Yonsei Med J.
2005 Dec;46(6):827-834.
Expression of Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein in Hepatocytes Does Not Modulate Proliferation or Apoptosis of CD8+ T Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1The David H Smith Center for Vaccine Biology and Immunology, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 14642, USA.
Abstract
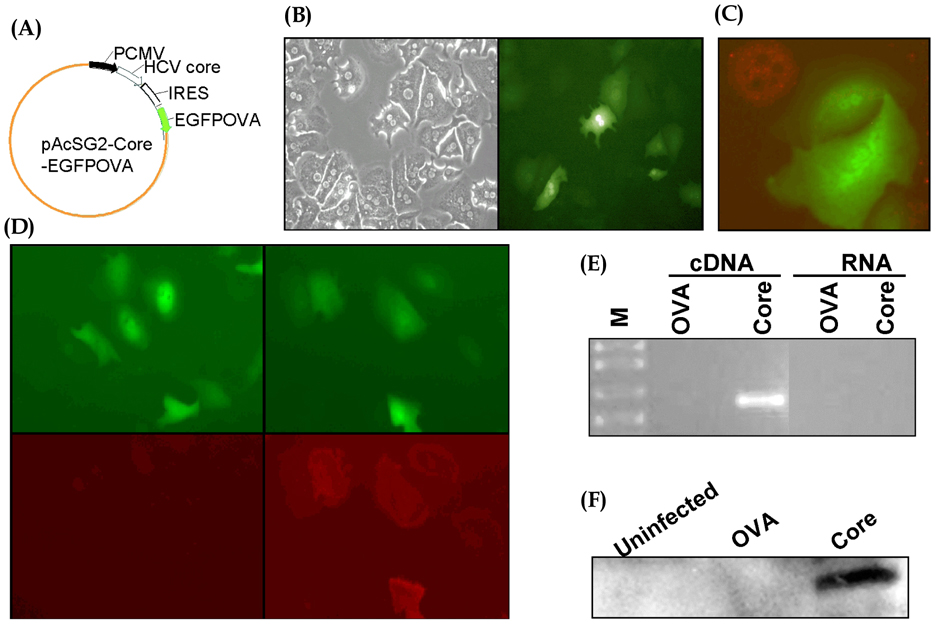
- Hepatocytes are the primary targets of the hepatitis C virus (HCV). While immunosuppressive roles of HCV core protein have been found in several studies, it remains uncertain whether core protein expressed in hepatocytes rather than in immune cells affects the CD8+ T cell response. In order to transduce genes selectively into hepatocytes, we developed a baculoviral vector system that enabled primary hepatocytes to express a target epitope for CD8+ T cells, derived from ovalbumin (OVA), with or without HCV core protein. Culture of OVA-specific CD8+ T cells with hepatocytes infected with these baculoviral vectors revealed that core protein has no effect on proliferation or apoptosis of CD8+ T cells. Our results suggest that HCV core protein does not exert its suppressive role on the CD8+ T cell immune response through expression in hepatocytes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mattsson L, Sonnerborg A, Weiland O. Outcome of acute symptomatic non-A, non-B hepatitis: a 13-year follow-up study of hepatitis C virus markers. Liver. 1993. 13:274–278.2. Lechner F, Gruener NH, Urbani S, Uggeri J, Santantonio T, Kammer AR, et al. CD8+ T lymphocyte responses are induced during acute hepatitis C virus infection but are not sustained. Eur J Immunol. 2000. 30:2479–2487.3. Lechner F, Wong DK, Dunbar PR, Chapman R, Chung RT, Dohrenwend P, et al. Analysis of successful immune responses in persons infected with hepatitis C virus. J Exp Med. 2000. 191:1499–1512.4. Cooper S, Erickson AL, Adams EJ, Kansopon J, Weiner AJ, Chien DY, et al. Analysis of a successful immune response against hepatitis C virus. Immunity. 1999. 10:439–449.5. Simmonds P. Viral heterogeneity of the hepatitis C virus. J Hepatol. 1999. 31:Suppl 1. 54–60.6. Yeh BI, Kim HW, Kim HS, Lee JY, Lee KH, Lee KM, et al. The prediction of interferon-alpha therapeutic effect by sequence variation of the HCV hypervariable region 1. Yonsei Med J. 1999. 40:430–438.7. Large MK, Kittlesen DJ, Hahn YS. Suppression of host immune response by the core protein of hepatitis C virus: possible implications for hepatitis C virus persistence. J Immunol. 1999. 162:931–938.8. Kittlesen DJ, Chianese-Bullock KA, Yao ZQ, Braciale TJ, Hahn YS. Interaction between complement receptor gC1qR and hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest. 2000. 106:1239–1249.9. Eisen-Vandervelde AL, Waggoner SN, Yao ZQ, Cale EM, Hahn CS, Hahn YS. Hepatitis C virus core selectively suppresses interleukin-12 synthesis in human macrophages by interfering with AP-1 activation. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:43479–43486.10. Yao ZQ, Eisen-Vandervelde A, Waggoner SN, Cale EM, Hahn YS. Direct binding of hepatitis C virus core to gC1qR on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells leads to impaired activation of Lck and Akt. J Virol. 2004. 78:6409–6419.11. Accapezzato D, Francavilla V, Rawson P, Cerino A, Cividini A, Mondelli MU, et al. Subversion of effector CD8+ T cell differentiation in acute hepatitis C virus infection: the role of the virus. Eur J Immunol. 2004. 34:438–446.12. Soguero C, Joo M, Chianese-Bullock KA, Nguyen DT, Tung K, Hahn YS. Hepatitis C virus core protein leads to immune suppression and liver damage in a transgenic murine model. J Virol. 2002. 76:9345–9354.13. Liu ZX, Nishida H, He JW, Lai MM, Feng N, Dennert G. Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b core protein does not exert immunomodulatory effects on virus-induced cellular immunity. J Virol. 2002. 76:990–997.14. Sun J, Bodola F, Fan X, Irshad H, Soong L, Lemon SM, et al. Hepatitis C virus core and envelope proteins do not suppress the host's ability to clear a hepatic viral infection. J Virol. 2001. 75:11992–11998.15. Hofmann C, Sandig V, Jennings G, Rudolph M, Schlag P, Strauss M. Efficient gene transfer into human hepatocytes by baculovirus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. 92:10099–10103.16. Condreay JP, Witherspoon SM, Clay WC, Kost TA. Transient and stable gene expression in mammalian cells transduced with a recombinant baculovirus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999. 96:127–132.17. Nagelkerke JF, Barto KP, van Berkel TJ. In vivo and in vitro uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein by rat liver endothelial, Kupffer, and parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1983. 258:12221–12227.18. Knolle PA, Germann T, Treichel U, Uhrig A, Schmitt E, Hegenbarth S, et al. Endotoxin down-regulates T cell activation by antigen-presenting liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1999. 162:1401–1407.19. Porgador A, Yewdell JW, Deng Y, Bennink JR, Germain RN. Localization, quantitation, and in situ detection of specific peptide-MHC class I complexes using a monoclonal antibody. Immunity. 1997. 6:715–726.20. Hogquist KA, Jameson SC, Heath WR, Howard JL, Bevan MJ, Carbone FR. T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection. Cell. 1994. 76:17–27.21. Nuti S, Rosa D, Valiante NM, Saletti G, Caratozzolo M, Dellabona P, et al. Dynamics of intra-hepatic lymphocytes in chronic hepatitis C: enrichment for Vα24+ T cells and rapid elimination of effector cells by apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1998. 28:3448–3455.22. Emi K, Nakamura K, Yuh K, Sugyo S, Shijo H, Kuroki M, et al. Magnitude of activity in chronic hepatitis C is influenced by apoptosis of T cells responsible for hepatitis C virus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999. 14:1018–1024.23. Huang L, Soldevila G, Leeker M, Flavell R, Crispe IN. The liver eliminates T cells undergoing antigen-triggered apoptosis in vivo. Immunity. 1994. 1:741–749.24. Belz GT, Altman JD, Doherty PC. Characteristics of virus-specific CD8(+) T cells in the liver during the control and resolution phases of influenza pneumonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:13812–13817.25. Hahn CS, Cho YG, Kang BS, Lester IM, Hahn YS. The HCV core protein acts as a positive regulator of fas-mediated apoptosis in a human lymphoblastoid T cell line. Virology. 2000. 276:127–137.26. Moorman JP, Prayther D, McVay D, Hahn YS, Hahn CS. The C-terminal region of hepatitis C core protein is required for Fas-ligand independent apoptosis in Jurkat cells by facilitating Fas oligomerization. Virology. 2003. 312:320–329.27. Sarobe P, Lasarte JJ, Casares N, Lopez-Diaz de Cerio A, Baixeras E, Labarga P, et al. Abnormal priming of CD4(+) T cells by dendritic cells expressing hepatitis C virus core and E1 proteins. J Virol. 2002. 76:5062–5070.28. Lee CH, Choi YH, Yang SH, Lee CW, Ha SJ, Sung YC. Hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits interleukin 12 and nitric oxide production from activated macrophages. Virology. 2001. 279:271–279.29. Nakamoto Y, Kaneko S, Kobayashi K. Monocyte-dependent cell death of T lymphocyte subsets in chronic hepatitis C. Immunol Lett. 2001. 78:169–174.30. Crispe IN, Dao T, Klugewitz K, Mehal WZ, Metz DP. The liver as a site of T-cell apoptosis: graveyard, or killing field? Immunol Rev. 2000. 174:47–62.31. Mehal WZ, Azzaroli F, Crispe IN. Antigen presentation by liver cells controls intrahepatic T cell trapping, whereas bone marrow-derived cells preferentially promote intrahepatic T cell apoptosis. J Immunol. 2001. 167:667–673.32. Qian S, Wang Z, Lee Y, Chiang Y, Bonham C, Fung J, et al. Hepatocyte-induced apoptosis of activated T cells, a mechanism of liver transplant tolerance, is related to the expression of ICAM-1 and hepatic lectin. Transplant Proc. 2001. 33:226.33. Jin Y, Fuller L, Carreno M, Zucker K, Roth D, Esquenazi V, et al. The immune reactivity role of HCV-induced liver infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatocellular damage. J Clin Immunol. 1997. 17:140–153.34. Horiike N, Onji M, Kumon I, Kanaoka M, Michitaka K, Ohta Y. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on the hepatocyte membrane of patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. Liver. 1993. 13:10–14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein in Hepatocytes Suppresses CD8+ T Cell Activity
- IKKγ Facilitates the Activation of NF-κB by Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein
- Hepatitis B Core Antigen Expression in Hepatocytes Reflects Viral Response to Entecavir in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- Hepatocytes infected with hepatitis C virus change immunological features in the liver microenvironment
- Pro-apoptotic function of hepatitis B virus X protein