Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2019 May;11(3):433-437. 10.4168/aair.2019.11.3.433.
Hyperresponsiveness to Boiled Egg Yolk in Early Life Leads to Prolonged Egg Allergy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy, Miyagi Children's Hospital, Sendai, Japan. horino-thk@umin.ac.jp
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Tohoku Medical and Pharmaceutical University Hospital, Sendai, Japan.
- KMID: 2442053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.3.433
Abstract
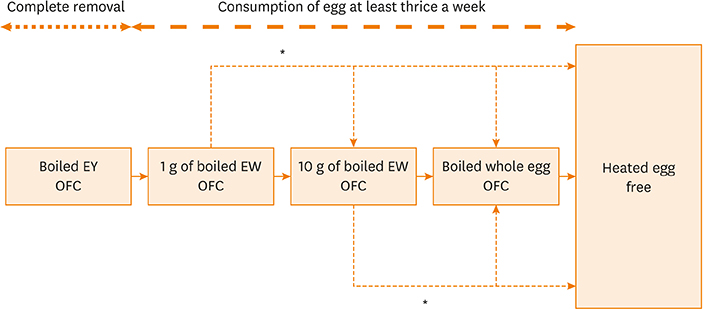
- Hen's egg is the most common allergen in IgE-mediated food allergy among children in Japan. Although the majority of patients with egg allergy can eat heated egg yolk safely because of its low allergenicity, severely allergic patients show an immediate-type reaction to heated egg yolk. We hypothesized that patients with hyperresponsiveness to boiled egg yolk may have difficulty in acquiring tolerance to egg. The purpose of this study was to examine the prognosis of patients with hyperresponsiveness to boiled egg yolk. Data from 121 patients with egg allergy who underwent oral food challenge (OFC) with boiled egg yolk between January 2012 and December 2013 were analyzed retrospectively. The proportion of patients who could consume heated whole egg 3 years after OFC was 15.4% in the OFC-positive group and 75.8% in the OFC-negative group. Hyperresponsiveness to boiled egg yolk in early life might lead to prolonged egg allergy in children. This finding might aid in the selection of an appropriate population requiring practical immunotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rona RJ, Keil T, Summers C, Gislason D, Zuidmeer L, Sodergren E, et al. The prevalence of food allergy: a meta-analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:638–646.
Article2. Ohtani K, Sato S, Syukuya A, Asaumi T, Ogura K, Koike Y, et al. Natural history of immediate-type hen's egg allergy in Japanese children. Allergol Int. 2016; 65:153–157.
Article3. Ibáñez MD, Escudero C, Sánchez-García S, Rodríguez del Río P. Comprehensive review of current knowledge on egg oral immunotherapy. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2015; 25:316–328.4. Feuille E, Nowak-Wegrzyn A. Allergen-specific immunotherapies for food allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:189–206.
Article5. Bernhisel-Broadbent J, Dintzis HM, Dintzis RZ, Sampson HA. Allergenicity and antigenicity of chicken egg ovomucoid (Gal d III) compared with ovalbumin (Gal d I) in children with egg allergy and in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994; 93:1047–1059.
Article6. Caubet JC, Wang J. Current understanding of egg allergy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2011; 58:427–443.
Article7. Quirce S, Marañón F, Umpiérrez A, de las Heras M, Fernández-Caldas E, Sastre J. Chicken serum albumin (Gal d 5*) is a partially heat-labile inhalant and food allergen implicated in the bird-egg syndrome. Allergy. 2001; 56:754–762.8. Yanagida N, Sato S, Asaumi T, Ogura K, Borres MP, Ebisawa M. Safety and feasibility of heated egg yolk challenge for children with egg allergies. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017; 28:348–354.
Article9. Sampson HA. Anaphylaxis and emergency treatment. Pediatrics. 2003; 111:1601–1608.10. Okada Y, Yanagida N, Sato S, Ebisawa M. Heated egg yolk challenge predicts the natural course of hen's egg allergy: a retrospective study. World Allergy Organ J. 2016; 9:31.
Article