Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2019 Feb;12(1):66-71. 10.21053/ceo.2017.01704.
Is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Effective in Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Karadeniz Technical University Faculty of Medicine, Trabzon, Turkey. benguyc@gmail.com
- 2Department of Underwater and Hyperbaric Medicine, Meram University, Faculty of Medicine, Konya, Turkey.
- 3Department of Underwater and Hyperbaric Medicine, Istanbul University, Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2437493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2017.01704
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Cisplatin is an antineoplastic agent, used in the treatment of different types of malignant neoplasms. Side effects such as ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and bone marrow toxicity are the main limitations of its clinical use. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the possible effects of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy as a protective agent in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats.
METHODS
A total of 30 adult Wistar rats (60 ears) were divided into five equal groups. Group 1 is a control group; group 2 is HBO therapy group; group 3 received 15 mg/kg cisplatin intraperitoneally; group 4 received 15 mg/kg cisplatin intraperitoneally and HBO treatment on the same day; group 5 received 15 mg/kg cisplatin intraperitoneally and HBO treatment 72 hours later. The effect of ototoxicity was measured with distortion product otoacoustic emission testing performed on the days 1, 3, and 7.
RESULTS
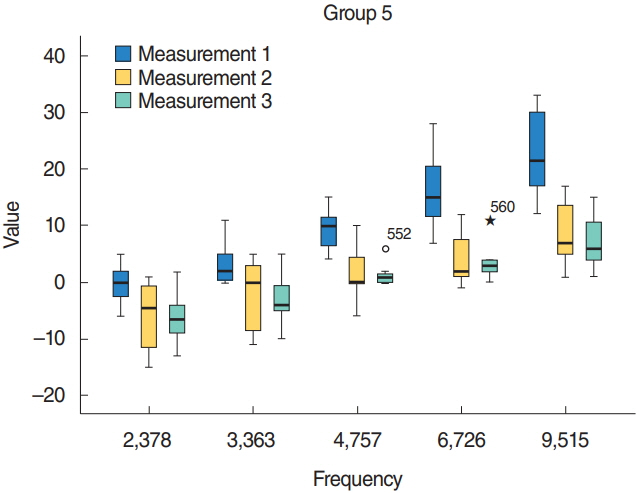
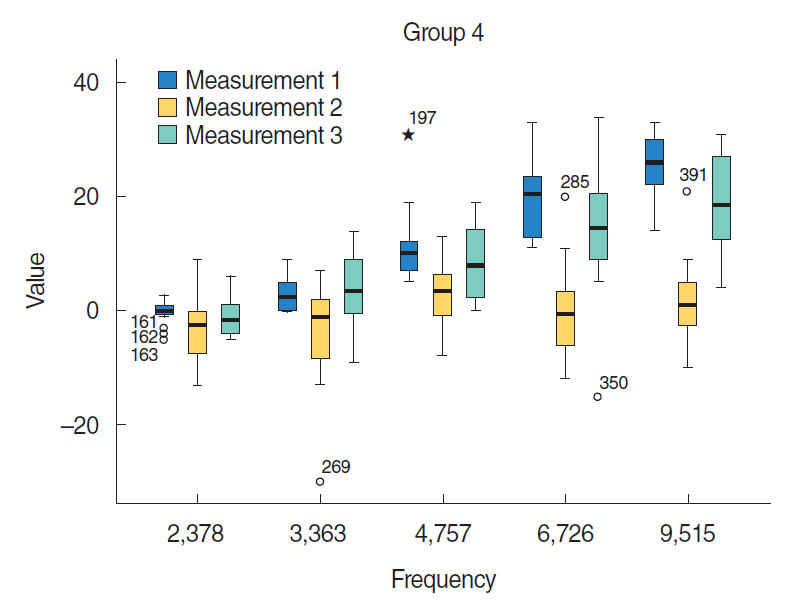
Groups 4 and 5 that received HBO treatment after cisplatin had better signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) values compared with group 3 that received only cisplatin (P < 0.05). Compared with group 5, group 4 (same day HBO treatment) had better SNR values (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
HBO was found effective for prevention of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Our study differs from other studies regarding using a promising treatment, which does not expose subjects to extra stress.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fram RJ. Cisplatin and platinum analogues: recent advances. Curr Opin Oncol. 1992; Dec. 4(6):1073–9.2. Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V. Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009; Nov. 219(3):177–86.
Article3. Feghali JG, Liu W, Van De Water TR. L-n-acetyl-cysteine protection against cisplatin-induced auditory neuronal and hair cell toxicity. Laryngoscope. 2001; Jul. 111(7):1147–55.
Article4. Bayindir T, Iraz M, Kelles M, Kaya S, Tan M, Filiz A, et al. The effect of beta glucan on cisplatin ototoxicity. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; Jun. 66(2):131–4.
Article5. Rybak LP. Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity and progress in otoprotection. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; Oct. 15(5):364–9.
Article6. Yassuda CC, Righetti AE, Cury MC, Hyppolito MA, Oliveira JA, Feres O. The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (hot) as an otoprotection agent against cisplatin ototoxicity. Acta Cir Bras. 2008; 23 Suppl 1:72–6.
Article7. Tokgoz SA, Vuralkan E, Sonbay ND, Caliskan M, Saka C, Besalti O, et al. Protective effects of vitamins E, B and C and L-carnitine in the prevention of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. J Laryngol Otol. 2012; May. 126(5):464–9.8. Wang J, Ladrech S, Pujol R, Brabet P, Van De Water TR, Puel JL. Caspase inhibitors, but not c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase inhibitor treatment, prevent cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Cancer Res. 2004; Dec. 64(24):9217–24.
Article9. Chirtes F, Albu S. Prevention and restoration of hearing loss associated with the use of cisplatin. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:925485.
Article10. Ozturk M, Ucar S, Sari F, Erdogan S, Topdag M, Iseri M. Possible protective effect of sertraline against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: an experimental study. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013; Oct. 2013:523480.
Article11. Rybak LP, Whitworth C, Somani S. Application of antioxidants and other agents to prevent cisplatin ototoxicity. Laryngoscope. 1999; Nov. 109(11):1740–4.
Article12. Simsek G, Tokgoz SA, Vuralkan E, Caliskan M, Besalti O, Akin I. Protective effects of resveratrol on cisplatin-dependent inner-ear damage in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; May. 270(6):1789–93.
Article13. European Committee for Hyperbaric Medicine. Recommendations of the jury of the 7th European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine, Lille (December 3-4, 2004) [Internet]. Lille: European Committee for Hyperbaric Medicine;[cited 2018 Jul 31]. Available from: http://www.echm.org/ECHM-Conferences.htm.14. Mathieu D, Schmutz J, Cronje F. Indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy. In : Mathieu D, editor. Handbook of hyperbaric medicine. Dordrecht: Springer;2006. p. 163–70.15. Vuralkan E, Cobanoglu HB, Arslan A, Arslan S, Mungan S, Tatar S, et al. Effects of topical nasal steroids and diclofenac on the nasal mucosa during hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a double-blind experimental study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; Aug. 271(8):2213–7.
Article16. Cavallazzi GM. Relations between O2 and hearing function. In : International Joint Meeting on Hyperbaric and Underwater Medicine; 1996 Sep 4-8; Milano, Italy. p. 633–45.17. Matschinsky FM, Thalmann R. Quantitative histochemistry of microscopic structures of the cochlea. II. Ischemic alterations of levels of glycolytic intermediates and cofactors in the organ of corti and stria vascularis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1967; Aug. 76(3):638–46.18. Moen I, Stuhr LE. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and cancer: a review. Target Oncol. 2012; Dec. 7(4):233–42.19. Daruwalla J, Christophi C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for malignancy: a review. World J Surg. 2006; Dec. 30(12):2112–31.
Article20. Gore A, Muralidhar M, Espey MG, Degenhardt K, Mantell LL. Hyperoxia sensing: from molecular mechanisms to significance in disease. J Immunotoxicol. 2010; Oct-Dec. 7(4):239–54.
Article21. Lee CK, Shin JI, Cho YS. Protective effect of minocycline against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2011; Jun. 4(2):77–82.
Article22. Amora Lde A, Murashima Ade A, Rossato M, Moreira MB, Hyppolito MA, Fagundes DJ. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy upon ototoxic injuries produced by amikacin in guinea pigs. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; May-Jun. 79(3):342–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of radiation-induced cystitis with hyperbaric oxygen
- Early experience of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in radiation-induced cystitis
- Morphologic Study of Effect of Fosfomycin and Pentoxifylline on Cisplatin Induced Ototoxicity in Guinea Pig
- A Basic Survey for Regional Capability of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy to Multiple Fire Victims
- Effect of Melatonin on the Cisplatin Induced Ototoxicity in Rats