Ann Lab Med.
2018 Sep;38(5):431-439. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.5.431.
Postprandial Lipid Concentrations and Daytime Biological Variation of Lipids in a Healthy Chinese Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
- 2School of Nursing, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China. yunxianzhou@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2434732
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.5.431
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Several latest guidelines and consensus statements from Europe and the United States specify that there is no need for fasting prior to routine lipid tests. However, the latest Chinese guidelines still recommend fasting tests owing to a lack of local evidence. This study aimed to investigate postprandial lipid concentrations and daytime biological variation of lipids in a healthy Chinese population.
METHODS
Venous blood samples were collected from 41 ostensibly healthy Chinese volunteers at five time points during the day (06:30, 09:00, 12:00, 15:00, and 18:30). The same batch of reagents was used to determine lipid concentrations. A nested ANOVA was performed to calculate within-subject biological variation (CVI) and between-subject biological variation (CVG).
RESULTS
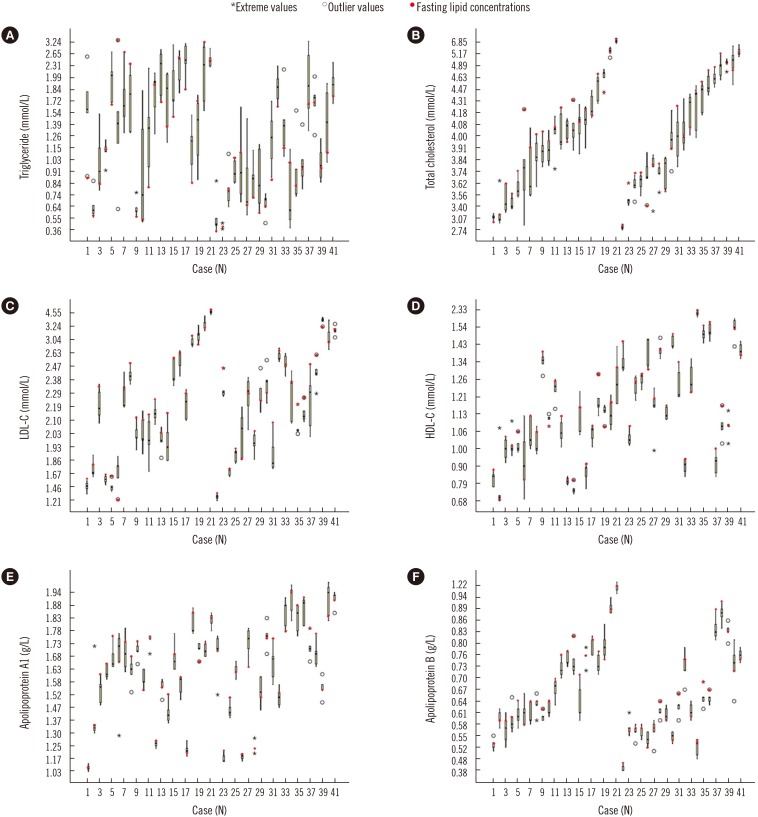
Postprandial concentrations of triglyceride were higher than fasting concentrations, with the maximum change occurring at 12:00 (0.5 hours after lunch, 0.21±0.65 mmol/L difference). The daytime biological variation of triglycerides was relatively high (CVI=25%, CVG=35.9%). The postprandial concentrations of total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoprotein A1, and apolipoprotein B were mostly lower than the fasting concentrations, and their daytime biological variations were relatively low (CVI=2.4-4.4%, CVG=11.8-18.7%).
CONCLUSIONS
As most daytime lipid concentrations changed only slightly, non-fasting samples could be used for routine lipid tests. However, in cases of abnormal postprandial triglyceride concentrations, dietary factors and fasting time should be considered when interpreting the results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
HDL Subclass Analysis in Predicting Metabolic Syndrome in Koreans With High HDL Cholesterol Levels
Hyun Suk Yang, Mina Hur, Hanah Kim, Sun Jong Kim, Sojung Shin, Salvatore Di Somma,
Ann Lab Med. 2020;40(4):297-305. doi: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.4.297.
Reference
-
1. Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, et al. 2016 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:2999–3058. PMID: 27567407.2. Joint Committee for Revising the Chinese Guidelines on Prevention and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Adults. Chinese guidelines on prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults (Revised in 2016) (in Chinese). Chin J Cardiol. 2016; 44:833–853.3. Nordestgaard BG, Langsted A, Mora S, Kolovou G, Baum H, Bruckert E, et al. Fasting is not routinely required for determination of a lipid profile: clinical and laboratory implications including flagging at desirable concentration cut-points-a joint consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society and European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:1944–1958. PMID: 27122601.4. Rifai N, Young IS, Nordestgaard BG, Wierzbicki AS, Vesper H, Mora S, et al. Nonfasting sample for the determination of routine lipid profile: is it an idea whose time has come? Clin Chem. 2016; 62:428–435. PMID: 26787760.5. Farukhi Z, Mora S. Re-assessing the role of non-fasting lipids; a change in perspective. Ann Transl Med. 2016; 4:431. PMID: 27942522.6. Driver SL, Martin SS, Gluckman TJ, Clary JM, Blumenthal RS, Stone NJ. Fasting or non-fasting lipid measurements: it depends on the question. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 67:1227–1234. PMID: 26965545.7. Langsted A, Nordestgaard BG. Nonfasting lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins in individuals with and without diabetes: 58,434 individuals from the Copenhagen general population study. Clin Chem. 2011; 57:482–489. PMID: 21189274.8. Mihas C, Kolovou GD, Mikhailidis DP, Kovar J, Lairon D, Nordestgaard BG, et al. Diagnostic value of postprandial triglyceride testing in healthy subjects: a meta-analysis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2011; 9:271–280. PMID: 21314631.9. Liu AB, Li WD, Xin J, Zhang SH, Hu T. Fat-tolerance test of 460 Chinese healthy subjects. Chin J Lab Med. 2001; 24:161–164.10. Huang WJ, Li GY, Chen HC. Dynamic analysis of postprandial lipid levels in patients with hypertension. Chin Lab Sci. 2003; 21:25–27.11. Gu JQ, Zhang J, Meng X. The dynamic change of postprandial lipid in patients of normotriglyceridemic type 2 diabetes. Chin J Arterioscler. 2006; 14:243–246.12. Zhu J, Shao WQ, Wu J, Guo W, Pan BS. Prospects for the application of nonfasting lipids. Chin J Lab Med. 2016; 39:720–725.13. Braga F, Panteghini M. Generation of data on within-subject biological variation in laboratory medicine: an update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2016; 53:313–325. PMID: 26856991.14. Fraser CG, Cummings ST, Wilkinson SP, Neville RG, Knox JD, Ho O, et al. Biological variability of 26 clinical chemistry analytes in elderly people. Clin Chem. 1989; 35:783–786. PMID: 2720971.15. Marcovina SM, Gaur VP, Albers JJ. Biological variability of cholesterol, triglyceride, low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, lipoprotein(a), and apolipoproteins A-I and B. Clin Chem. 1994; 40:574–578. PMID: 8149613.16. Simundic AM, Bartlett WA, Fraser CG. Biological variation: a still evolving facet of laboratory medicine. Ann Clin Biochem. 2015; 52:189–190. PMID: 25605975.17. Carobene A. Reliability of biological variation data available in an online database: need for improvement. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015; 53:871–877. PMID: 25883200.18. Minchinela J, Ricós C, Perich C, Fernández-Calle P, Alvarez V, Domenech M, et al. Biological variation database and quality specifications for imprecision, bias and total error (desirable and minimum). The 2014 update. Updated in 2014. http://www.westgard.com/biodatabase-2014-update.htm.19. Bartlett WA, Braga F, Carobene A, Coşkun A, Prusa R, Fernandez-Calle P, et al. A checklist for critical appraisal of studies of biological variation. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015; 53:879–885. PMID: 25996385.20. Røraas T, Petersen PH, Sandberg S. Confidence intervals and power calculations for within-person biological variation: effect of analytical imprecision, number of replicates, number of samples, and number of individuals. Clin Chem. 2012; 58:1306–1313. PMID: 22761475.21. Burdick RK, Graybill FA, editors. Confidence intervals on variance components. New York: Marcel Dekker;1992. p. 78–83.22. Langsted A, Freiberg JJ, Nordestgaard BG. Fasting and nonfasting lipid levels influence of normal food intake on lipids, lipoproteins, apolipoproteins, and cardiovascular risk prediction. Circulation. 2008; 118:2047–2056. PMID: 18955664.23. Sidhu D, Naugler C. Fasting time and lipid levels in a community-based population: a cross-sectional study. Arch Intern Med. 2012; 172:1707–1710. PMID: 23147400.24. Gruchot M, Graeter T, Oeztuerk S, Haenle MM, Koenig W, Imhof A, et al. Fasting time and lipid parameters: association with hepatic steatosis--data from a random population sample. Lipids Health Dis. 2014; 13:18. PMID: 24447492.25. Aronov DM, Bubnova MG, Perova NV, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. The effect of maximal vs submaximal exertion on postprandial lipid levels in individuals with and without coronary heart disease. J Clin Lipidol. 2017; 11:369–376. PMID: 28502493.26. Chen ZJ, Zhang C, Song BB, Wu J, Wang BL, Zhang CY, et al. Biological variation in 32 clinical laboratory routine tests. Chin J Lab Med. 2012; 10:926–931.27. Sennels HP, Jørgensen HL, Fahrenkrug J. Diurnal changes of biochemical metabolic markers in healthy young males - the Bispebjerg study of diurnal variations. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015; 75:686–692. PMID: 26378655.28. Rivera-Coll A, Fuentes-Arderiu X, Díez-Noguera A. Circadian rhythmic variations in serum concentrations of clinically important lipids. Clin Chem. 1994; 40:1549–1553. PMID: 8044995.29. Pineda-Tenor D, Laserna-Mendieta EJ, Timón-Zapata J, Rodelgo-Jiménez L, Ramos-Corral R, Recio-Montealegre A, et al. Biological variation and reference change values of common clinical chemistry and haematologic laboratory analytes in the elderly population. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013; 51:851–862. PMID: 23518452.30. Zhu ZN, Wu CF, Guo CY, Zou SP, Song J, Wang ZY, et al. Cross-sectional study on fat intake and correlates in Shanghai residents. J Environ Occup Med. 2016; 33:103–107.31. Wang SS, Lay S, Yu HN, Shen SR. Dietary guidelines for Chinese residents (2016): comments and comparisons. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016; 17:649–656. PMID: 27604857.32. Adamska E, Ostrowska L, Goşcik J, Waszczeniuk M, Krętowski A, Górska M. Intake of meals containing high levels of carbohydrates or high levels of unsaturated fatty acids induces postprandial dysmetabolism in young overweight/obese men. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:147196. PMID: 26609520.33. Yang W, Xiao J, Yang Z, Ji L, Jia W, Weng J, et al. Serum lipids and lipoproteins in Chinese men and women. Circulation. 2012; 125:2212–2221. PMID: 22492668.34. van Wijk JP, van Oostrom AJ, Castro Cabezas M. Normal ranges of non-fasting triglycerides in healthy Dutch males and females. Clin Chim Acta. 2003; 337:49–57. PMID: 14568180.35. Klop B, Cohn JS, van Oostrom AJ, van Wijk JP, Birnie E, Castro Cabezas M. Daytime triglyceride variability in men and women with different levels of triglyceridemia. Clin Chim Acta. 2011; 412:2183–2189. PMID: 21864522.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between Lipids Measured in the Interstitial Fluid from Suction Blister and the Serum
- Effect of Lipid Peroxide in Skin Surface Lipid on the Clinical Aspect of Acne and Melasma
- Seasonal Variations of Serum Lipid Concentrations in Health Screened Population
- Associations between Hemoglobin Concentrations and the Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Lipids in Ginseng (Panax ginseng) and Their Analysis