J Rheum Dis.
2018 Oct;25(4):239-247. 10.4078/jrd.2018.25.4.239.
Antiphospholipid Antibody Positivity and the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea. sungyk@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2429710
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2018.25.4.239
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To identify the prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and determine the relationship between aPL and the clinical outcomes.
METHODS
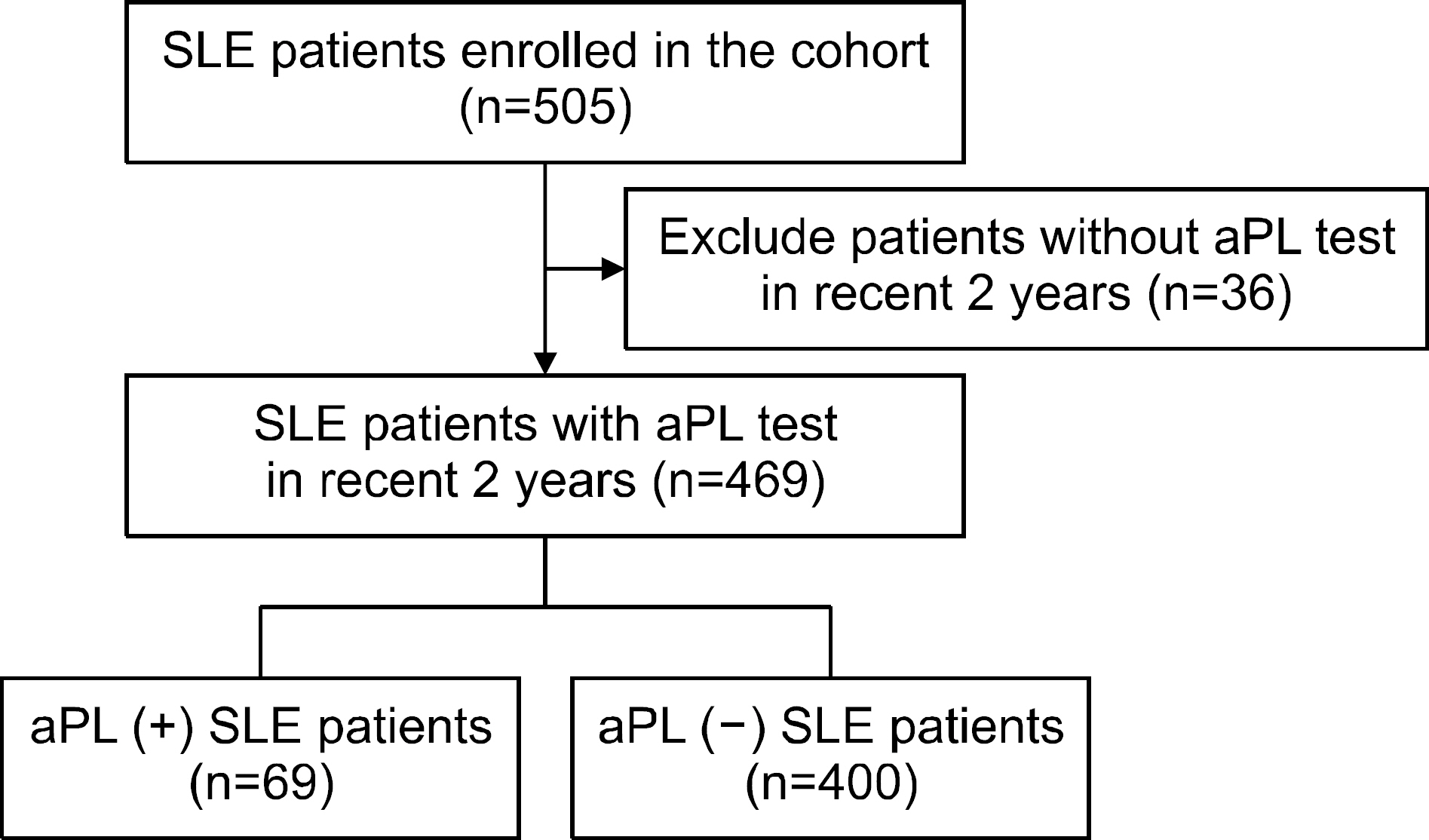
SLE patients with aPL test results within 2 years of enrollment were selected from Korean lupus network study. They were classified into two groups: aPL (+) group, patients positive for at least one aPL, and aPL (−) group, patients without an aPL. The clinical characteristics of the two groups were compared and the role of aPL in the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in SLE patients was examined.
RESULTS
Among the 469 SLE patients, 69 (14.7%) had at least one aPL. The prevalence of cerebrovascular disease and CKD was higher in the aPL (+) group than in the aPL (−) group (10.1% vs. 1.8% and 13.8% vs. 5.1%, p < 0.05). Multivariable regression analysis showed that the aPL positivity (odds ratio=3.93, 95% confidence interval=1.48∼10.47) was associated with the risk of CKD after adjusting for age, disease duration, and lupus nephritis history.
CONCLUSION
Among the 469 SLE patients, 69 (14.7%) had at least one aPL. The prevalence of cerebrovascular disease and CKD was higher in the aPL (+) group than in the aPL (−) group (10.1% vs. 1.8% and 13.8% vs. 5.1%, p < 0.05). Multivariable regression analysis showed that the aPL positivity (odds ratio=3.93, 95% confidence interval=1.48∼10.47) was associated with the risk of CKD after adjusting for age, disease duration, and lupus nephritis history.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Management of Women with Antiphospholipid Antibodies or Antiphospholipid Syndrome during Pregnancy
Eunyoung Emily Lee, Jong Kwan Jun, Eun Bong Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(4):e24. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e24.
Reference
-
1. George D, Erkan D. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2009; 52:115–25.
Article2. Petri M. Epidemiology of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2000; 15:145–51.
Article3. Cervera R, Serrano R, Pons-Estel GJ, Ceberio-Hualde L, Shoenfeld Y, de Ramón E, et al. Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74:1011–8.
Article4. Mok CC, Tang SS, To CH, Petri M. Incidence and risk factors of thromboembolism in systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of three ethnic groups. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:2774–82.
Article5. Pons-Estel GJ, Andreoli L, Scanzi F, Cervera R, Tincani A. The antiphospholipid syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2017; 76:10–20.
Article6. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Egurbide MV, Ugalde J, Aguirre C. High impact of antiphospholipid syndrome on irreversible organ damage and survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:77–82.
Article7. Broder A, Mowrey WB, Kim M, Murakhovskaya I, Billett H, Neugarten J, et al. Association between antiphospholipid antibodies and all-cause mortality among end-stage renal disease patients with and without SLE: a retrospective cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016; 55:817–25.
Article8. Yelnik CM, Urbanski G, Drumez E, Sobanski V, Maillard H, Lanteri A, et al. Persistent triple antiphospholipid antibody positivity as a strong risk factor of first thrombosis, in a long-term follow-up study of patients without history of thrombosis or obstetrical morbidity. Lupus. 2017; 26:163–9.
Article9. Horbach DA, van Oort E, Donders RC, Derksen RH, de Groot PG. Lupus anticoagulant is the strongest risk factor for both venous and arterial thrombosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Comparison between different assays for the detection of antiphospholipid antibodies. Thromb Haemost. 1996; 76:916–24.10. Wahl DG, Guillemin F, de Maistre E, Perret C, Lecompte T, Thibaut G. Risk for venous thrombosis related to anti-phospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus– a meta-analysis. Lupus. 1997; 6:467–73.11. Empson M, Lassere M, Craig J, Scott J. Prevention of recurrent miscarriage for women with antiphospholipid anti-body or lupus anticoagulant. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; (2):CD002859.
Article12. Daugas E, Nochy D, Huong DL, Duhaut P, Beaufils H, Caudwell V, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:42–52.
Article13. Tektonidou MG, Sotsiou F, Nakopoulou L, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Moutsopoulos HM. Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid antibodies: prevalence, clinical associations, and long-term outcome. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:2569–79.
Article14. Gerhardsson J, Sundelin B, Zickert A, Padyukov L, Svenungsson E, Gunnarsson I. Histological antiphospholipid-associated nephropathy versus lupus nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: an observational cross-sectional study with longitudinal follow-up. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015; 17:109.
Article15. Zheng H, Chen Y, Ao W, Shen Y, Chen XW, Dai M, et al. Antiphospholipid antibody profiles in lupus nephritis with glomerular microthrombosis: a prospective study of 124 cases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11:R93.
Article16. Moroni G, Ventura D, Riva P, Panzeri P, Quaglini S, Banfi G, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies are associated with an increased risk for chronic renal insufficiency in patients with lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004; 43:28–36.
Article17. Parodis I, Arnaud L, Gerhardsson J, Zickert A, Sundelin B, Malmström V, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies in lupus nephritis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0158076.
Article18. Mehrani T, Petri M. IgM anti-β 2 glycoprotein I is protective against lupus nephritis and renal damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2011; 38:450–3.19. Frampton G, Hicks J, Cameron JS. Significance of anti-phospholipid antibodies in patients with lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1991; 39:1225–31.
Article20. Costenbader KH, Desai A, Alarcón GS, Hiraki LT, Shaykevich T, Brookhart MA, et al. Trends in the incidence, demographics, and outcomes of end-stage renal disease due to lupus nephritis in the US from 1995 to 2006. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:1681–8.
Article21. Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite anti-phospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4:295–306.
Article22. Lee JW, Park DJ, Kang JH, Choi SE, Yim YR, Kim JE, et al. The rate of and risk factors for frequent hospitalization in systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the Korean lupus network registry. Lupus. 2016; 25:1412–9.
Article23. Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40:1725.
Article24. Weening JJ, D'Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004; 65:521–30.
Article25. Maroz N, Segal MS. Lupus nephritis and end-stage kidney disease. Am J Med Sci. 2013; 346:319–23.
Article26. Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999; 130:461–70.27. Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, Kausz AT, Levin A, Steffes MW, et al. National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 139:137–47.
Article28. Stevens PE, Levin A. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2013; 158:825–30.
Article29. Skare T, Borba EA, Utiyama SR, Nisihara R. Lymphocytope-nia is associated with anti-Beta-2 glycoprotein-1 in patients with 220 systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Reumatol Port. 2016; 41:220–5.30. Taraborelli M, Leuenberger L, Lazzaroni MG, Martinazzi N, Zhang W, Franceschini F, et al. The contribution of anti-phospholipid antibodies to organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2016; 25:1365–8.
Article31. Sarabi ZS, Sahebari M, Rezaie AE, Norouzi MT, Hashemzadeh K, Mirfeizi Z. The relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus activity and persistent positive antiphospholipid antibodies. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018; 14:145–52.
Article32. Alarcón-Segovia D, Delezé M, Oria CV, Sánchez-Guerrero J, Gómez-Pacheco L, Cabiedes J, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective analysis of 500 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1989; 68:353–65.33. Buyon JP, Petri MA, Kim MY, Kalunian KC, Grossman J, Hahn BH, et al. The effect of combined estrogen and proges-terone hormone replacement therapy on disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 142:953–62.
Article34. Meroni PL, Borghi MO, Raschi E, Tedesco F. Pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome: understanding the antibodies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7:330–9.
Article35. Gustafsson JT, Gunnarsson I, Källberg H, Pettersson S, Zickert A, Vikerfors A, et al. Cigarette smoking, anti-phospholipid antibodies and vascular events in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74:1537–43.
Article36. Abreu MM, Danowski A, Wahl DG, Amigo MC, Tektonidou M, Pacheco MS, et al. The relevance of “non-criteria” clinical manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome: 14th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies Technical Task Force Report on Antiphospholipid Syndrome Clinical Features. Autoimmun Rev. 2015; 14:401–14.
Article37. Sciascia S, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta M, Roccatello D. Renal involvement in antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014; 10:279–89.
Article38. Ünlü O, Zuily S, Erkan D. The clinical significance of anti-phospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Rheumatol. 2016; 3:75–84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Leg Ulcer with SLE and Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- A patient with chorea associated with hyperthyroidism and primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Secondary AntiphospholipidSyndrome Presenting as Livedo Reticularis
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Abdominal Aorta Thrombosis Associated with Protein C and S Deficiency
- Anticardiolipin Antibody in Graves' Disease