J Korean Soc Transplant.
2018 Dec;32(4):92-103. 10.4285/jkstn.2018.32.4.92.
Proposal of a Selective Prophylaxis Strategy Based on Risk Factors to Prevent Early and Late Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia after Renal Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwhamd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2430589
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2018.32.4.92
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Currently, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is used for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) prophylaxis, but it is associated with frequent adverse effects. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of the current protocol and proposes an individualized risk-based prophylaxis protocol.
METHODS
The PJP incidence and risk factors during the first 6 months (early PJP) and afterwards (late PJP) was assessed in renal transplant recipients with (prophylaxis group) and without (no-prophylaxis group) 6-month PJP prophylaxis.
RESULTS
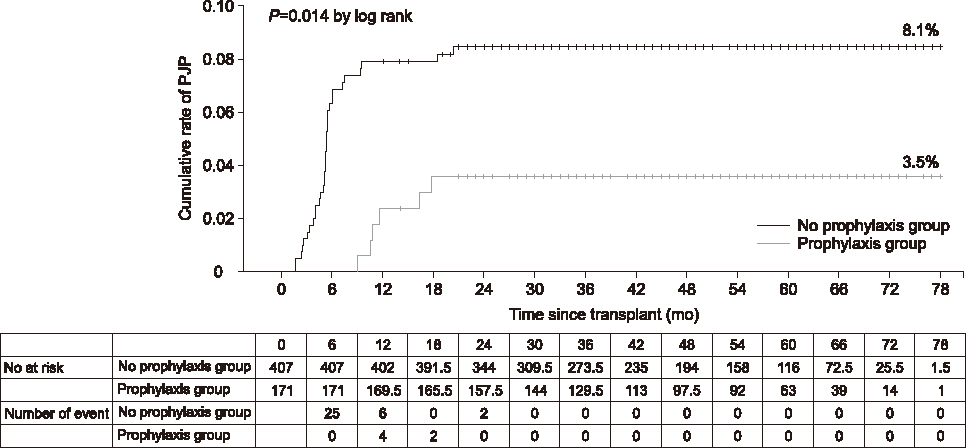
In 578 patients, there were 39 cases of PJP during a median follow-up of 51 months. Renal adverse events were encountered frequently during trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis, leading to premature discontinuation. Patients without the prophylaxis had a significantly higher incidence of early PJP (n=27, 6.6%) compared to patients with the prophylaxis (n=0). The incidence of late PJP was 2.2%, without between-group differences. The factors associated with early PJP were preoperative desensitization and acute rejection within 1 month, whereas late PJP was associated with age, deceased donor transplant, and acute rejection requiring antithymocyte globulin treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the simulation results of several risk-based scenarios, the authors recommend universal prophylaxis up to 6 months post-transplant and extended selective prophylaxis in patients aged ≥57 years and those with a transplant from deceased donors.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thomas CF Jr, Limper AH. Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2487–2498.
Article2. Iriart X, Bouar ML, Kamar N, Berry A. Pneumocystis pneumonia in solid-organ transplant recipients. J Fungi (Basel). 2015; 1:293–331.
Article3. Martin SI, Fishman JA. AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Pneumocystis pneumonia in solid organ transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13:Suppl 4. 272–279.4. EBPG Expert Group on Renal Transplantation. European best practice guidelines for renal transplantation. Section IV: long-term management of the transplant recipient. IV.7.1 Late infections. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002; 17:Suppl 4. 36–39.5. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2009; 9:Suppl 3. S1–S155.6. Stern A, Green H, Paul M, Vidal L, Leibovici L. Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in non-HIV immunocompromised patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; 10:CD005590.7. Mitsides N, Greenan K, Green D, Middleton R, Lamerton E, Allen J, et al. Complications and outcomes of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole as chemoprophylaxis for pneumocystis pneumonia in renal transplant recipients. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014; 19:157–163.
Article8. Iriart X, Challan Belval T, Fillaux J, Esposito L, Lavergne RA, Cardeau-Desangles I, et al. Risk factors of Pneumocystis pneumonia in solid organ recipients in the era of the common use of posttransplantation prophylaxis. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15:190–199.
Article9. Yiannakis EP, Boswell TC. Systematic review of outbreaks of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: evidence that P. jirovecii is a transmissible organism and the implications for healthcare infection control. J Hosp Infect. 2016; 93:1–8.
Article10. Goto N, Takahashi-Nakazato A, Futamura K, Okada M, Yamamoto T, Tsujita M, et al. Lifelong prophylaxis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for prevention of outbreak of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Direct. 2017; 3:e151.
Article11. de Boer MG, Kroon FP, le Cessie S, de Fijter JW, van Dissel JT. Risk factors for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients and appraisal of strategies for selective use of chemoprophylaxis. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011; 13:559–569.
Article12. Fishman JA. Prevention of infection caused by Pneumocystis carinii in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 33:1397–1405.
Article13. Urbancic KF, Ierino F, Phillips E, Mount PF, Mahony A, Trubiano JA. Taking the challenge: a protocolized approach to optimize Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis in renal transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2018; 18:462–466.
Article14. Delanaye P, Mariat C, Cavalier E, Maillard N, Krzesinski JM, White CA. Trimethoprim, creatinine and creatininebased equations. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011; 119:c187–c193.
Article15. Fraser TN, Avellaneda AA, Graviss EA, Musher DM. Acute kidney injury associated with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:1271–1277.
Article16. Alexandre K, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Versini M, Sailler L, Benhamou Y. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients treated with rituximab for systemic diseases: report of 11 cases and review of the literature. Eur J Intern Med. 2018; 50:e23–e24.
Article17. Opata MM, Hollifield ML, Lund FE, Randall TD, Dunn R, Garvy BA, et al. B lymphocytes are required during the early priming of CD4+ T cells for clearance of pneumocystis infection in mice. J Immunol. 2015; 195:611–620.
Article18. Lee SH, Huh KH, Joo DJ, Kim MS, Kim SI, Lee J, et al. Risk factors for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) in kidney transplantation recipients. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:1571.
Article19. Faure E, Lionet A, Kipnis E, Noel C, Hazzan M. Risk factors for Pneumocystis pneumonia after the first 6 months following renal transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017; 19:e12735.20. Schurmann M, Schurmann D, Schindler R, Meisel C, Liman P, Kruse J, et al. Impaired thymic function and CD4+ T lymphopenia, but not mannose-binding lectin deficiency, are risk factors for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients. Transpl Immunol. 2013; 28:159–163.
Article21. Haynes L, Maue AC. Effects of aging on T cell function. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009; 21:414–417.
Article22. Wang EH, Partovi N, Levy RD, Shapiro RJ, Yoshida EM, Greanya ED. Pneumocystis pneumonia in solid organ transplant recipients: not yet an infection of the past. Transpl Infect Dis. 2012; 14:519–525.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Late Onset Infection of Pneumocystis jirovecii Infection in a Renal Transplant Recipient
- Risk factors for pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in liver transplantation recipients
- Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in pediatric patients: an analysis of 15 confirmed consecutive cases during 14 years
- Two Cases of Pneumocystis Pneumonia after Liver Transplantation Presenting with Different Clinical Manifestations
- Pneumonia Caused by Fungus, Pneumocystis Jirovecii and Cytomegalovirus Coinfection in Patient with Renal Transplantation: A Case Report