Infect Chemother.
2016 Dec;48(4):285-293. 10.3947/ic.2016.48.4.285.
Current Situation of Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Differences in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Complex Isolates by Multilocus Variable Number of Tandem Repeat Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Asia Pacific Foundation for Infectious Diseases, Seoul, Korea. ksko@skku.edu
- 4Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2441322
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2016.48.4.285
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is one of several opportunistic pathogens of growing significance. Several studies on the molecular epidemiology of S. maltophilia have shown clinical isolates to be genetically diverse.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 121 clinical isolates tentatively identified as S. malophilia from seven tertiary-care hospitals in Korea from 2007 to 2011 were included. Species and groups were identified using partial gyrB gene sequences and antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed using a broth microdilution method. Multi locus variable number of tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) surveys are used for subtyping.
RESULTS
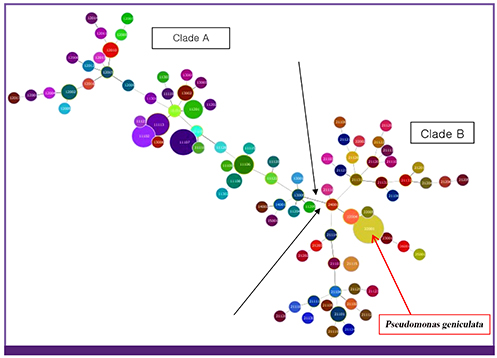
Based on partial gyrB gene sequences, 118 isolates were identified as belonging to the S. maltophilia complex. For all S. maltophilia isolates, the resistance rates to trimethoprime-sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) and levofloxacin were the highest (both, 30.5%). Resistance rate to ceftazidime was 28.0%. 11.0% and 11.9% of 118 S. maltophilia isolates displayed resistance to piperacillin/tazobactam and tigecycline, respectively. Clade 1 and Clade 2 were definitely distinguished from the data of MLVA with amplification of loci. All 118 isolates were classified into several clusters as its identification.
CONCLUSION
Because of high resistance rates to TMP/SMX and levofloxacin, the clinical laboratory department should consider providing the data about other antimicrobial agents and treatment of S. maltophilia infections with a combination of antimicrobials can be considered in the current practice. The MLVA evaluated in this study provides a fast, portable, relatively low cost genotyping method that can be employed in genotypic linkage or transmission networks comparing to analysis of the gyrB gene.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brooke JS. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25:2–41.
Article2. Looney WJ, Narita M, Mühlemann K. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging opportunist human pathogen. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009; 9:312–323.3. Chung HS, Hong SG, Lee Y, Kim M, Yong D, Jeong SH, Lee K, Chong Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates from a Korean tertiary care hospital. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:439–441.
Article4. Nicodemo AC, Araujo MR, Ruiz AS, Gales AC. In vitro susceptibility of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates: comparison of disc diffusion, Etest and agar dilution methods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 53:604–608.
Article5. Roscetto E, Rocco F, Carlomagno MS, Casalino M, Colonna B, Zarrilli R, Di Nocera PP. PCR-based rapid genotyping of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2008; 8:202.6. Valdezate S, Vindel A, Martín-Dávila P, Del Saz BS, Baquero F, Cantón R. High genetic diversity among Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strains despite their originating at a single hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:693–699.
Article7. Cho S, Boxrud DJ, Bartkus JM, Whittam TS, Saeed M. Multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis isolates from human and non-human sources using a single multiplex PCR. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007; 275:16–23.
Article8. van Belkum A. Tracing isolates of bacterial species by multilocus variable number of tandem repeat analysis (MLVA). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007; 49:22–27.
Article9. Tan CK, Liaw SJ, Yu CJ, Teng LJ, Hsueh PR. Extensively drug-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in a tertiary care hospital in Taiwan: microbiologic characteristics, clinical features, and outcomes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008; 60:205–210.
Article10. Toleman MA, Bennett PM, Bennett DM, Jones RN, Walsh TR. Global emergence of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia mediated by acquisition of sul gene. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007; 13:559–565.
Article11. Fihman V, Le Monnier A, Corvec S, Jaureguy F, Tankovic J, Jacquier H, Carbonnelle E, Bille E, Illiaquer M, Cattoir V, Zahar JR. Stenotrophomonas maltophiliae-the most worrisome threat among unusual non-fermentative gram-negative bacilli from hospitalized patients: a prospective multicenter study. J Infect. 2012; 64:391–398.
Article12. Samonis G, Karageorgopoulos DE, Maraki S, Levis P, Dimopoulou D, Spernovasilis NA, Kofteridis DP, Falagas ME. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections in a general hospital: patient characteristics, antimicrobial susceptibility, and treatment outcome. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e37375.13. Cantó R, Valdezate S, Vindel A, Sáchez Del Saz B, Maíz L, Baquero F. Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of molecular typed cystic fibrosis Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates and differences with noncystic fibrosis isolates. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003; 35:99–107.14. Song JH, Sung JY, Kwon KC, Park JW, Cho HH, Shin SY, Ko YH, Kim JM, Shin KS, Koo SH. Analysis of acquired resistance genes in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Korean J Lab Med. 2010; 30:295–300.
Article15. Rhee JY, Choi JY, Choi MJ, Song JH, Peck KR, Ko KS. Distinct groups and antimicrobial resistance of clinical Stenotrophomonas maltophilia complex isolates from Korea. J Med Microbiol. 2013; 62:748–753.
Article16. Svensson-Stadler LA, Mihaylova SA, Moore ER. Stenotrophomonas interspecies differentiation and identification by gyrB sequence analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012; 327:15–24.
Article17. Valenza G, Tappe D, Turnwald D, Frosch M, König C, Hebestreit H, Abele-Horn M. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from sputa of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2008; 7:123–127.
Article18. Luber P, Bartelt E, Genschow E, Wagner J, Hahn H. Comparison of Broth Microdilution, E Test, and agar dilution methods for antibiotic susceptibility testing of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli . J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:1062–1068.
Article19. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 21st informational supplement. Wayne, PA: CLSI;2011. p. M100-S21.20. Wang WS, Liu CP, Lee CM, Huang FY. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia in adults: four years’ experience in a medical center in northern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2004; 37:359–365.21. Galles AC, Jones RN, Sader HS. Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of contemporary clinical strains of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates: can moxifloxacin activity be predicted by levofloxacin MIC results? J Chemother. 2008; 20:38–42.22. Vartivarian S, Anaissie E, Bodey G, Sprigg H, Rolston K. A changing pattern of susceptibility of Xanthomonas maltophilia to antimicrobial agents: implications for therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994; 38:624–627.
Article23. Gülmez D, Hascelik G. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: antimicrobial resistance and molecular typing of an emerging pathogen in a Turkish university hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005; 11:880–886.
Article24. Cho HH, Sung JY, Kwon KC, Koo SH. Expression of Sme efflux pumps and multilocus sequence typing in clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Ann Lab Med. 2012; 32:38–43.
Article25. Kaiser S, Biehler K, Jonas D. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia multilocus sequence typing scheme for inferring population structure. J Bacteriol. 2009; 91:2934–2943.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Sme Efflux Pumps and Multilocus Sequence Typing in Clinical Isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from a Korean Tertiary Care Hospital
- Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Multilocus Sequence Typing for Clonality Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains
- Analysis of Acquired Resistance Genes in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia