Korean J Neurotrauma.
2012 Oct;8(2):149-152. 10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.2.149.
Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome after Craniectomy in a Patient Who Previously Underwent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. chl68@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1427730
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.2.149
Abstract
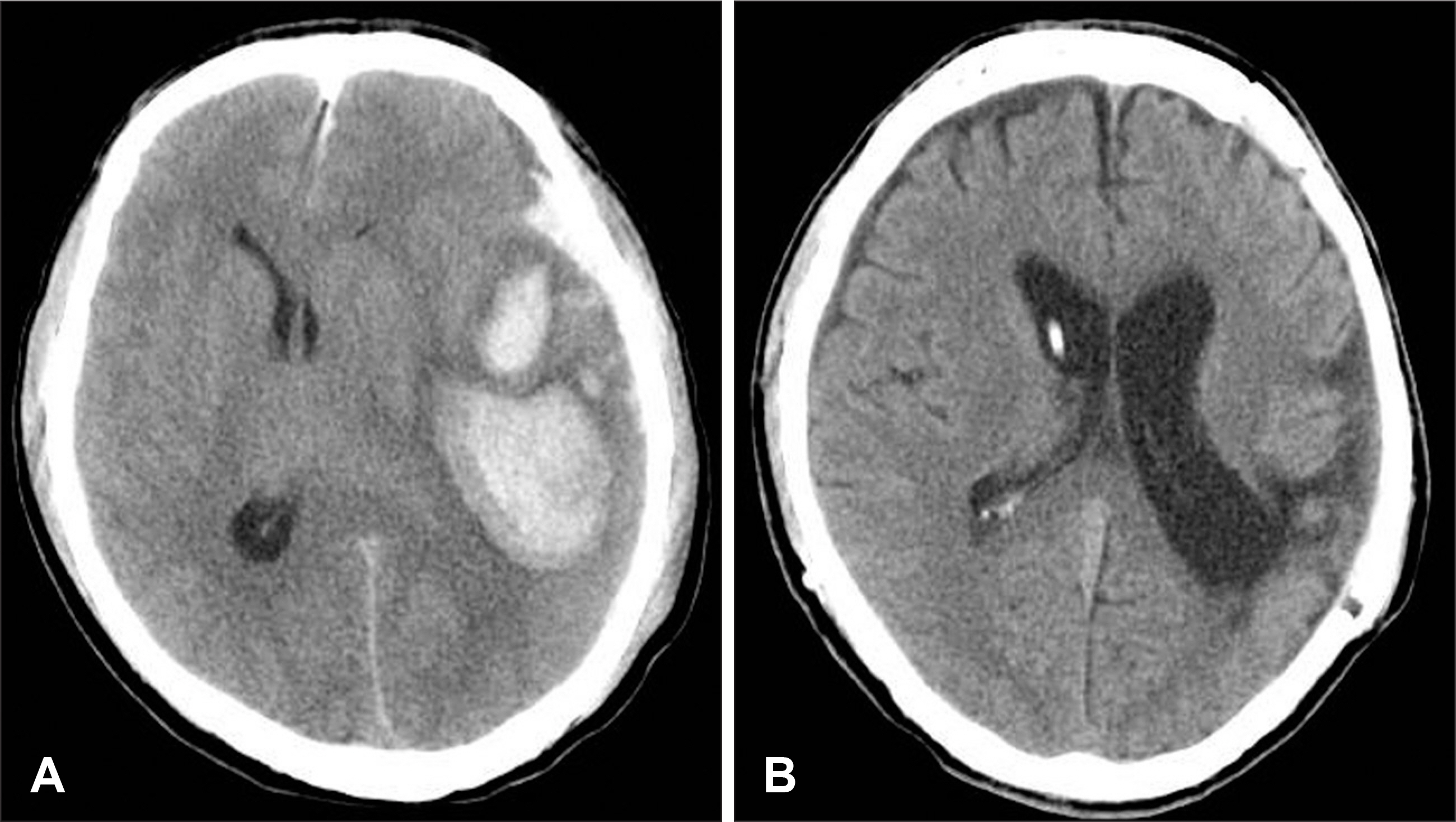
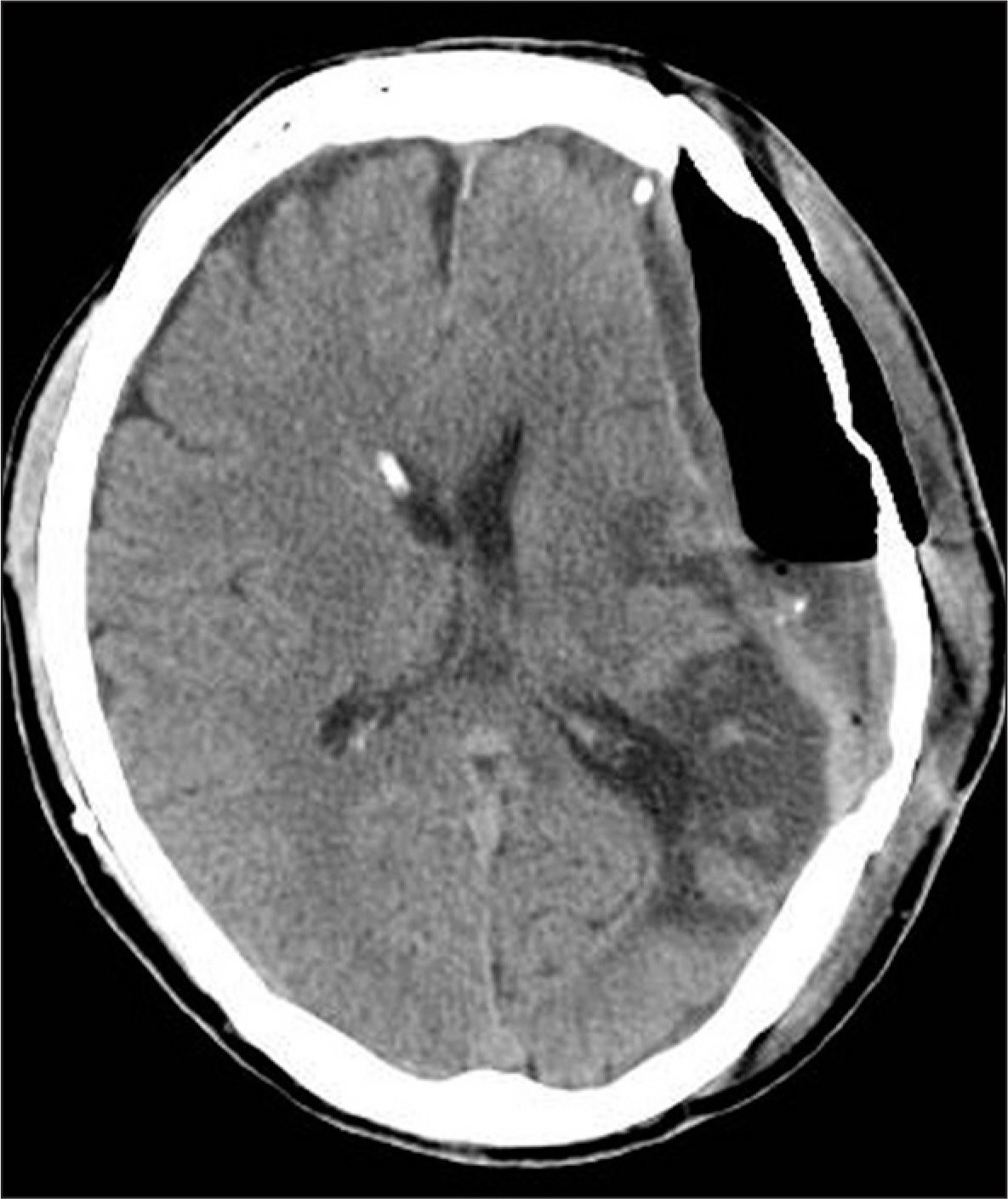
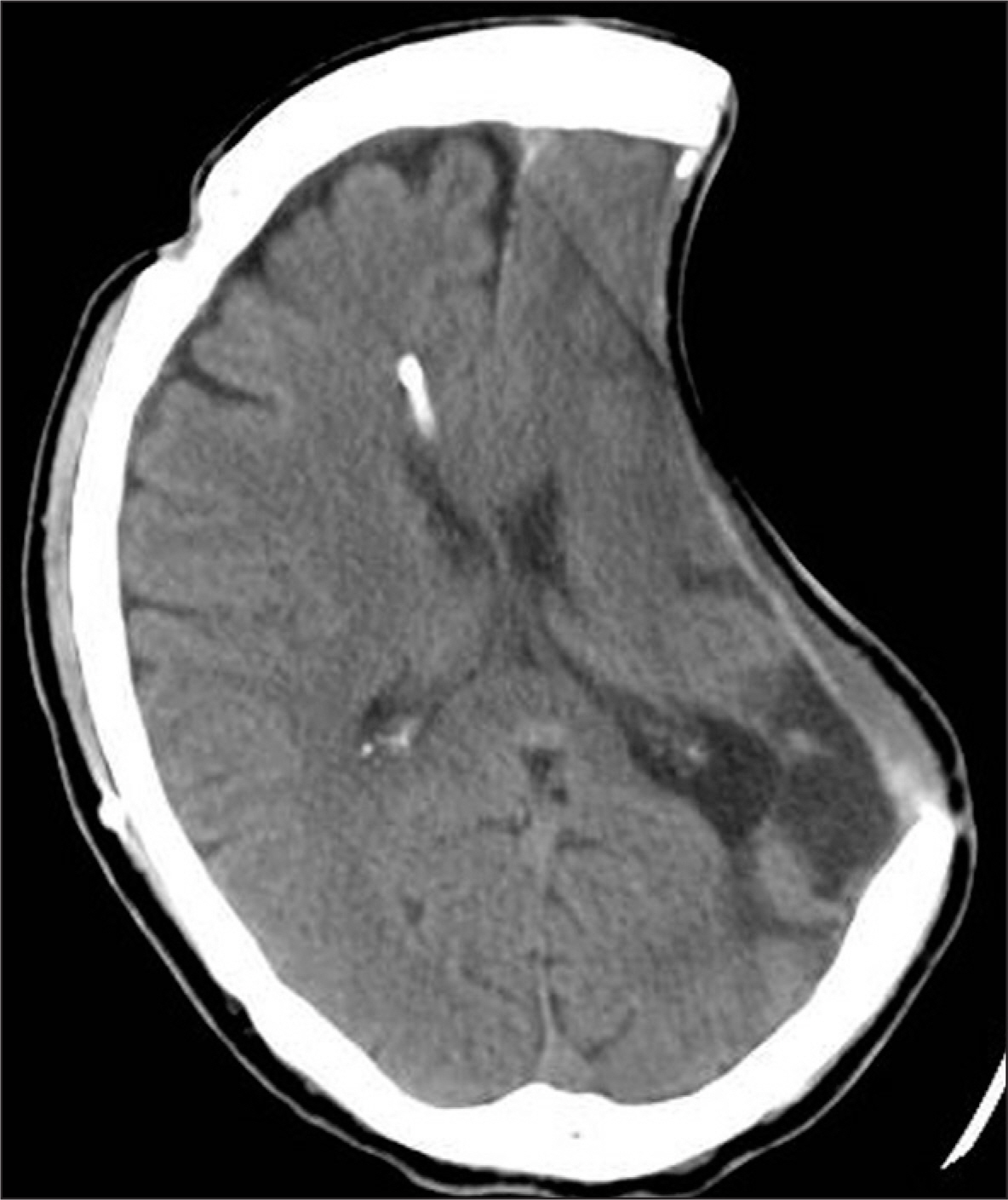
- Sinking skin flap syndrome, resulting from decompressive craniectomy, is defined as a series of neurologic symptoms with skin depression at the site of cranial defect. A 61-year-old male was hospitalized with high fever and operative site swelling. He underwent decompressive craniectomy on his left side for treatment for acute subdural hematoma and traumatic intracerebral hematoma 5 years ago. Four months later, a ventriculoperitoneal shunt was performed for treatment for hydrocephalus and cranioplasty was also performed. We suspected infection at the previous operative site and proceeded with craniectomy and epidural abscess removal. Following the procedure, the depression of the sinking flap became significant, and he has suffered from right hemiparesis. We performed a shunt catheter tie at the level of the right clavicle under local anesthesia, and the patient recovered his health to his baseline. We present a patient who was successfully managed with a tie of the shunt catheter for sinking skin flap syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Aarabi B., Hesdorffer DC., Ahn ES., Aresco C., Scalea TM., Eisenberg HM. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant swelling due to severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 104:469–479. 2006.
Article2). Akins PT., Guppy KH. Sinking skin flaps, paradoxical herniation, and external brain tamponade: a review of decompressive craniectomy management. Neurocrit Care. 9:269–276. 2008.
Article3). George AE., Morantz RA., Abad RM., Rovit RL., Chase N. Neuroradiology of the posthemicraniectomy patient with special emphasis on the radiology of unilateral atrophy. Radiology. 111:627–631. 1974.
Article4). Han PY., Kim JH., Kang HI., Kim JS. “Syndrome of the sinking skin-flap” secondary to the ventriculoperitoneal shunt after craniectomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 43:51–53. 2008.
Article5). Isago T., Nozaki M., Kikuchi Y., Honda T., Nakazawa H. Sinking skin flap syndrome: a case of improved cerebral blood flow after cranioplasty. Ann Plast Surg. 53:288–292. 2004.6). Jiao QF., Liu Z., Li S., Zhou LX., Li SZ., Tian W., You C. Influencing factors for posttraumatic hydrocephalus in patients suffering from severe traumatic brain injuries. Chin J Traumatol. 10:159–162. 2007.7). Kelley GR., Johnson PL. Sinking brain syndrome: craniotomy can precipitate brainstem herniation in CSF hypovolemia. Neurology. 62:157. 2004.
Article8). Langfitt TW. Increased intracranial pressure. Clin Neurosurg. 16:436–471. 1969.
Article9). Li G., Wen L., Zhan RY., Shen F., Yang XF., Fu WM. Cranioplasty for patients developing large cranial defects combined with posttraumatic hydrocephalus after head trauma. Brain Inj. 22:333–337. 2008.
Article10). Liao CC., Kao MC. Cranioplasty for patients with severe depressed skull bone defect after cerebrospinal fluid shunting. J Clin Neurosci. 9:553–555. 2002.
Article11). Oyelese AA., Steinberg GK., Huhn SL., Wijman CA. Paradoxical cerebral herniation secondary to lumbar puncture after decompressive craniectomy for a large space-occupying hemispheric stroke: case report. Neurosurgery 57: E594; discussion E594. 2005.
Article12). Piek J. Decompressive surgery in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 8:134–138. 2002.
Article13). Polin RS., Shaffrey ME., Bogaev CA., Tisdale N., Germanson T., Bocchicchio B, et al. Decompressive bifrontal craniectomy in the treatment of severe refractory posttraumatic cerebral edema. Neurosurgery. 41:84–92. discussion 92-94. 1997.
Article14). Timofeev I., Hutchinson PJ. Outcome after surgical decompression of severe traumatic brain injury. Injury. 37:1125–1132. 2006.
Article15). Yamaura A., Makino H. Neurological deficits in the presence of the sinking skin flap following decompressive craniectomy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 17(1 Pt 1): 43-53. 1977.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- "Syndrome of the Sinking Skin-Flap" Secondary to the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt after Craniectomy
- A Case of “Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome” in Vegetative State Patient
- Reperfusion Injury after Autologous Cranioplasty in a Patient with Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome
- Cranial Defect Overlying a Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: Pressure Gradient Leading to Free Flap Deterioration?
- Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Infarction after Cranioplasty in a Patient with Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome