Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2018 Nov;10(6):686-697. 10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.686.
Montelukast Reduces Serum Levels of Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin in Preschool Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Asthma & Allergy Center, Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2School of Biological Sciences, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Mie Prefectural General Medical Center, Tsu, Japan.
- 4Niko Niko Child Clinic, Tsu, Japan.
- 5Institute for Clinical Research, Mie National Hospital, Tsu, Japan. fujisawa@mie-m.hosp.go.jp
- KMID: 2441817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.686
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Several markers for eosinophilic inflammation have been proposed to predict response to asthma treatment. However, definitive criteria for treatment decisions have not yet been established. We investigate a potentially useful relatively non-invasive biomarker, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), to predict favorable responses to budesonide or montelukast, common treatment for children with asthma.
METHODS
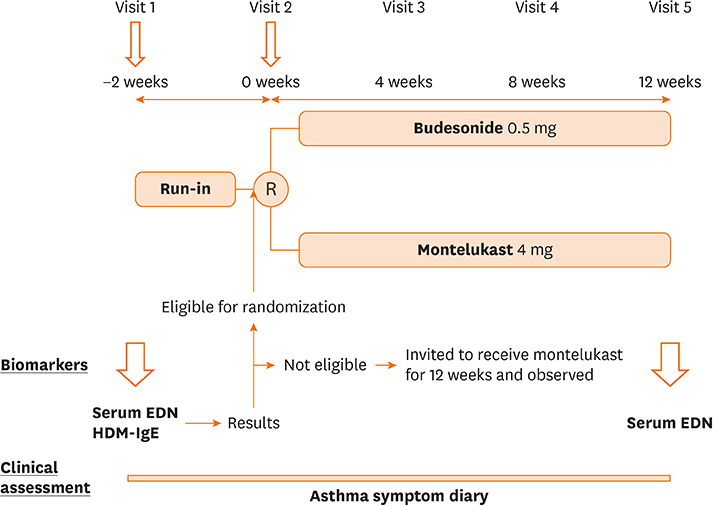
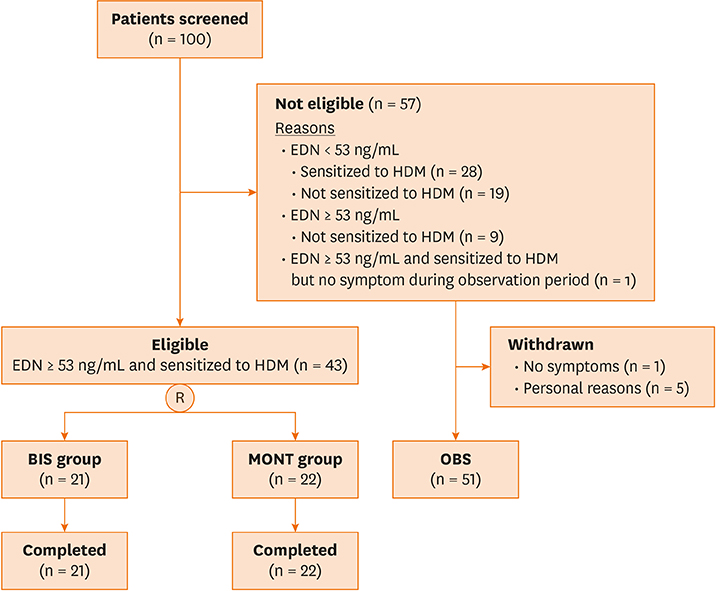
Young children (1 to 6 years old) were enrolled in this randomized, parallel, 2-group, open-label trial. Criteria for eligibility included: 1) being symptomatic during the run-in period; and 2) having a serum EDN (sEDN) level ≥ 53 ng/mL, with positive specific immunoglobulin E to house dust mite. Eligible patients were randomly placed into 2 groups: the BIS group received budesonide inhalation suspension (BIS) 0.5 mg once daily; the MONT group received montelukast 4 mg once daily. Ineligible patients were invited to receive montelukast 4 mg once daily (OBS group). Treatment period was 12 weeks.
RESULTS
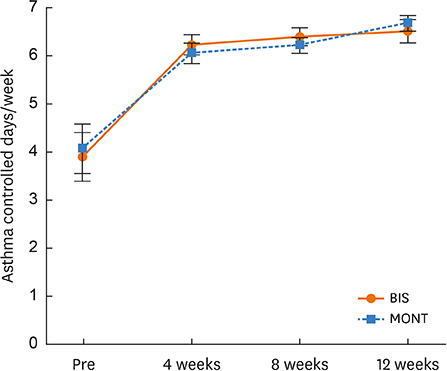
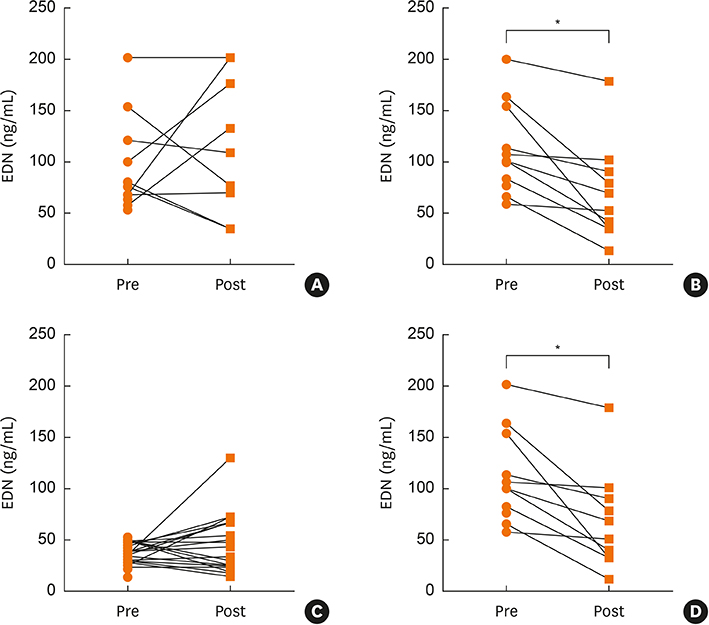
Asthma control days increased significantly in the BIS and MONT groups (P < 0.000) over the 12-week study period. There was no significant change in sEDN in the BIS group but there was a significant decrease in the MONT group (P < 0.000). Patients in the OBS group with high EDN levels (< 53 ng/mL) showed a significant decrease due to MONT treatment (P = 0.023). Rescue medication usage significantly decreased in the BIS and MONT groups (P < 0.000).
CONCLUSIONS
EDN is a useful relatively non-invasive biomarker for predicting responses to montelukast and budesonide treatment of preschool children with beta2-agonist responsive recurrent wheeze and multiple-trigger wheeze (Trial registry at UMIN Clinical Trials Registry, UMIN000008335).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Biomarkers for Recurrent Wheezing and Asthma in Preschool Children
Yong Ju Lee, Takao Fujisawa, Chang-Keun Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(1):16-28. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.16.
Reference
-
1. Liu AH, Covar RA, Spahn JD, Leung DY. Childhood asthma. In : Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton B, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 18th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders;2007. p. 953–970.2. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention [Internet]. place unknown: Global Initiative for Asthma;2017. 2017 Aug 18. Available from: http://www.ginasthma.org.3. Obase Y, Shimoda T, Tomari SY, Mitsuta K, Kawano T, Matsuse H, et al. Effects of pranlukast on chemical mediators in induced sputum on provocation tests in atopic and aspirin-intolerant asthmatic patients. Chest. 2002; 121:143–150.
Article4. Zeiger RS, Szefler SJ, Phillips BR, Schatz M, Martinez FD, Chinchilli VM, et al. Response profiles to fluticasone and montelukast in mild-to-moderate persistent childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:45–52.
Article5. Szefler SJ, Phillips BR, Martinez FD, Chinchilli VM, Lemanske RF Jr, Strunk RC, et al. Characterization of within-subject responses to fluticasone and montelukast in childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 115:233–242.
Article6. Lemanske RF Jr, Mauger DT, Sorkness CA, Jackson DJ, Boehmer SJ, Martinez FD, et al. Step-up therapy for children with uncontrolled asthma receiving inhaled corticosteroids. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:975–985.
Article7. Sporik R, Holgate ST, Platts-Mills TA, Cogswell JJ. Exposure to house-dust mite allergen (Der p I) and the development of asthma in childhood. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1990; 323:502–507.8. Green RH, Brightling CE, McKenna S, Hargadon B, Parker D, Bradding P, et al. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 360:1715–1721.
Article9. Szefler SJ, Mitchell H, Sorkness CA, Gergen PJ, O'Connor GT, Morgan WJ, et al. Management of asthma based on exhaled nitric oxide in addition to guideline-based treatment for inner-city adolescents and young adults: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008; 372:1065–1072.
Article10. Koh YY, Kang H, Kim CK. Ratio of serum eosinophil cationic protein/blood eosinophil counts in children with asthma: comparison between acute exacerbation and clinical remission. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003; 24:269–274.11. Yoshihara S, Yamada Y, Abe T, Lindén A, Arisaka O. Association of epithelial damage and signs of neutrophil mobilization in the airways during acute exacerbations of paediatric asthma. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006; 144:212–216.
Article12. Kim CK, Callaway Z, Fletcher R, Koh YY. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in childhood asthma: correlation with disease severity. J Asthma. 2010; 47:568–573.
Article13. Kim CK, Seo JK, Ban SH, Fujisawa T, Kim DW, Callaway Z. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels at 3 months post-respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis are a predictive biomarker of recurrent wheezing. Biomarkers. 2013; 18:230–235.
Article14. Hamasaki Y, Kohno Y, Ebisawa M, Kondo N, Nishima S, Nishimuta T, et al. Japanese guideline for childhood asthma 2014. Allergol Int. 2014; 63:335–356.
Article15. Matsson P, Hamilton RG, Esch RE. Analytical performance characteristics and clinical utility of immunological assays for human immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies and defined allergen specificities: approved guidelines. 2nd ed. Wayne (PA): Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.16. Motojima S, Akutsu I, Fukuda T, Makino S, Takatsu K. Clinical significance of measuring levels of sputum and serum ECP and serum IL-5 in bronchial asthma. Allergy. 1993; 48:98–106.
Article17. Venge P. Monitoring the allergic inflammation. Allergy. 2004; 59:26–32.
Article18. Abu-Ghazaleh RI, Dunnette SL, Loegering DA, Checked JL, Kita H, Thomas LL, et al. Eosinophil granule proteins in peripheral blood granulocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1992; 52:611–618.
Article19. Morioka J, Kurosawa M, Inamura H, Nakagami R, Mizushima Y, Omura Y, et al. Increased END/EPX in ongoing asthma. Allergy. 2000; 55:1203–1204.
Article20. Kim CK, Choi J, Kim HB, Callaway Z, Shin BM, Kim JT, et al. A randomized intervention of montelukast for post-bronchiolitis: effect on eosinophil degranulation. J Pediatr. 2010; 156:749–754.
Article21. Hofhuis W, van der Wiel EC, Nieuwhof EM, Hop WC, Affourtit MJ, Smit FJ, et al. Efficacy of fluticasone propionate on lung function and symptoms in wheezy infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:328–333.
Article22. Chauhan BF, Ducharme FM. Anti-leukotriene agents compared to inhaled corticosteroids in the management of recurrent and/or chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 5:CD002314.
Article23. Taniuchi S, Chihara J, Kojima T, Yamamoto A, Sasai M, Kobayashi Y. Serum eosinophil derived neurotoxin may reflect more strongly disease severity in childhood atopic dermatitis than eosinophil cationic protein. J Dermatol Sci. 2001; 26:79–82.
Article24. Sedgwick JB, Vrtis RF, Jansen KJ, Kita H, Bartemes K, Busse WW. Peripheral blood eosinophils from patients with allergic asthma contain increased intracellular eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:568–574.
Article25. Garofalo R, Kimpen JL, Welliver RC, Ogra PL. Eosinophil degranulation in the respiratory tract during naturally acquired respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Pediatr. 1992; 120:28–32.
Article26. Moqbel R, Lace P, Adamko DJ, Odemuyiwa SO. Biology of eosinophils. In : Adkinson NF, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF, Simons FE, editors. Allergy: principles & practice. St. Louis (MO): Mosby;2008. p. 295–310.27. Kim CK, Callaway Z, Gern JE. Viral infections and associated factors that promote acute exacerbations of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:12–17.
Article28. Petsky HL, Kynaston JA, Turner C, Li AM, Cates CJ, Lasserson TJ, et al. Tailored interventions based on sputum eosinophils versus clinical symptoms for asthma in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; 2:CD005603.
Article29. Chlumský J, Striz I, Terl M, Vondracek J. Strategy aimed at reduction of sputum eosinophils decreases exacerbation rate in patients with asthma. J Int Med Res. 2006; 34:129–139.
Article30. Jayaram L, Pizzichini MM, Cook RJ, Boulet LP, Lemière C, Pizzichini E, et al. Determining asthma treatment by monitoring sputum cell counts: effect on exacerbations. Eur Respir J. 2006; 27:483–494.
Article31. Adamko DJ, Odemuyiwa SO, Vethanayagam D, Moqbel R. The rise of the phoenix: the expanding role of the eosinophil in health and disease. Allergy. 2005; 60:13–22.
Article32. Kim KW, Lee KE, Kim ES, Song TW, Sohn MH, Kim KE. Serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) in diagnosis and evaluation of severity and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in childhood asthma. Lung. 2007; 185:97–103.
Article33. Kim CK, Callaway Z, Park JS, Kwon E. Utility of serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) measurement by ELISA in young children with asthma. Allergol Int. 2017; 66:70–74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Montelukast use over the past 20 years: monitoring of its effects and safety issues
- The Association of Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in Mycoplasma pneumonia and Asthma
- Biomarkers for Recurrent Wheezing and Asthma in Preschool Children
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: a novel biomarker for diagnosis and monitoring of asthma
- The Efficacy of Eosinophilic Degranulation Proteins for Diagnosing Asthma in Chronic Cough Patients