Nutr Res Pract.
2016 Oct;10(5):487-493. 10.4162/nrp.2016.10.5.487.
Korean Curcuma longa L. induces lipolysis and regulates leptin in adipocyte cells and rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, International University of Korea, 965, Dongbu-ro, Munsan-eup, Jinju, Gyeongnam 52833, Korea. jhappychoi@naver.com
- KMID: 2434082
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2016.10.5.487
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) has been reported to have many biological functions including anti-obesity. Leptin, peptide hormone produced by adipocytes and its concentration is increased in proportion to the amount of the adipocytes. In the present study, we examined the effects of Korean turmeric on the regulation of adiposity and leptin levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and rats fed a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet.
MATERIALS/METHODS
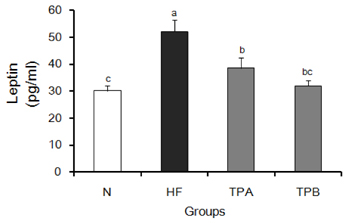
Leptin secretion, free fatty acid and glycerol contents in 3T3-L1 adipocytes were measured after incubation of cells with turmeric for 24 hours. Rats were divided into four experimental groups: a normal diet group (N), a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet group (HF), a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet group supplemented with 2.5% turmeric extracts (TPA group) and a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet group supplemented with 5% turmeric extracts (TPB group). Serum samples were used for the measurement of leptin concentration.
RESULTS
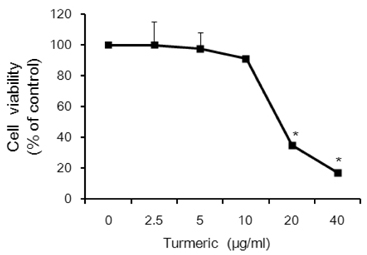
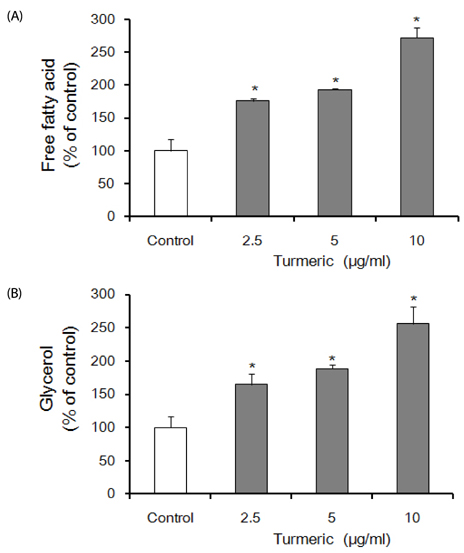
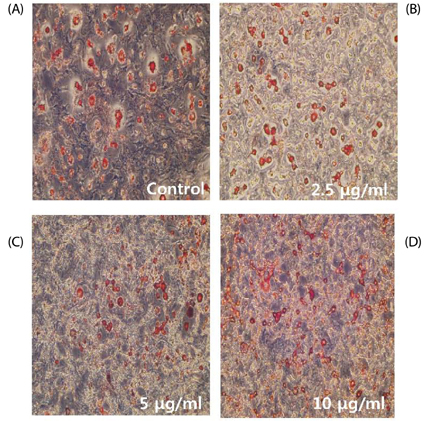
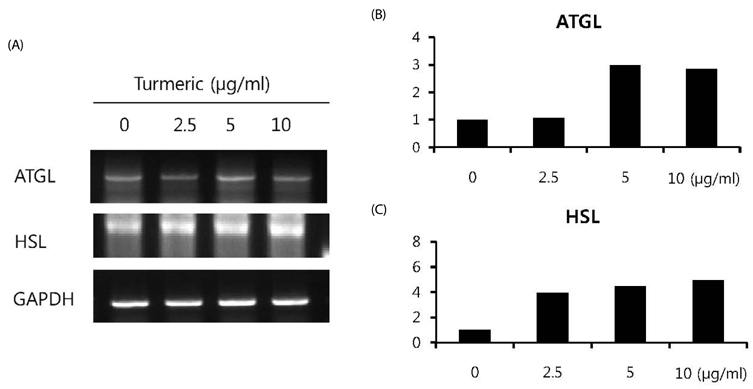
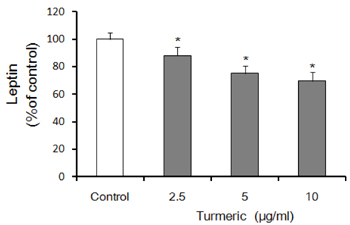
Contents of free fatty acid and glycerol showed concentration dependent increase in response to turmeric extracts. Effects of turmeric extracts on reduction of lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells were examined by Oil Red O staining. Treatment with turmeric extracts resulted in increased expression levels of adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase mRNA. The concentration of leptin from 3T3-L1 adipocytes was significantly decreased by turmeric. Proportional abdominal and epididymal fats weights of the turmeric 5% supplemented group, TPB has significantly decreased compared to the HF group. The serum levels of leptin in the TPA and TPB groups were significantly lower than those of the HF group.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on these results, we suggested that Korean turmeric may contribute to the decreasing of body fat and regulating leptin secretion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ho JN, Jang JY, Yoon HG, Kim Y, Kim S, Jun W, Lee J. Anti-obesity effect of a standardised ethanol extract from Curcuma longa L. fermented with Aspergillus oryzae in ob/ob mice and primary mouse adipocytes. J Sci Food Agric. 2012; 92:1833–1840.
Article2. Alappat L, Awad AB. Curcumin and obesity: evidence and mechanisms. Nutr Rev. 2010; 68:729–738.
Article3. Lee M, Nam DE, Kim OK, Heo SH, Lee J. Lipolytic effect of supercritical extraction from Pine Cone (Pinus koraiensis) in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2014; 43:1342–1348.
Article4. Homan P, Grob S, Milos G, Schnyder U, Eckert A, Lang U, Hasler G. The role of BDNF, leptin, and catecholamines in reward learning in bulimia nervosa. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014; 18:1–8.
Article5. Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S, Kern PA, Friedman JM. Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med. 1995; 1:1155–1161.
Article6. Hennes MM, Dua A, Maas DL, Sonnenberg GE, Krakower GR, Kissebah AH. Relationships of plasma leptin levels to changes in plasma free fatty acids in women who are lean and women who are abdominally obese. Obes Res. 1997; 5:442–446.
Article7. Chan JL, Heist K, DePaoli AM, Veldhuis JD, Mantzoros CS. The role of falling leptin levels in the neuroendocrine and metabolic adaptation to short-term starvation in healthy men. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111:1409–1421.
Article8. Welt CK, Chan JL, Bullen J, Murphy R, Smith P, DePaoli AM, Karalis A, Mantzoros CS. Recombinant human leptin in women with hypothalamic amenorrhea. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:987–997.
Article9. Havel PJ, Kasim-Karakas S, Mueller W, Johnson PR, Gingerich RL, Stern JS. Relationship of plasma leptin to plasma insulin and adiposity in normal weight and overweight women: effects of dietary fat content and sustained weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996; 81:4406–4413.
Article10. Friedman JM, Halaas JL. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 1998; 395:763–770.
Article11. Myers MG Jr, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW. Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 21:643–651.
Article12. Bradford PG. Curcumin and obesity. Biofactors. 2013; 39:78–87.
Article13. Ammon HP, Wahl MA. Pharmacology of Curcuma longa. Planta Med. 1991; 57:1–7.14. Weisberg SP, Leibel R, Tortoriello DV. Dietary curcumin significantly improves obesity-associated inflammation and diabetes in mouse models of diabesity. Endocrinology. 2008; 149:3549–3558.
Article15. Shao W, Yu Z, Chiang Y, Yang Y, Chai T, Foltz W, Lu H, Fantus IG, Jin T. Curcumin prevents high-fat diet induced insulin resistance and obesity via attenuating lipogenesis in liver and inflammatory pathway in adipocytes. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e28784.16. Ejaz A, Wu D, Kwan P, Meydani M. Curcumin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and angiogenesis and obesity in C57/BL mice. J Nutr. 2009; 139:919–925.
Article17. Ciardi C, Jenny M, Tschoner A, Ueberall F, Patsch J, Pedrini M, Ebenbichler C, Fuchs D. Food additives such as sodium sulphite, sodium benzoate and curcumin inhibit leptin release in lipopolysaccharide-treated murine adipocytes in vitro. Br J Nutr. 2012; 107:826–833.
Article18. Ling J, Wei B, Lv G, Ji H, Li S. Anti-hyperlipidaemic and antioxidant effects of turmeric oil in hyperlipidaemic rats. Food Chem. 2012; 130:229–235.
Article19. Dixit VP, Jain P, Joshi SC. Hypolipidaemic effects of Curcuma longa L and Nardostachys jatamansi, DC in triton-induced hyperlipidaemic rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1988; 32:299–304.20. Kim MS, Chun SS, Kim SH, Choi JH. Effect of tumeric (Curcuma longa) on bile acid and UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity in rats fed a high-fat and -cholesterol diet. J Life Sci. 2012; 22:1064–1070.
Article21. Kim TH, Son YK, Hwang KH, Kim MH. Effects of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi and turmeric extract supplementation on serum lipid parameters in hypercholesterolemic diet or P-407-induced hyperlipidemic rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2008; 37:708–713.
Article22. Hong JH, Hwang EY, Kim HJ, Jeong YJ, Lee IS. Artemisia capillaris inhibits lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and obesity in C57BL/6J mice fed a high fat diet. J Med Food. 2009; 12:736–745.
Article23. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976; 72:248–254.
Article24. Carmichael J, DEGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Mitchell JB. Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of radiosensitivity. Cancer Res. 1987; 47:943–946.25. Navarro-Escobar E, González-Rodríguez MP, Ferrer-Luque CM. Cytotoxic effects of two acid solutions and 2.5% sodium hypochlorite used in endodontic therapy. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010; 15:e90–e94.
Article26. Sreel RG, Torrie JH. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. New York: Mcgrow Hill;1980.27. Green H, Kehinde O. Sublines of mouse 3T3 cells that accumulate lipid. Cell. 1974; 1:113–116.
Article28. Jang YS, Jeong JM. Effects of phyto-extract mixture on adiposity and serum lipid levels in obese mice induced by high fat diet. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2010; 39:1439–1445.
Article29. Apfelbaum M, Vague P, Ziegler O. IIanotin C, Thomas F, Leutenegger E. Long-term maintenance of weight loss after a very low calorie diet: efficacy and tolerability of sibutramine. Am J Med. 1999; 106:179–184.
Article30. Elahi RK. Preventive effects of turmeric (Curcuma longa Linn.) powder on hepatic steatosis in the rats fed with high fat diet. Life Sci J. 2012; 9:5462–5468.31. Sengupta K, Golakoti T, Chirravuri VR, Marasetti AK. An herbal formula LI85008F inhibits lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Nutr Sci. 2011; 2:809–817.
Article32. Frayn KN, Coppack SW, Fielding BA, Humphreys SM. Coordinated regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase and lipoprotein lipase in human adipose tissue in vivo: implications for the control of fat storage and fat mobilization. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1995; 35:163–178.
Article33. Hsu CL, Yen GC. Phenolic compounds: evidence for inhibitory effects against obesity and their underlying molecular signaling mechanisms. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008; 52:53–61.
Article34. Zimmermann R, Strauss JG, Haemmerle G, Schoiswohl G, Birner-Gruenberger R, Riederer M, Lass A, Neuberger G, Eisenhaber F, Hermetter A, Zechner R. Fat mobilization in adipose tissue is promoted by adipose triglyceride lipase. Science. 2004; 306:1383–1386.
Article35. Lee J, Jun W. Methanolic extract of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) enhanced the lipolysis by up-regulation of lipase mRNA expression in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2009; 18:1500–1504.36. Caro JF, Sinha MK, Kolaczynski JW, Zhang PL, Considine RV. Leptin: the tale of an obesity gene. Diabetes. 1996; 45:1455–1462.
Article37. Sari A. The relationship between leptin and fatty acid. J Mol Biomark Diagn. 2013; 4:1–4.
Article38. Kim CY, Le TT, Chen C, Cheng JX, Kim KH. Curcumin inhibits adipocyte differentiation through modulation of mitotic clonal expansion. J Nutr Biochem. 2011; 22:910–920.
Article39. Burdakov D, González JA. Physiological functions of glucose-inhibited neurones. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009; 195:71–78.
Article40. Kim J, Park J, Jun W. Anti-obesity effect of ethyl acetate fraction from 50% ethanol extract of fermented Curcuma longa L. in 3T3-L1 cells. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2014; 43:1681–1687.
Article41. Ahn J, Lee H, Kim S, Ha T. Curcumin-induced suppression of adipogenic differentiation is accompanied by activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010; 298:C1510–C1516.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Signaling Role of Adipocyte Leptin in Prostate Cell Proliferation Induced by Trichomonas vaginalis
- The Effect of Leptin Level Fluctuations by a Repeated Fasting/Refeeding on the Leptin Sensitivity in OLETF Rats
- Role of TRPV4 Channel in Human White Adipocytes Metabolic Activity
- The Effects of Ginseng Saponin-Re, Rc and Green Tea Catechine; ECGC (Epigallocatechin Gallate) on Leptin, Hormone Sensitive Lipase and Resistin mRNA Expressions in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- Identification and cDNA Cloning of the Leptin Receptor Long from ( OB-Rb ) from Rat Splenocytes