Epidemiology and Clinical Severity of the Hospitalized Children with Viral Croup
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, the Republic of Korea. khm9120@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2438749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/piv.2018.25.1.8
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In this study, the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of patients admitted for viral croup were analyzed to evaluate disease severity based on the organism that caused the infection.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 302 patients who were admitted to the Department of Pediatrics at the Wonju Severance Hospital between May 2013 and December 2016 for viral croup. Patients who showed positive results on multiplex polymerase chain reaction were subsequently diagnosed with respiratory virus infection. The Westley scoring system was used to evaluate the severity of viral croup.
RESULTS
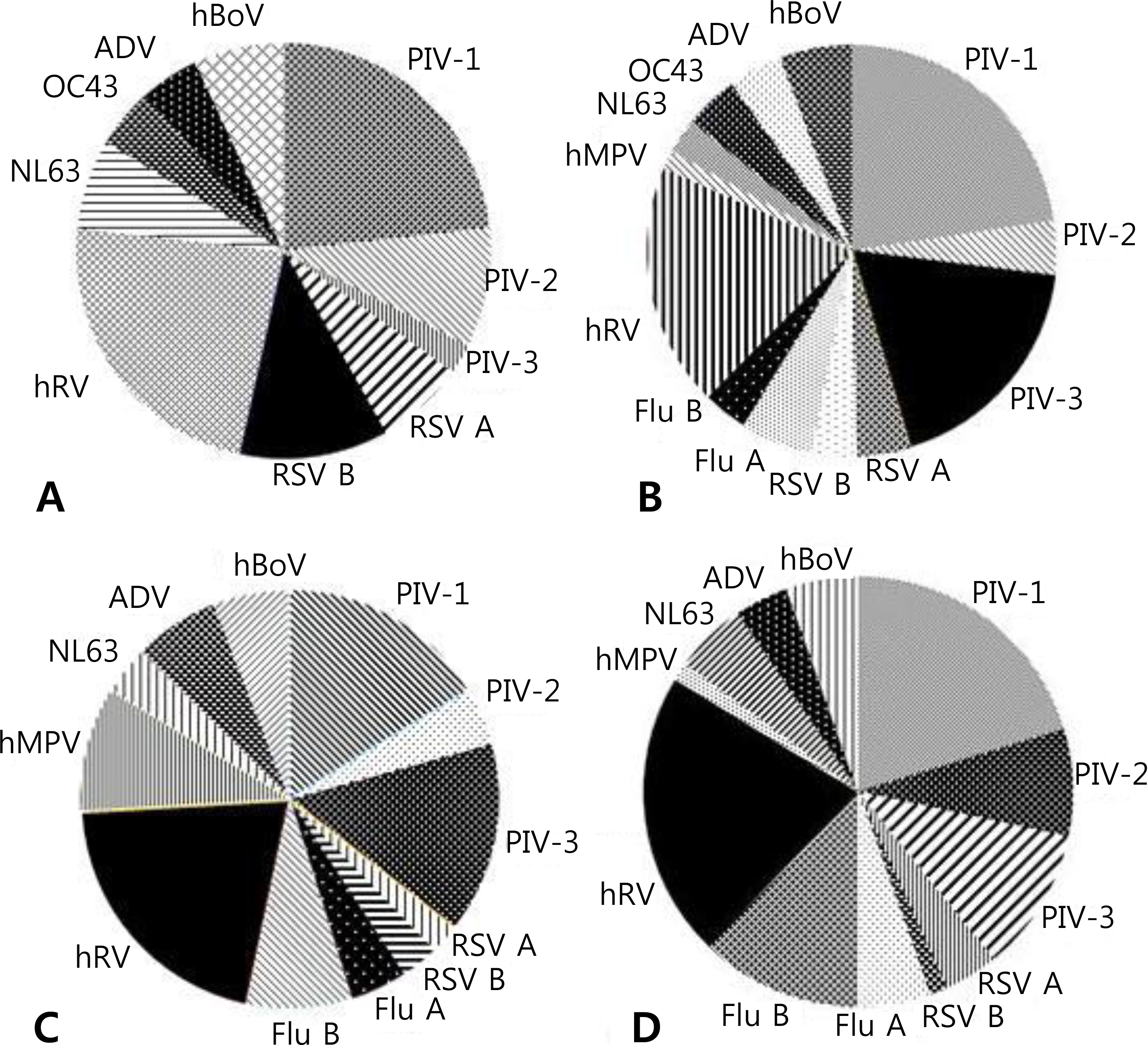
Of the 302 patients, 149 were admitted due to severe viral croup, including 88 boys and 61 girls, with a boy-to-girl ratio of 1.44:1. About 110 cases of parainfluenza virus infection have been reported, which accounted for almost half of the total cases. The other identified viruses included influenza virus, human rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. Analysis of the association between severe viral croup and causative pathogen revealed that only parainfluenza type 2 virus showed a significantly high risk. Parainfluenza type 2 virus did not show an age-based difference in frequency but showed relatively a higher frequency of infections during the summer and fall.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, parainfluenza virus type 2 was the only virus associated with severe viral croup. To facilitate proper preventive management, treatment, and prognosis evaluation of viral croup, prospective and multicenter studies should assess the additional variables and the severity of the virus. Additionally, further studies should be conducted to assess age-dependent influences, as well as the regional and seasonal incidence of viral infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Child
Child, Hospitalized*
Croup*
Epidemiology*
Female
Gangwon-do
Humans
Incidence
Medical Records
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Orthomyxoviridae
Parainfluenza Virus 2, Human
Paramyxoviridae Infections
Pediatrics
Prognosis
Prospective Studies
Respiratory Syncytial Viruses
Retrospective Studies
Rhinovirus
Seasons
Severity of Illness Index
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Clinical presentation of croup in children according to causative viruses
Ga Eun Kim, Suk Won Shin, Hee Joung Choi, Bo Geum Choi
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(6):290-294. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.290.Etiology of respiratory virus in croup with children in Korea
Jeong Hee Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2019;7(2):65-66. doi: 10.4168/aard.2019.7.2.65.Seasonality and etiology of croup in pediatric patients hospitalized with lower respiratory tract infections: A long-term study between 2009 and 2017
Kyung Jin Oh, Dong Hwa Yang, Hyeong Rok Shin, Eun Jin Kim, Yong Han Sun, Eell Ryoo, Hye Kyung Cho, Hye Jung Cho
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2019;7(1):28-36. doi: 10.4168/aard.2019.7.1.28.Seasonal patterns and etiologies of croup in children during the period 2010–2015: A multicenter retrospective study
Yong Ju Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Chang-Keun Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Hyung Young Kim, Sangyoung Kim, Yunsun Kim, Chorong Park, Ju-Hee Seo, In Suk Sol, Myongsoon Sung, Min Seob Song, Dae Jin Song, Young Min Ahn, Ju Suk Lee, Yoon Young Jang, Eun Hee Chung, Hai Lee Chung, Sung-Min Choi, Yun Jung Choi, Man Yong Han, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Jung Yeon Shim, Jin-Tack Kim, Hea Lin Oh, Jinho Yu, Kyung Suk Lee, Eun Lee, Gwang Cheon Jang
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2019;7(2):78-85. doi: 10.4168/aard.2019.7.2.78.Antibiotics for Pediatric Patients With Laryngotracheobronchitis in Korea: A Nationwide Study Based on Administrative Data
Seung Beom Han, Kil Seong Bae, Ui Yoon Choi, Jong-Hyun Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2024;39(24):e189. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e189.
Reference
-
References
1. Dawson KP, Capaldi N. Acute laryngo-tracheo-bronchitis (croup): an audit of hospital practice. Aust Clin Rev. 1993; 13:63–8.2. Osmond M. Croup. Clin Evid. 2002. 319–29.3. Rosekrans JA. Viral croup: current diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 1998; 73:1102–6.
Article4. Westley CR, Cotton EK, Brooks JG. Nebulized racemic epinephrine by IPPB for the treatment of croup: a double-blind study. Am J Dis Child. 1978; 132:484–7.
Article5. Henrickson KJ, Kuhn SM, Savatski LL. Epidemiology and cost of infection with human parainfluenza virus types 1 and 2 in young children. Clin Infect D is. 1994; 18:770–9.
Article6. Williams JV. The clinical presentation and outcomes of children infected with newly identified respiratory tract viruses. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2005; 19:569–84.
Article7. Osiowy C. Direct detection of respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus, and adenovirus in clinical respiratory specimens by a multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:3149–54.
Article8. Henrickson KJ, Hoover S, Kehl KS, Hua W. National disease burden of respiratory viruses detected in children by polymerase chain reaction. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23(1 Suppl):S11–8.
Article9. Rihkanen H, Ronkko E, Nieminen T, Komsi KL, Raty R, Saxen H, et al. Respiratory viruses in laryngeal croup of young children. J Pediatr. 2008; 152:661–5.
Article10. Wall SR, Wat D, Spiller OB, Gelder CM, Kotecha S, Doull IJ. The viral aetiology of croup and recurrent croup. Arch Dis Child. 2009; 94:359–60.
Article11. Kim KH, Lee JH, Sun DS, Kim YB, Choi YJ, Park JS, et al. Detection and clinical manifestations of twelve respiratory viruses in hospitalized children with acute lower respiratory tract infections: focus on human metapneumovirus, human rhinovirus and human coronavirus. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:834–41.12. Lim JS, Woo SI, Kwon HI, Baek YH, Choi YK, Hahn YS. Clinical characteristics of acute lower respiratory tract infections due to 13 respiratory viruses detected by multiplex PCR in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2010; 53:373–9.
Article13. Sung JY, Lee HJ, Eun BW, Kim SH, Lee SY, Lee JY, et al. Role of human coronavirus NL63 in hospitalized children with croup. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2010; 29:822–6.
Article14. Kaditis AG, Wald ER. Viral croup: current diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998; 17:827–34.
Article15. Johnson D. Croup. BMJ Clin Evid. 2009; 2009:0321.16. Syrmis MW, Whiley DM, Thomas M, Mackay IM, Williamson J, Siebert DJ, et al. A sensitive, specific, and cost-effective multiplex reverse transcriptase-PCR assay for the detection of seven common respiratory viruses in respiratory samples. J Mol Diagn. 2004; 6:125–31.
Article17. Hindiyeh M, Levy V, Azar R, Varsano N, Regev L, Shalev Y, et al. Evaluation of a multiplex real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assay for detection and differentiation of influenza viruses A and B during the 2001–2002 influenza season in Israel. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:589–95.
Article18. Knott AM, Long CE, Hall CB. Parainfluenza viral infections in pediatric outpatients: seasonal patterns and clinical characteristics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1994; 13:269–73.19. Marx A, Torok TJ, Holman RC, Clarke MJ, Anderson LJ. Pediatric hospitalizations for croup (laryngotracheobronchitis): biennial increases associated with human parainfluenza virus 1 epidemics. J Infect Dis. 1997; 176:1423–7.
Article20. Peltola V, Heikkinen T, Ruuskanen O. Clinical courses of croup caused by influenza and parainfluenza viruses. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002; 21:76–8.
Article21. Campbell AJP. Parainfluenza viruses. Kliegman RM, Nelson WE, editors. editors.Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 20th Ed.Philadelphia: Elsevier;2016. p. 1603–6.
Article22. Denny FW, Murphy TF, Clyde WA Jr, Collier AM, Henderson FW. Croup: an 11-year study in a pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 1983; 71:871–6.
Article23. van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, et al. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001; 7:719–24.
Article24. Yeom HH, Park JS, Jeong DJ, Kim CJ, Kim YB, Lee DH, et al. Human metapneumovirus infection in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:401–9.
Article25. Kim YK, Lee HJ. Human metapneumovirus-associated lower respiratory tract infections in korean infants and young children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005; 24:1111–2.
Article26. Chiu SS, Chan KH, Chu KW, Kwan SW, Guan Y, Poon LL, et al. Human coronavirus NL63 infection and other coronavirus infections in children hospitalized with acute respiratory disease in Hong Kong, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:1721–9.
Article27. Choi EH, Lee HJ, Kim SJ, Eun BW, Kim NH, Lee JA, et al. The association of newly identified respiratory viruses with lower respiratory tract infections in Korean children, 2000–2005. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 43:585–92.
Article28. Han TH, Chung JY, Kim SW, Hwang ES. Human coronavirus-NL63 infections in Korean children, 2004–2006. J Clin Virol. 2007; 38:27–31.
Article29. Tuffaha A, Gern JE, Lemanske RF Jr. The role of respiratory viruses in acute and chronic asthma. Clin Chest Med. 2000; 21:289–300.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of etiology and clinical presentation between children with laryngotracheobronchopneumonitis and croup
- Clinical Characteristics of Acute Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Hospitalized Children
- Pharmacological treatment of the patients with croup
- Seasonality and etiology of croup in pediatric patients hospitalized with lower respiratory tract infections: A long-term study between 2009 and 2017
- Viral etiology and Epidemiology of Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Hospitalized Children (Choongchung Province in May 2001 through April 2004)