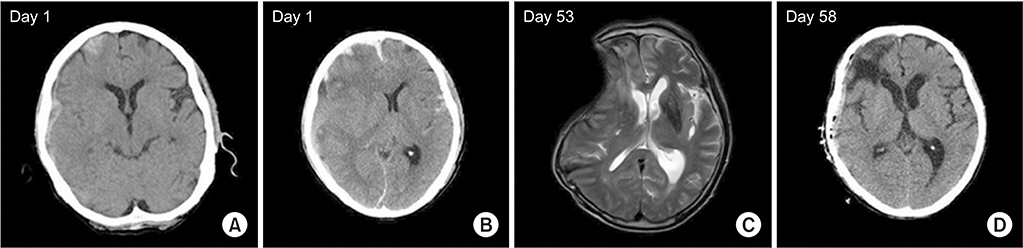
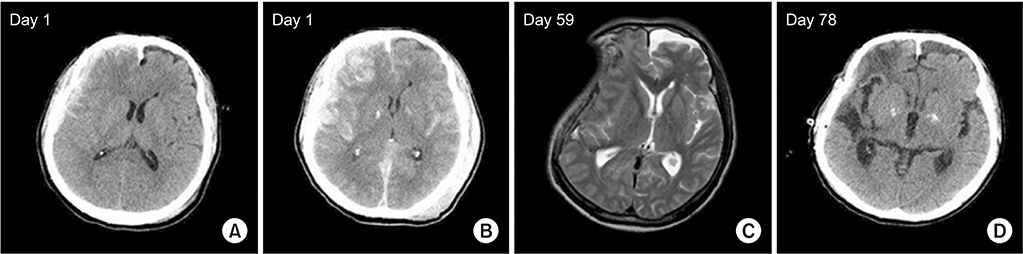
Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Feb;43(1):111-114. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.111.
Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome or Syndrome of the Trephined: A Report of Two Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. byhong@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2440959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.111
Abstract
- Decompressive craniectomy (DC) is commonly performed in patients with intracranial hypertension or brain edema due to traumatic brain injury. Infrequently, neurologic deteriorations accompanied by sunken scalp may occur after DC. We report two patients with traumatic subdural hemorrhage who had neurologic deteriorations accompanied by sunken scalp after DC. Neurologic function improved dramatically in both patients after cranioplasty. Monitoring for neurologic deterioration after craniectomy is advised. For patients showing neurologic deficit with a sunken scalp, early cranioplasty should be considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Masel BE, DeWitt DS. Traumatic brain injury: a disease process, not an event. J Neurotrauma. 2010; 27:1529–40.
Article2. Kramer AH, Deis N, Ruddell S, Couillard P, Zygun DA, Doig CJ, et al. Decompressive craniectomy in patients with traumatic brain injury: are the usual indications congruent with those evaluated in clinical trials? Neurocrit Care. 2016; 25:10–9.
Article3. Kurland DB, Khaladj-Ghom A, Stokum JA, Carusillo B, Karimy JK, Gerzanich V, et al. Complications associated with decompressive craniectomy: a systematic review. Neurocrit Care. 2015; 23:292–304.
Article4. Xu H, Niu C, Fu X, Ding W, Ling S, Jiang X, et al. Early cranioplasty vs. late cranioplasty for the treatment of cranial defect: a systematic review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015; 136:33–40.
Article5. Tasiou A, Vagkopoulos K, Georgiadis I, Brotis AG, Gatos H, Fountas KN. Cranioplasty optimal timing in cases of decompressive craniectomy after severe head injury: a systematic literature review. Interdiscip Neurosurg. 2014; 1:107–11.
Article6. Salma A, Abou Al-Shaar H, Hassounah M. Letter to the Editor: Cranioplasty complications and the timing of surgery. J Neurosurg. 2016; 124:280–1.
Article7. Yamaura A, Makino H. Neurological deficits in the presence of the sinking skin flap following decompressive craniectomy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1977; 17(1 Pt 1):43–53.
Article8. Jeyaraj P. Importance of early cranioplasty in reversing the “syndrome of the trephine/motor trephine syndrome/sinking skin flap syndrome”. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015; 14:666–73.
Article9. Annan M, De Toffol B, Hommet C, Mondon K. Sinking skin flap syndrome (or syndrome of the trephined): a review. Br J Neurosurg. 2015; 29:314–8.
Article10. Kim BW, Kim TU, Hyun JK. Effects of early cranioplasty on the restoration of cognitive and functional impairments. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017; 41:354–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reperfusion Injury after Autologous Cranioplasty in a Patient with Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome
- "Syndrome of the Sinking Skin-Flap" Secondary to the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt after Craniectomy
- Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome after Decompressive Craniotomy
- Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome after Craniectomy in a Patient Who Previously Underwent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt
- Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Infarction after Cranioplasty in a Patient with Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome