J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2018 Dec;42(4):224-228. 10.11149/jkaoh.2018.42.4.224.
Ethanol changes atpB gene expression and proton permeability in Streptococcus mutans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. jsokang@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive & Community Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3BK21 PLUS Project, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2430546
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2018.42.4.224
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
As a first step to study the anticaries effect of ethanol alone, we investigated the effects of ethanol on the expression levels of the atpB gene and proton permeability of Streptococcus mutans in suspension cultures.
METHODS
S. mutans UA159 was grown in brain heart infusion medium at either pH 4.8 or 6.8. The total extracted RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a Superscriptâ„¢ First-Strand Synthesis System. The resulting cDNA and negative controls were amplified by ABI PRISM 7700 real-time PCR system with SYBR Green PCR Master Mix. For proton flux assay, bacterial suspensions were titrated to pH 4.6 with 0.5 M HCl, and then additional 0.5 M HCl was added to decrease the pH values by approximately 0.4 units. The subsequent increase in pH was monitored using a glass electrode. Ten percent (v/v) butanol was added to the suspensions at 80 min to disrupt the cell membrane.
RESULTS
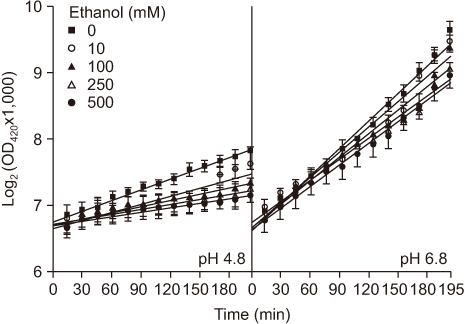
In a concentration-dependent manner, ethanol alone not only decreased the growth rate of S. mutans and the expression of the atpB gene but also increased the proton permeability at both pH 4.8 and 6.8.
CONCLUSIONS
These findings suggest that ethanol has the potential for an anticaries ingredient. We believe that ethanol may be used together with fluoride and/or other cariostatic agents in order to develop better anticaries toothpastes and/or mouthrinses.
MeSH Terms
-
Brain
Cariostatic Agents
Cell Membrane
DNA, Complementary
Electrodes
Ethanol*
Fluorides
Gene Expression*
Glass
Heart
Hydrogen-Ion Concentration
Permeability*
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Protons*
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA
Streptococcus mutans*
Streptococcus*
Suspensions
Toothpastes
Cariostatic Agents
DNA, Complementary
Ethanol
Fluorides
Protons
RNA
Suspensions
Toothpastes
Figure
Reference
-
1. Loesche WJ. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986; 50(4):353–380.2. Baker JL, Abranches J, Faustoferri RC, Hubbard CJ, Lemos JA, Courtney MA, et al. Transcriptional profile of glucose-shocked and acid-adapted strains of Streptococcus mutans. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2015; 30(6):496–517.
Article3. Baker JL, Faustoferri RC, Quivey RG. Acid-adaptive mechanisms of Streptococcus mutans-the more we know, the more we don't. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2017; 32(2):107–117.
Article4. Quivey RG, Grayhack EJ, Faustoferri RC, Hubbard CJ, Baldeck JD, Wolf AS, et al. Functional profiling in Streptococcus mutans: construction and examination of a genomic collection of gene deletion mutants. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2015; 30(6):474–495.
Article5. Belli WA, Marquis RE. Adaptation of Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus hirae to acid stress in conuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991; 57(4):1134–1138.
Article6. Bender GR, Sutton SV, Marquis RE. Acid tolerance, proton permeabilities, and membrane ATPases of oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1986; 53(2):331–338.
Article7. Hamilton IR, Buckley ND. Adaptation by Streptococcus mutans to acid tolerance. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1991; 6(2):65–71.
Article8. Lemos JA, Abranches J, Burne RA. Responses of cariogenic streptococci to environmental stresses. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2005; 7(1):95–108.9. Quivey RG Jr, Kuhnert WL, Hahn K. Adaptation of oral streptococci to low pH. Adv Microb Physiol. 2000; 42:239–274.
Article10. Hamilton IR, St Martin EJ. Evidence for the involvement of proton motive force in the transport of glucose by a mutant of Streptococcus mutans strain DR0001 defective in glucose-phosphoenopyruvate phosphotransferase activity. Infect Immun. 1982; 36(2):567–575.
Article11. Seydlová G, Halada P, Fišer R, Toman O, Ulrych A, Svobodová J. DnaK and GroEL chaperones are recruited to the Bacillus subtilis membrane after short-term ethanol stress. J Appl Microbiol. 2012; 112(4):765–774.
Article12. Ban SH, Kim JE, Pandit S, Jeon JG. Influences of Dryopteris crassirhizoma extract on the viability, growth and virulence properties of Streptococcus mutans. Molecules. 2012; 17(8):9231–9244.
Article13. Petrackova D, Vecer J, Svobodova J, Herman P. Long-term adaptation of Bacillus subtilis 168 to extreme pH affects chemical and physical properties of the cellular membrane. J Membr Biol. 2010; 233(1-3):73–83.
Article14. Phan TN, Buckner T, Sheng J, Baldeck JD, Marquis RE. Physiologic actions of zinc related to inhibition of acid and alkali production by oral streptococci in suspensions and biofilms. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2004; 19(1):31–38.
Article15. Hwang G, Liu Y, Kim D, Sun V, Aviles-Reyes A, Kajfasz JK, et al. Simultaneous spatiotemporal mapping of in situ pH and bacterial activity within an intact 3D microcolony structure. Sci Rep. 2016; 09. 08. DOI: 10.1038/srep32841. [Epub].
Article16. Kuhnert WL, Zheng G, Faustoferri RC, Quivey RG. The F-ATPase operon promoter of Streptococcus mutans is transcriptionally regulated in response to external pH. J Bacteriol. 2004; 186(24):8524–8528.
Article17. Gong Y, Tian XL, Sutherland T, Sisson G, Mai J, Ling J, et al. Global transcriptional analysis of acid-inducible genes in Streptococcus mutans: multiple two-component systems involved in acid adaptation. Microbiology. 2009; 155:3322–3332.
Article18. Lee SA, Jung SI, Kim JB, Kang JS. The pH-dependent effects of combining ethanol with fluoride on proton permeability in Streptococcus mutans. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2016; 40(4):255–260.
Article19. Gurtovenko AA, Anwar J. Interaction of ethanol with biological membranes: the formation of non-bilayer structures within the membrane interior and their significance. J Phys Chem B. 2009; 113(7):1983–1992.
Article20. Cho CM, Jung SI, Kim MS, Lee SA, Kang JS. pH stress alters cytoplasmic membrane fluidity and atpB gene expression in Streptococcus mutans. J Life Sci. 2017; 27(1):15–22.
Article21. FDI commission. Mouthrinses and dental caries. Int Dent J. 2002; 52(5):337–345.22. Moorer WR. Antiviral activity of alcohol for surface disinfection. Int J Dent Hyg. 2003; 1(3):138–142.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The pH-dependent effects of combining ethanol with fluoride on proton permeability in Streptococcus mutans
- Effect of the Ethanol Extract of Propolis on Formation of Streptococcus mutans Biofilm
- Inhibitory effect of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on the biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans
- The Ethanol Extract of Croton Seed Inhibits the Oral Pathogen, Streptococcus mutans
- Virulence genes of Streptococcus mutans and dental caries