Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2019 Jan;7(1):37-43. 10.4168/aard.2019.7.1.37.
Association between lead exposure and increased risk of bronchial asthma in Korean adolescents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Asthma and Allergy Center, Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kimck@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2434128
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2019.7.1.37
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Several studies have reported an association between lead exposure and increased risk of allergic sensitization and asthma. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines, An elevated blood lead level (BLL) is defined as a BLL of ≥5 µg/dL. However, no safe BLL has been identified, and it is controversial whether a BLL of <5 µg/dL affects the risk of asthma.
METHODS
We examined asthma prevalences and BLLs using data from the 2010-2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), which was a cross-sectional survey of 1,478 adolescence (aged 10-19 years) throughout the country. The adjusted odds ratios (ORs) (with 95% confidence intervals [CIs]) for the prevalence of asthma in adolescence with elevated BLLs were calculated by complex samples multivariate logistic regression analysis. The presence of asthma was based on self-reported, physician-diagnosed asthma in the Health Interview Surveys.
RESULTS
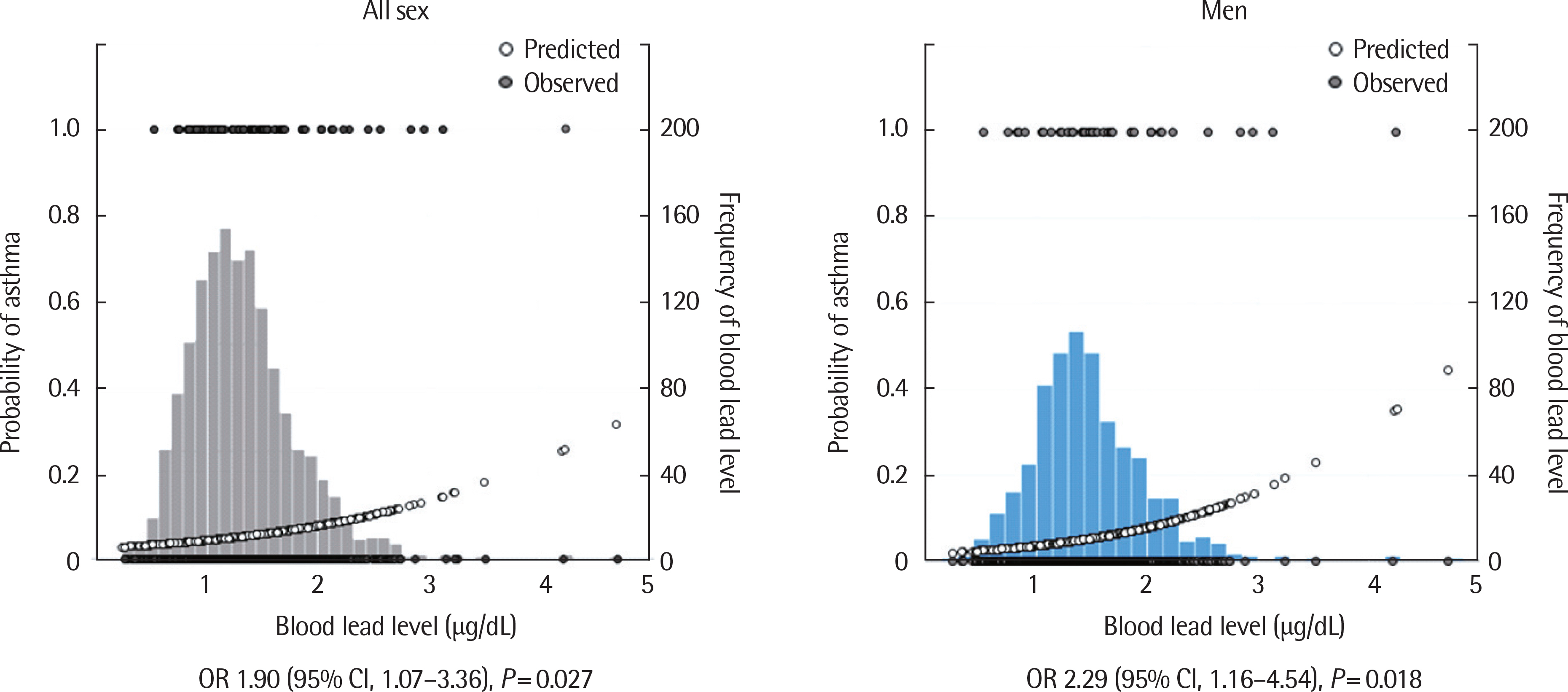
The mean of total BLLs was 1.33 µg/dL. Overall, 5.1% (n=71) of the subjects were physician diagnosed asthma. In the model controlling for population characteristics, the adjusted odds ratio for asthma per 1 µg/dL increase in blood lead was 1.94, 95% CI (1.06, 3.57), and stronger associations were observed among boys (adjusted OR, 2.31; 95% CI, [1.18, 4.51]). The group of BLL≥2 µg/dL was associated with an OR of 2.84 (95% CI, 1.06, 7.63) for asthma, after adjusting for potential confounding factors in boys.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest an association between total BLLs and asthma in Korean adolescent boys, although confirmation is warranted in further prospective studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Korean guideline for asthma Korean Academy of Asthma [Internet]. Seoul (Korea): Korean Academy of Allergy and Respiratory Disease;2015. [cited 2018 Apr 30]. Available from:. http://www.allergy.or.kr/file/150527_01.pdf.2. Lemanske RF Jr, Busse WW. Asthma: clinical expression and molecular mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125(2 Suppl 2):S95–102.
Article3. Lee JH, Kim CK, Park JH, Jung JW, Kim SH, Seol HS, et al. Multi-media and multi-pathway aggregate risk assessment(IV)-Lead (Pb) -. Institute of Environmental Protection and Safety; Neo Environmental Business Co.; Institute for Environmental Research; Yonsei University. 2014.4. Dietert RR, Lee JE, Hussain I, Piepenbrink M. Developmental immuno-toxicology of lead. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004; 198:86–94.
Article5. Bellanger AP, Bosch-Cano F, Millon L, Ruffaldi P, Franchi M, Bernard N. Reactions of airway epithelial cells to birch pollen grains previously exposed to in situ atmospheric Pb concentrations: a preliminary assay of allergenicity. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012; 150:391–5.
Article6. Boskabaddy MH, Farkhondeh T. Inhaled lead exposure affects tracheal responsiveness and lung inflammation in guinea pigs during sensitization. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013; 154:363–71.
Article7. Farkhondeh T, Boskabady MH, Jalali S, Bayrami G. The effect of lead exposure on tracheal responsiveness to methacholine and ovalbumin, total and differential white blood cells count, and serum levels of immunoglobulin E, histamine, and cytokines in guinea pigs. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014; 33:325–33.
Article8. Gao D, Mondal TK, Lawrence DA. Lead effects on development and function of bone marrowderived dendritic cells promote Th2 immune responses. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007; 222:69–79.
Article9. Heo Y, Parsons PJ, Lawrence DA. Lead differentially modifies cytokine production in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996; 138:149–57.10. Hsiao CL, Wu KH, Wan KS. Effects of environmental lead exposure on T-helper cell-specific cytokines in children. J Immunotoxicol. 2011; 8:284–7.
Article11. Joseph CL, Havstad S, Ownby DR, Peterson EL, Maliarik M, McCabe MJ Jr, et al. Blood lead level and risk of asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 2005; 113:900–4.
Article12. Motosue AM, Petronella S, Sullivan J, Castillo S, Garcia T, Murillo M, et al. Lead exposure risk is associated with asthma in a low-income urban hispanic population: results of the Communities Organized against Asthma and Lead (COAL) project. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123(2 Suppl):S20.
Article13. Pugh Smith P, Nriagu JO. Lead poisoning and asthma among low-income and African American children in Saginaw, Michigan. Environ Res. 2011; 111:81–6.
Article14. Wang IJ, Karmaus WJ, Yang CC. Lead exposure, IgE, and the risk of asthma in children. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2017; 27:478–83.
Article15. Zeng X, Xu X, Zheng X, Reponen T, Chen A, Huo X. Heavy metals in PM2.5 and in blood, and children's respiratory symptoms and asthma from an e-waste recycling area. Environ Pollut. 2016; 210:346–53.16. What do parents need to know to protect their children? [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;[updated 2017 May 17; cited 2018 Jun 24]. Available from:. https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/lead/acclpp/blood_lead_levels.htm.17. Adult Blood Lead Epidemiology and Surveillance (ABLES) [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;[cited 2018 Jun 24]. Available from:. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/ables/description.html.18. Gidlow D. Lead toxicity. Occup Med (Lond). 2015; 65:770.
Article19. Ahn HS, Shin HY. Hong Chang Yee textbook of pediatrics. 11th ed.Seoul: MiraeN;2016.20. The Aisa-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications Australia;2000.21. Janson S. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program, Expert Panel Report. II: overview and application to primary care. Lippincotts Prim Care Pract. 1998; 2:578–88.22. Kim JW, So WY, Kim YS. Association between asthma and physical activity in Korean adolescents: the 3rd Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (KYRBWS-III). Eur J Public Health. 2012; 22:864–8.
Article23. Mohammed AA, Mohamed FY, El-Okda el-S, Ahmed AB. Blood lead levels and childhood asthma. Indian Pediatr. 2015; 52:303–6.
Article24. Wells EM, Bonfield TL, Dearborn DG, Jackson LW. The relationship of blood lead with immunoglobulin E, eosinophils, and asthma among children: NHANES 2005–2006. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2014; 217:196–204.
Article25. Kim JH, Chang JH, Choi HS, Kim HJ, Kang JW. The association between serum lead and total immunoglobulin E levels according to allergic sensitization. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016; 30:e48–52.
Article26. Min JY, Min KB, Kim R, Cho SI, Paek D. Blood lead levels and increased bronchial responsiveness. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2008; 123:41–6.
Article27. Dong J, Zhang S, Xia L, Yu Y, Hu S, Sun J, et al. Physical activity, a critical exposure factor of environmental pollution in children and adolescents health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018; 15.
Article28. Zahran S, Laidlaw MA, McElmurry SP, Filippelli GM, Taylor M. Linking source and effect: resuspended soil lead, air lead, and children's blood lead levels in Detroit, Michigan. Environ Sci Technol. 2013; 47:2839–45.
Article29. Lin S, Wang X, Yu IT, Tang W, Miao J, Li J, et al. Environmental lead pollution and elevated blood lead levels among children in a rural area of China. Am J Public Health. 2011; 101:834–41.
Article30. Richmond-Bryant J, Meng Q, Davis JA, Cohen J, Svendsgaard D, Brown JS, et al. A multi-level model of blood lead as a function of air lead. Sci Total Environ. 2013; 461–462:207–13.
Article31. Chen K, Huang L, Yan B, Li H, Sun H, Bi J. Effect of lead pollution control on environmental and childhood blood lead level in Nantong, China: an interventional study. Environ Sci Technol. 2014; 48:12930–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of the association between bronchial hyperresponsiveness and genetic polymorphism of beta2-adrenoceptor in adolescents with long-term asthma remission
- Genetic Factors in Bronchial Asthma
- Long-term asthma remission during adolescence
- Sex-based differences in factors associated with bronchial hyperresponsiveness in adolescents with childhood asthma
- Association of Blood Pressure with Blood Lead and Cadmium Levels in Korean Adolescents: Analysis of Data from the 2010–2016 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey