel-wise differences in rCBF between the 2 groups were examined. Association between rCBF and levels of apathy in the apathetic group was also assessed.
RESULTS
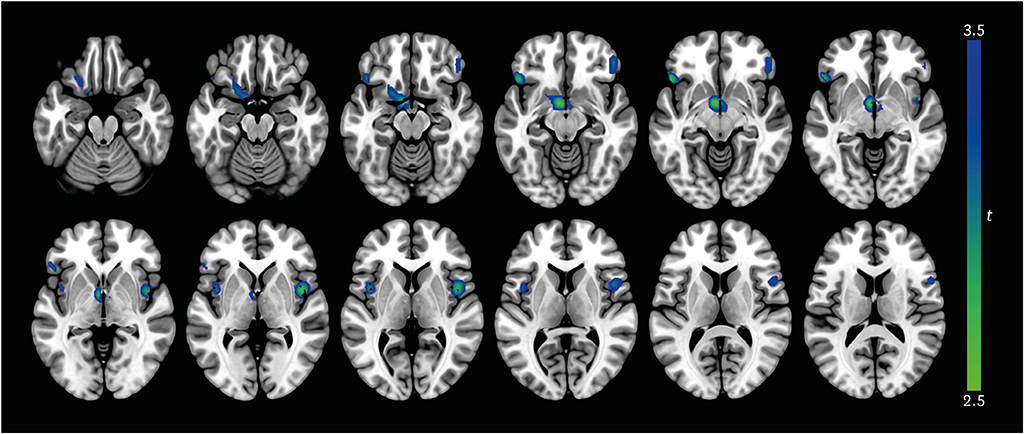
AD patients with apathy showed lower rCBF in the bilateral orbitofrontal cortex, left putamen, left nucleus accumbens, left thalamus, and bilateral insula than those without (all p < 0.005). Mean perfusion across all significant clusters showed a negative linear correlation with NPI apathy score in AD patients with apathy (β = −0.25; p = 0.04).
CONCLUSIONS
Hypoperfusion in the prefrontal, striatal, and insular areas may be neural correlates of apathy in AD patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lyketsos CG, Carrillo MC, Ryan JM, Khachaturian AS, Trzepacz P, Amatniek J, et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7:532–539.
Article2. Mega MS, Cummings JL, Fiorello T, Gornbein J. The spectrum of behavioral changes in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1996; 46:130–135.
Article3. Shin IS, Carter M, Masterman D, Fairbanks L, Cummings JL. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and quality of life in Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2005; 13:469–474.
Article4. Starkstein SE, Petracca G, Chemerinski E, Kremer J. Syndromic validity of apathy in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Psychiatry. 2001; 158:872–877.
Article5. Landes AM, Sperry SD, Strauss ME, Geldmacher DS. Apathy in Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001; 49:1700–1707.
Article6. Brodaty H, Burns K. Nonpharmacological management of apathy in dementia: a systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012; 20:549–564.
Article7. Theleritis C, Politis A, Siarkos K, Lyketsos CG. A review of neuroimaging findings of apathy in Alzheimer's disease. Int Psychogeriatr. 2014; 26:195–207.
Article8. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Forth edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association;1994.9. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984; 34:939–944.
Article10. Choi SH, Na DL, Kwon HM, Yoon SJ, Jeong JH, Ha CK. The Korean version of the neuropsychiatric inventory: a scoring tool for neuropsychiatric disturbance in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2000; 15:609–615.
Article11. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997; 15:300–308.12. Morris JC, Heyman A, Mohs RC, Hughes JP, van Belle G, Fillenbaum G, et al. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part I. Clinical and neuropsychological assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1989; 39:1159–1165.13. Chang LT. A method for attenuation correction in radionuclide computed tomography. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1978; 25:638–643.
Article14. Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage. 2002; 15:273–289.
Article15. Pickut BA, Dierckx RA, Dobbeleir A, Audenaert K, Van Laere K, Vervaet A, et al. Validation of the cerebellum as a reference region for SPECT quantification in patients suffering from dementia of the Alzheimer type. Psychiatry Res. 1999; 90:103–112.
Article16. Soonawala D, Amin T, Ebmeier KP, Steele JD, Dougall NJ, Best J, et al. Statistical parametric mapping of (99m)Tc-HMPAO-SPECT images for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: normalizing to cerebellar tracer uptake. Neuroimage. 2002; 17:1193–1202.
Article17. Wallis JD. Orbitofrontal cortex and its contribution to decision-making. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007; 30:31–56.
Article18. Lopez OL, Zivkovic S, Smith G, Becker JT, Meltzer CC, DeKosky ST. Psychiatric symptoms associated with cortical-subcortical dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001; 13:56–60.
Article19. Marshall GA, Monserratt L, Harwood D, Mandelkern M, Cummings JL, Sultzer DL. Positron emission tomography metabolic correlates of apathy in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2007; 64:1015–1020.
Article20. Bruen PD, McGeown WJ, Shanks MF, Venneri A. Neuroanatomical correlates of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2008; 131:2455–2463.
Article21. Carriere N, Besson P, Dujardin K, Duhamel A, Defebvre L, Delmaire C, et al. Apathy in Parkinson's disease is associated with nucleus accumbens atrophy: a magnetic resonance imaging shape analysis. Mov Disord. 2014; 29:897–903.
Article22. Levy R, Dubois B. Apathy and the functional anatomy of the prefrontal cortex-basal ganglia circuits. Cereb Cortex. 2006; 16:916–928.
Article23. David R, Koulibaly M, Benoit M, Garcia R, Caci H, Darcourt J, et al. Striatal dopamine transporter levels correlate with apathy in neurodegenerative diseases A SPECT study with partial volume effect correction. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008; 110:19–24.
Article24. Bhatia KP, Marsden CD. The behavioural and motor consequences of focal lesions of the basal ganglia in man. Brain. 1994; 117:859–876.
Article25. Bonelli RM, Cummings JL. Frontal-subcortical circuitry and behavior. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2007; 9:141–151.
Article26. Stanton BR, Leigh PN, Howard RJ, Barker GJ, Brown RG. Behavioural and emotional symptoms of apathy are associated with distinct patterns of brain atrophy in neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurol. 2013; 260:2481–2490.
Article27. Reijnders JS, Scholtissen B, Weber WE, Aalten P, Verhey FR, Leentjens AF. Neuroanatomical correlates of apathy in Parkinson's disease: a magnetic resonance imaging study using voxel-based morphometry. Mov Disord. 2010; 25:2318–2325.
Article28. Robert G, Le Jeune F, Lozachmeur C, Drapier S, Dondaine T, Péron J, et al. Apathy in patients with Parkinson disease without dementia or depression: a PET study. Neurology. 2012; 79:1155–1160.
Article29. Jenkins IH, Jahanshahi M, Jueptner M, Passingham RE, Brooks DJ. Self-initiated versus externally triggered movements. II. The effect of movement predictability on regional cerebral blood flow. Brain. 2000; 123:1216–1228.30. Menon V, Uddin LQ. Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Struct Funct. 2010; 214:655–667.
Article31. Aalten P, van Valen E, Clare L, Kenny G, Verhey F. Awareness in dementia: a review of clinical correlates. Aging Ment Health. 2005; 9:414–422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- SPM Analysis of Changes in Cerebral Blood Flow in Alzheimer's Disease with Apathy
- Apathy: Neurobiology, Assessment and Treatment
- Post-Stroke Apathy and Anxiety
- Cerebral Perfusion Changes after Acetyl-L-Carnitine Treatment in Early Alzheimer's Disease Using Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
- Autopy Results of Clinically Diagnosed Alzheimer's Disease