Prog Med Phys.
2019 Mar;30(1):14-21. 10.14316/pmp.2019.30.1.14.
Initial Experience of Patient-Specific QA for Wobbling and Line-Scanning Proton Therapy at Samsung Medical Center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. youngyih@skku.edu
- KMID: 2442417
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2019.30.1.14
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the initial experience of patient-specific quality assurance (pQA) for the wobbling and line-scanning proton therapy at Samsung Medical Center.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
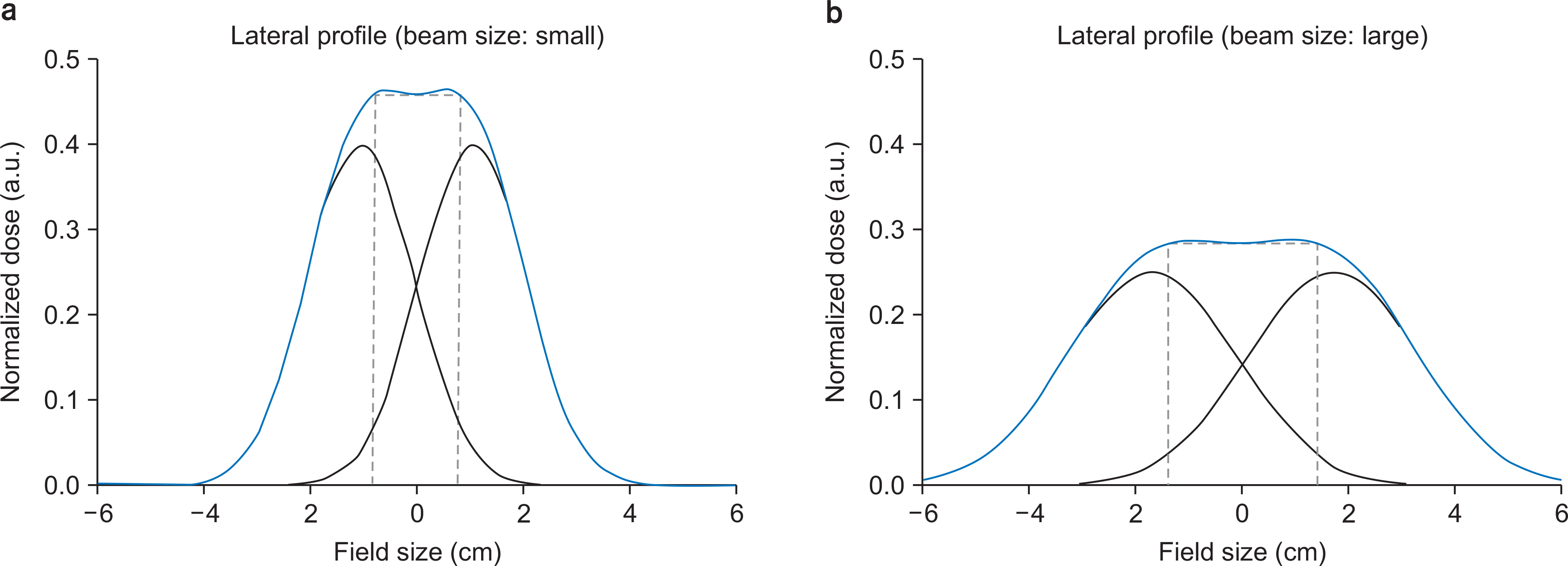
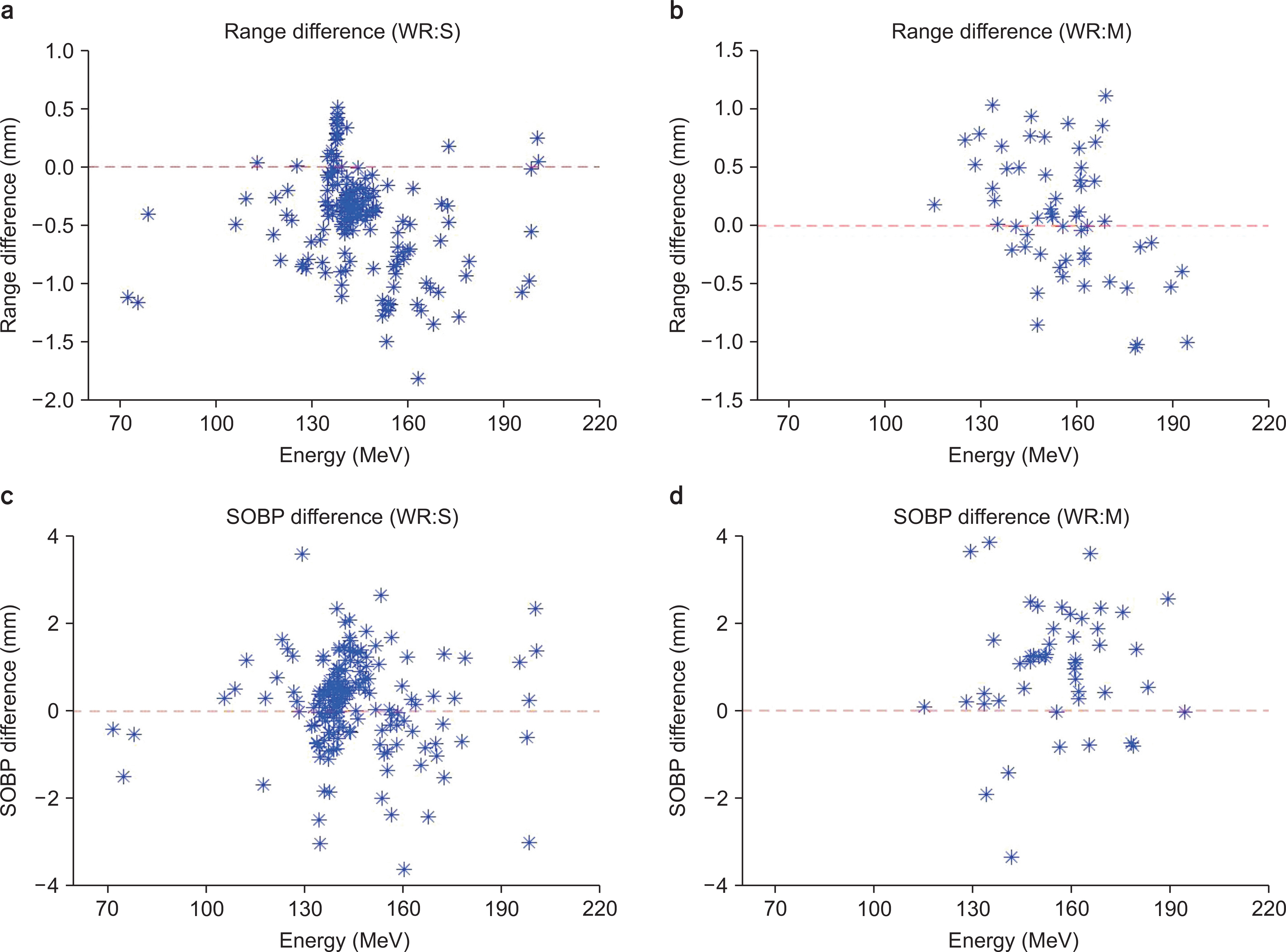
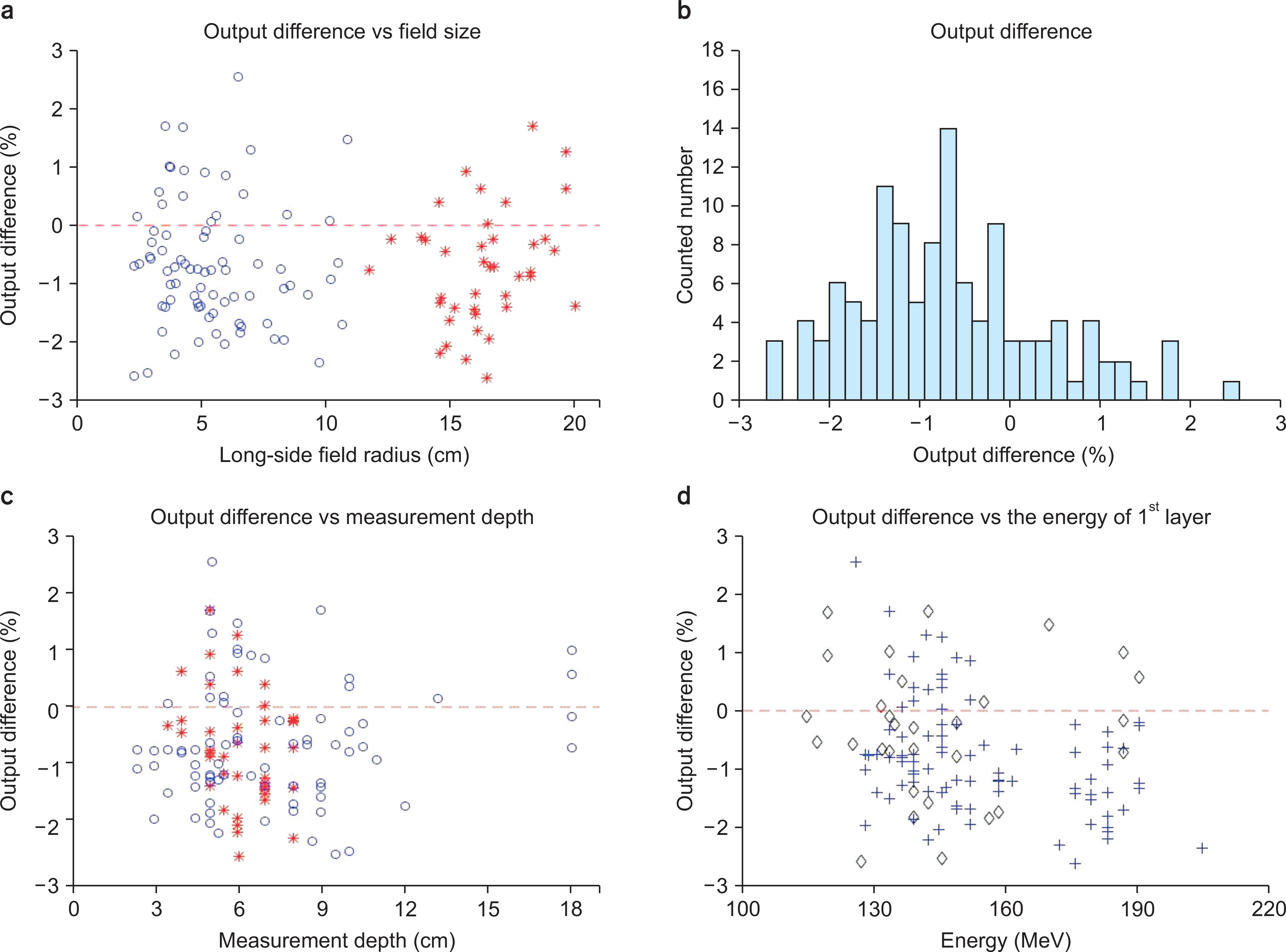
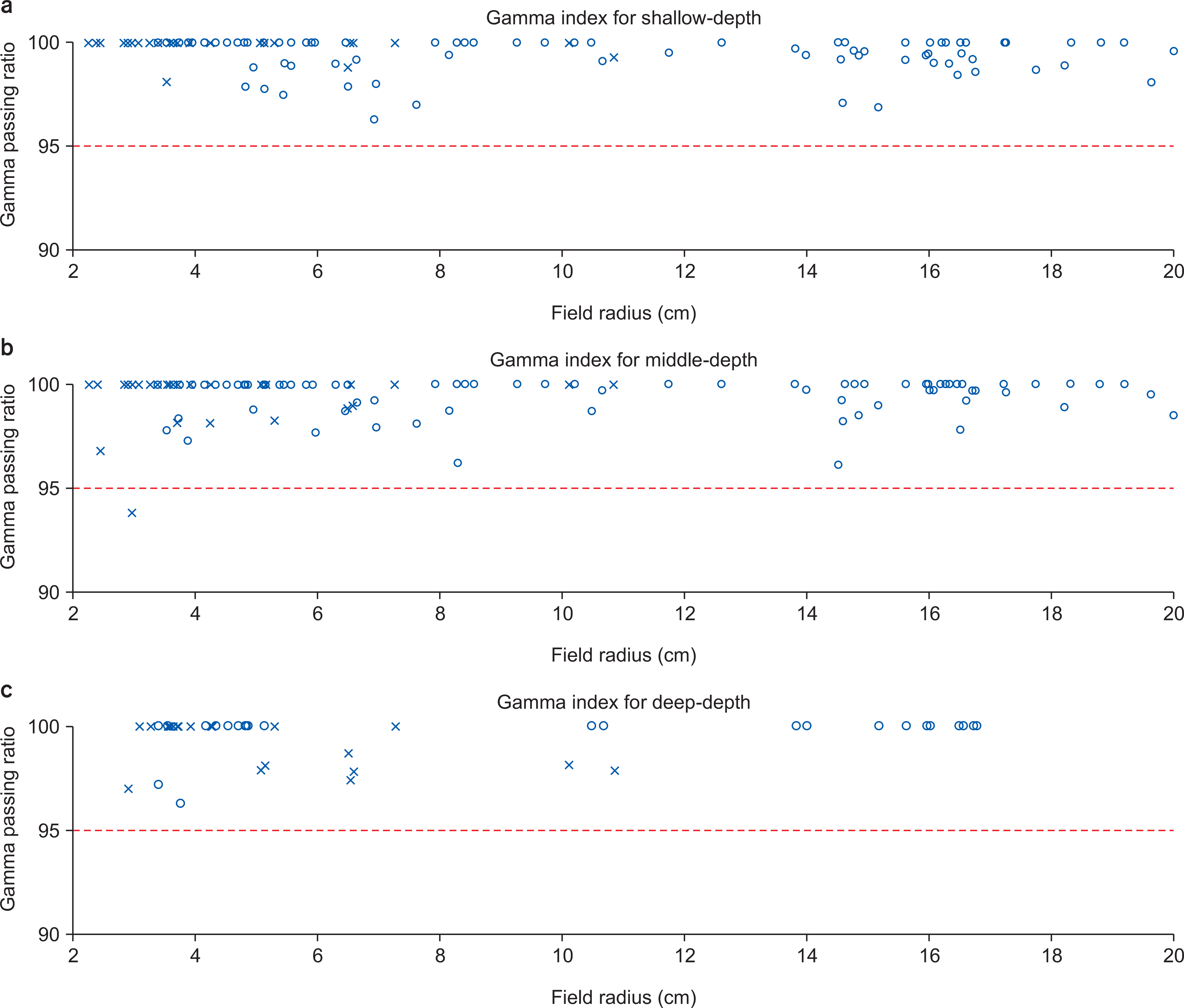
The pQA results of 89 wobbling treatments with 227 fields and 44 line-scanning treatments with 118 fields were analyzed from December 2015 to June 2016. For the wobbling method, proton range and spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) width were verified. For the line-scanning method, output and two-dimensional dose distribution at multiple depths were verified by gamma analysis with 3%/3 mm criterion.
RESULTS
The average range difference was −0.44 mm with a standard deviation (SD) of 1.64 mm and 0.1 mm with an SD of 0.53 mm for the small and middle wobbling radii, respectively. For the line-scanning method, the output difference was within ±3%. The gamma passing rates were over 95% with 3%/3 mm criterion for all depths.
CONCLUSIONS
For the wobbling method, proton range and SOBP width were within the tolerance levels. For the line-scanning method, the output and two-dimensional dose distribution showed excellent agreement with the treatment plans.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.PTCOG-PTCOG Patient Statistics. Ptcogch. 2017. URL:. https://www.ptcog.ch/index.php/ptcog-patient-statistics.2.Chang JY., Zhang X., Wang X., Kang Y., Riley B., Bilton S., Mohan R., Komaki R., Cox JD. Significant reduction of normal tissue dose by proton radiotherapy compared with three-dimensional conformal or intensity-modulated radiation therapy in Stage I or Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:1087–96.
Article3.Hall EJ. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, protons, and the risk of second cancers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:1–7.
Article4.Paganetti H. Range uncertainties in proton therapy and the role of Monte Carlo simulations. Phys Med Biol. 2012. 57:R99–117.
Article5.Lomax AJ., Bohringer T., Bolsi A., Coray D., Emert F., Goitein G., Jermann M., Lin S., Pedroni E., Rutz H., Stadelmann O., Timmermann B., Verwey J., Weber DC. Treatment planning and verification of proton therapy using spot scanning: initial experiences. Med Phys. 2004. 31:3150–7.
Article6.Furukawa T., Inaniwa T., Hara Y., Mizushima K., Shirai T., Noda K. Patient-specific QA and delivery verification of scanned ion beam at NIRS-HIMAC. Med Phys. 2013. 40:121707.
Article7.Mackin D., Zhu XR., Poenisch F., Li H., Sahoo N., Kerr M., Holmes C., Li Y., Lii M., Wu R., Suzuki K., Gillin MT., Frank SJ., Grosshans D., Zhang X. Spot-scanning proton therapy patient-specific quality assurance: results from 309 treatment plans. Int J Part Ther. 2014. 1:711–20.
Article8.Zhu XR., Poenisch F., Song X., Johnson JL., Ciangaru G., Taylor MB., Lii M., Martin C., Arjomandy B., Lee AK., Choi S., Nguyen QN., Gillin MT., Sahoo N. Patient-specific quality assurance for prostate cancer patients receiving spot scanning proton therapy using single-field uniform dose. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. 81:552–9.
Article9.Mackin D., Li Y., Taylor MB., Kerr M., Holmes C., Sahoo N., Poenisch F., Li H., Lii J., Amos R., Wu R., Suzuki K., Gillin MT., Zhu XR., Zhang X. Improving spot-scanning proton therapy patient specific quality assurance with HPlusQA, a second-check dose calculation engine. Med Phys. 2013. 40:121708.
Article10.Chung K., Han Y., Kim J., Ahn SH., Ju SG., Jung SH., Chung Y., Cho S., Jo K., Shin EH., Hong CS., Shin JS., Park S., Kim DH., Kim HY., Lee B., Shibagaki G., Nonaka H., Sasai K., Koyabu Y., Choi C., Huh SJ., Ahn YC., Pyo HR., Lim DH., Park HC., Park W., Oh DR., Noh JM., Yu JI., Song S., Lee JE., Lee B., Choi DH. The first private-hospital based proton therapy center in Korea; status of the Proton Therapy Center at Samsung Medical Center. Radiat Oncol J. 2015. 33:337–43.
Article11.Yonai S., Kanematsu N., Komori M., Kanai T., Takei Y., Takahashi O., Isobe Y., Tashiro M., Koikegami H., Tomita H. Evaluation of beam wobbling methods for heavy-ion radiotherapy. Med Phys. 2008. 35:927–38.
Article12.Torikoshi M., Minohara S., Kanematsu N., Komori M., Kanazawa M., Noda K., Miyahara N., Itoh H., Endo M., Kanai T. Irradiation system for HIMAC. J Radiat Res. 2007. 48(Suppl A):A15–25.
Article13.Haberer T., Becher W., Schardt D., Kraft G. Magnetic scanning system for heavy ion therapy. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 1993. 330:296–305.
Article14.St Clair WH., Adams JA., Bues M., Fullerton BC., La Shell S., Kooy HM., Loeffler JS., Tarbell NJ. Advantage of protons compared to conventional X-ray or IMRT in the treatment of a pediatric patient with medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 58:727–34.15.Low DA., Dempsey JF. Evaluation of the gamma dose distribution comparison method. Med Phys. 2003. 30:2455–64.
Article16.Arjomandy B., Sahoo N., Ding X., Gillin M. Use of a two-dimensional ionization chamber array for proton therapy beam quality assurance. Med Phys. 2008. 35:3889–94.
Article17.Arjomandy B., Sahoo N., Ciangaru G., Zhu R., Song X., Gillin M. Verification of patient-specific dose distributions in proton therapy using a commercial two-dimensional ion chamber array. Med Phys. 2010. 37:5831–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Treatment and Delay Times by Disease Site and Delivery Technique at Samsung Medical Center: Proton Therapy Center
- A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- Commissioning and Validation of a Dedicated Scanning Nozzle at Samsung Proton Therapy Center
- Proton therapy: the current status of the clinical evidences