Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2018 Sep;11(3):199-204. 10.21053/ceo.2018.00115.
Effect of Adenotonsillectomy on Attention in Korean Children With Sleep-Disordered Breathing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. doctordk@naver.com
- 2Institute of New Frontier Research, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2429010
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2018.00115
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Pediatric sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a common debilitating disorder that can adversely affect the attention and academic performance of school-age children. Unfortunately, only a few studies have examined the effect of SDB treatment on attention in pediatric populations. Therefore, the aim of this study was to prospectively investigate the effect of SDB treatment on attention in children.
METHODS
This study consecutively enrolled SDB children with adenotonsillar hypertrophy. All subjects underwent standard-of-care treatment (adenotonsillectomy or close observation) and were evaluated using a computerized comprehensive attention test at the initial visit. Comprehensive attention tests consisted of both sustained and divided attention tasks. Each completed task was assigned an attention score, which was based on the number of omission or commission errors. The comprehension attention test was repeated 1 year later.
RESULTS
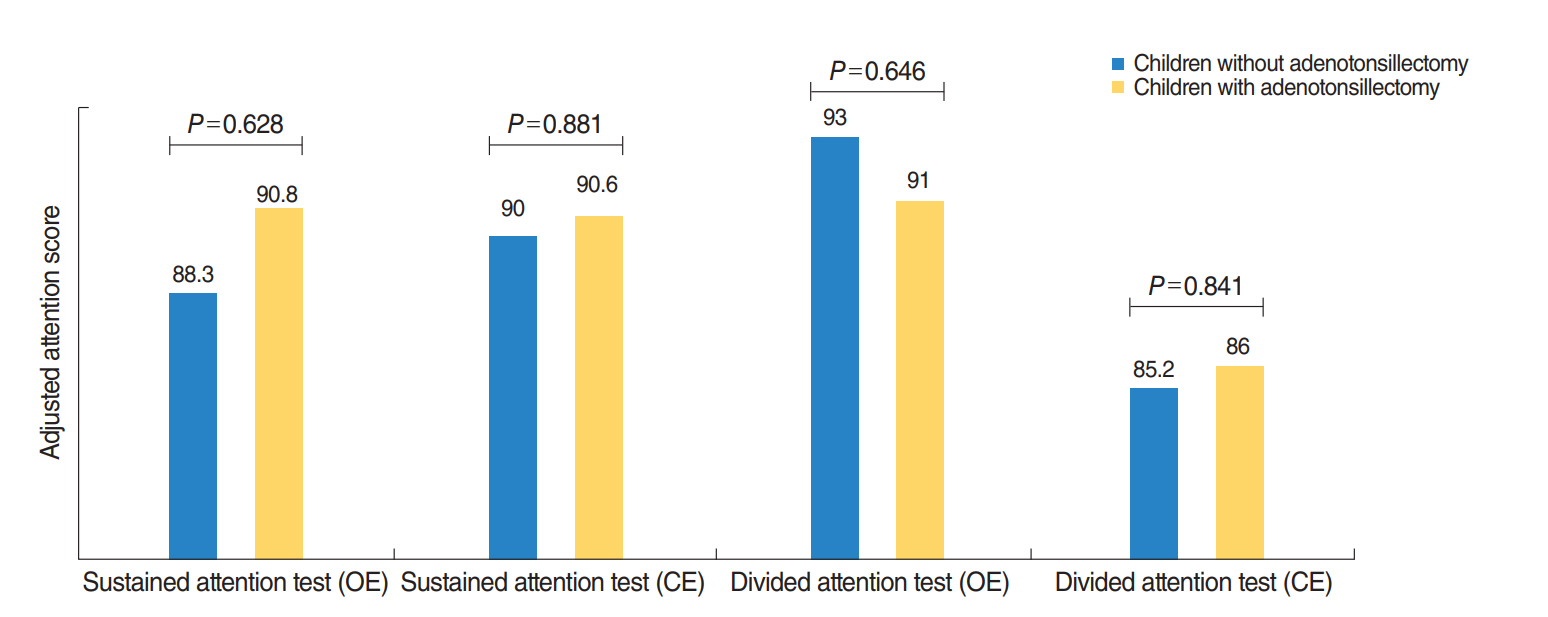
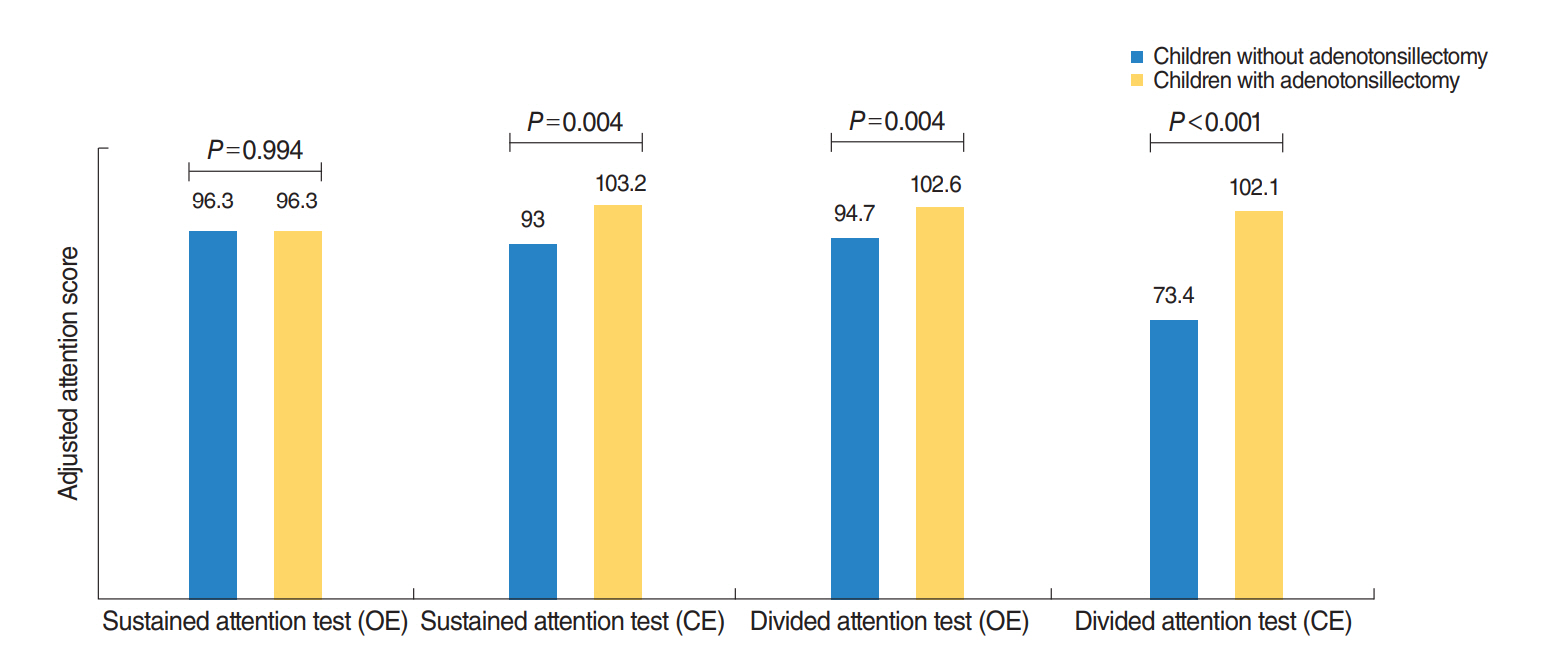
A total of 171 children who underwent adenotonsillectomy and 32 children who did not undergo adenotonsillectomy were included in this study. At baseline, there was no significant difference according to the score of all type comprehension attention tests between children in the adenotonsillectomy group and in the observation group. One year after treatment, children in the adenotonsillectomy group had significantly improved scores in all attention tasks. Children in the observation group had only significant improvement in omission errors on sustained attention tasks. Meanwhile, the attention score based on commission errors of divided attention tasks was significantly worse than at baseline for those.
CONCLUSION
Our study showed that adenotonsillectomy may be helpful in improving attention in children with SDB.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cluster Analysis of Inhalant Allergens in South Korea: A Computational Model of Allergic Sensitization
Dong-Kyu Kim, Young-Sun Park, Kyung-Joon Cha, Daeil Jang, Seungho Ryu, Kyung Rae Kim, Sang-Heon Kim, Ho Joo Yoon, Seok Hyun Cho
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;14(1):93-99. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2019.01921.
Reference
-
1. Rosen CL, Storfer-Isser A, Taylor HG, Kirchner HL, Emancipator JL, Redline S. Increased behavioral morbidity in school-aged children with sleep-disordered breathing. Pediatrics. 2004; Dec. 114(6):1640–8.
Article2. Chervin RD, Archbold KH, Dillon JE, Panahi P, Pituch KJ, Dahl RE, et al. Inattention, hyperactivity, and symptoms of sleep-disordered breathing. Pediatrics. 2002; Mar. 109(3):449–56.
Article3. Lande MB, Hooper SR, Batisky DL, Kupferman JC, Szilagyi PG, Samuels JA, et al. Sleep disordered breathing as measured by SRBD-PSQ and neurocognition in children with hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2015; Apr. 28(4):552–8.
Article4. Galland B, Spruyt K, Dawes P, McDowall PS, Elder D, Schaughency E. Sleep disordered breathing and academic performance: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2015; Oct. 136(4):e934–46.
Article5. Galland BC, Dawes PJ, Tripp EG, Taylor BJ. Changes in behavior and attentional capacity after adenotonsillectomy. Pediatr Res. 2006; May. 59(5):711–6.
Article6. Mitchell RB, Boss EF. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea in obese and normal-weight children: impact of adenotonsillectomy on quality-of-life and behavior. Dev Neuropsychol. 2009; 34(5):650–61.
Article7. Li HY, Huang YS, Chen NH, Fang TJ, Lee LA. Impact of adenotonsillectomy on behavior in children with sleep-disordered breathing. Laryngoscope. 2006; Jul. 116(7):1142–7.
Article8. Friedman M, Ibrahim H, Bass L. Clinical staging for sleep-disordered breathing. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; Jul. 127(1):13–21.
Article9. Kim SY, Lee WH, Rhee CS, Lee CH, Kim JW. Regrowth of the adenoids after coblation adenoidectomy: cephalometric analysis. Laryngoscope. 2013; Oct. 123(10):2567–72.
Article10. Kim DK, Rhee CS, Yun PY, Kim JW. Adenotonsillar hypertrophy as a risk factor of dentofacial abnormality in Korean children. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; Nov. 272(11):3311–6.
Article11. Kim SJ, Lee YJ, Cho SJ, Cho IH, Lim W, Lim W. Relationship between weekend catch-up sleep and poor performance on attention tasks in Korean adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2011; Sep. 165(9):806–12.
Article12. Kim DK, Rhee CS, Han DH, Won TB, Kim DY, Kim JW. Treatment of allergic rhinitis is associated with improved attention performance in children: the Allergic Rhinitis Cohort Study for Kids (ARCO-Kids). PLoS One. 2014; Oct. 9(10):e109145.
Article13. Kim SJ, Lee YJ, Jang JH, Lim W, Cho IH, Cho SJ. The relationship between psychotic-like experiences and attention deficits in adolescents. J Psychiatr Res. 2012; Oct. 46(10):1354–8.
Article14. Gozal D, Pope DW Jr. Snoring during early childhood and academic performance at ages thirteen to fourteen years. Pediatrics. 2001; Jun. 107(6):1394–9.15. Montgomery-Downs HE, Jones VF, Molfese VJ, Gozal D. Snoring in preschoolers: associations with sleepiness, ethnicity, and learning. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2003; Oct. 42(8):719–26.
Article16. Urschitz MS, Guenther A, Eggebrecht E, Wolff J, Urschitz-Duprat PM, Schlaud M, et al. Snoring, intermittent hypoxia and academic performance in primary school children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; Aug. 168(4):464–8.
Article17. Aljadeff G, Gozal D, Bailey-Wahl SL, Burrell B, Keens TG, Ward SL. Effects of overnight supplemental oxygen in obstructive sleep apnea in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; Jan. 153(1):51–5.
Article18. Gozal D, Kheirandish-Gozal L. Sleep apnea in children: treatment considerations. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2006; 7 Suppl 1:S58–61.19. Kennedy JD, Blunden S, Hirte C, Parsons DW, Martin AJ, Crowe E, et al. Reduced neurocognition in children who snore. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004; Apr. 37(4):330–7.
Article20. Meltzer EO, Blaiss MS, Derebery MJ, Mahr TA, Gordon BR, Sheth KK, et al. Burden of allergic rhinitis: results from the pediatric allergies in America survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; Sep. 124(3 Suppl):S43–70.
Article21. Chay OM, Goh A, Abisheganaden J, Tang J, Lim WH, Chan YH, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in obese Singapore children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000; Apr. 29(4):284–90.
Article22. Verhulst SL, Schrauwen N, Haentjens D, Suys B, Rooman RP, Van Gaal L, et al. Sleep-disordered breathing in overweight and obese children and adolescents: prevalence, characteristics and the role of fat distribution. Arch Dis Child. 2007; Mar. 92(3):205–8.
Article23. Barkley RA. Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull. 1997; Jan. 121(1):65–94.
Article24. Stins JF, Tollenaar MS, Slaats-Willemse DI, Buitelaar JK, Swaab-Barneveld H, Verhulst FC, et al. Sustained attention and executive functioning performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Neuropsychol. 2005; Jun. 11(3):285–94.
Article25. Miller J. Divided attention: evidence for coactivation with redundant signals. Cogn Psychol. 1982; Apr. 14(2):247–79.
Article26. Corbetta M, Miezin FM, Dobmeyer S, Shulman GL, Petersen SE. Selective and divided attention during visual discriminations of shape, color, and speed: functional anatomy by positron emission tomography. J Neurosci. 1991; Aug. 11(8):2383–402.
Article27. Taylor HG, Bowen SR, Beebe DW, Hodges E, Amin R, Arens R, et al. Cognitive effects of adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea. Pediatrics. 2016; Aug. 138(2):pii: e20154458.
Article28. Abreu CB, Fuchs SC, Pascoto GR, Weber R, Guedes MC, Pignatari SS, et al. Effect of adenotonsillectomy on visual attention tests among children with sleep-disordered breathing: a controlled prospective cohort study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2013; Dec. 38(6):487–93.
Article29. Kohler MJ, Lushington K, van den Heuvel CJ, Martin J, Pamula Y, Kennedy D. Adenotonsillectomy and neurocognitive deficits in children with sleep disordered breathing. PLoS One. 2009; Oct. 4(10):e7343.
Article30. Brouillette RT. Adenotonsillectomy in childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome improves polysomnographic measures of breathing and sleep, but not attention and executive function. J Pediatr. 2013; Nov. 163(5):1530–1.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Adenotonsillectomy on Inattention and Hyperactivity in Children with Sleep Disordered Breathing
- Effect of Adenotonsillectomy on Inattention and Hyperactivity in Children with Sleep Disordered Breathing
- Nasopharyngeal Width and Its Association With Sleep-Disordered Breathing Symptoms in Children
- Sleep-disordered breathing in children
- Allergic Rhinitis and Sleep-disordered Breathing