Korean J Radiol.
2017 Apr;18(2):279-288. 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.2.279.
No-Touch Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparison of Switching Bipolar and Switching Monopolar Ablation in Ex Vivo Bovine Liver
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 03080, Korea. leejm@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- KMID: 2427940
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2017.18.2.279
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the feasibility, efficiency, and safety of no-touch switching bipolar (SB) and switching monopolar (SM) radiofrequency ablation (RFA) using ex vivo bovine livers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
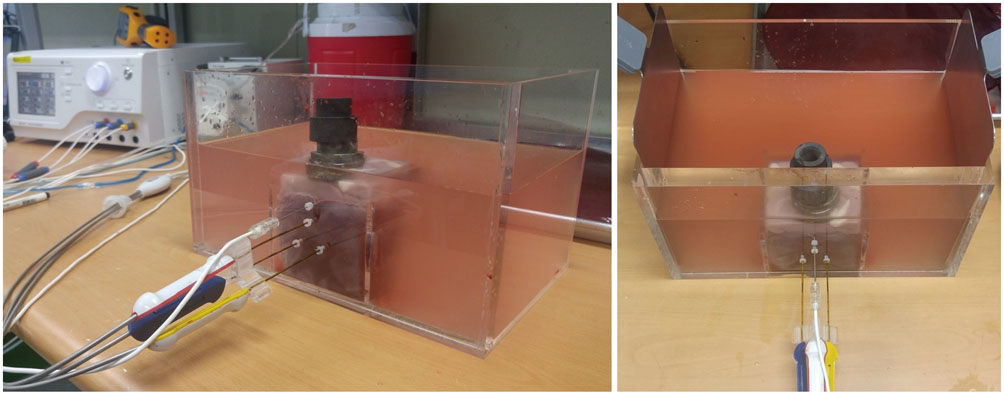
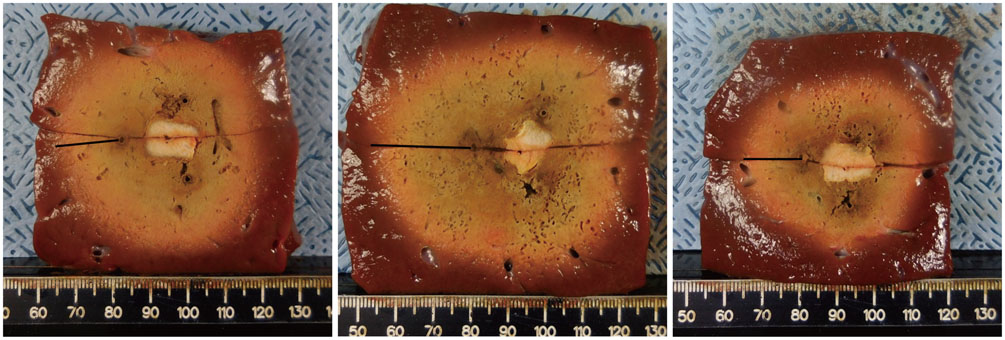
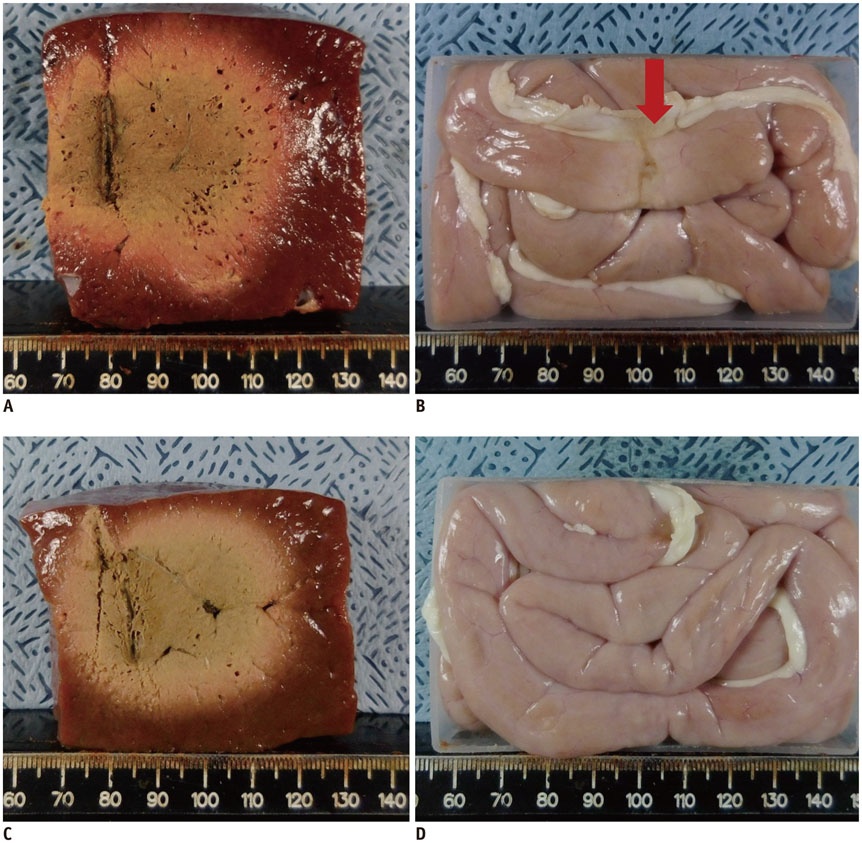
A pork loin cube was inserted as a tumor mimicker in the bovine liver block; RFA was performed using the no-touch technique in the SM (group A1; 10 minutes, n = 10, group A2; 15 minutes, n = 10) and SB (group B; 10 minutes, n = 10) modes. The groups were compared based on the creation of confluent necrosis with sufficient safety margins, the dimensions, and distance between the electrode and ablation zone margin (DEM). To evaluate safety, small bowel loops were placed above the liver surface and 30 additional ablations were performed in the same groups.
RESULTS
Confluent necroses with sufficient safety margins were created in all specimens. SM RFA created significantly larger volumes of ablation compared to SB RFA (all p < 0.001). The DEM of group B was significantly lower than those of groups A1 and A2 (all p < 0.001). Although thermal injury to the small bowel was noted in 90%, 100%, and 30% of the cases in groups A1, A2, and B, respectively, full depth injury was noted only in 60% of group A2 cases.
CONCLUSION
The no-touch RFA technique is feasible in both the SB and SM modes; however, SB RFA appears to be more advantageous compared to SM RFA in the creation of an ablation zone while avoiding the unnecessary creation of an adjacent parenchymal ablation zone or adjacent small bowel injuries.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.2. European Association for the Study of the Liver. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943.3. Salhab M, Canelo R. An overview of evidence-based management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Ther. 2011; 7:463–475.4. Wu YZ, Li B, Wang T, Wang SJ, Zhou YM. Radiofrequency ablation vs hepatic resection for solitary colorectal liver metastasis: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:4143–4148.5. Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y, Guo RP, Liang HH, Zhang YQ, et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2006; 243:321–328.6. Wang JH, Wang CC, Hung CH, Chen CL, Lu SN. Survival comparison between surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for patients in BCLC very early/early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:412–418.7. Ahmed M, Brace CL, Lee FT Jr, Goldberg SN. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology. 2011; 258:351–369.8. Goldberg SN. Science to practice: which approaches to combination interventional oncologic therapy hold the greatest promise of obtaining maximal clinical benefit? Radiology. 2011; 261:667–669.9. Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Haemmerich D, Brace CL, Fine JP, Frey TM, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation creates confluent areas of necrosis: in vivo porcine liver results. Radiology. 2006; 241:116–124.10. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim HC, Kim SH, Kim KW, Joo SM, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation of in vivo porcine liver: comparative studies of consecutive monopolar, switching monopolar versus multipolar modes. Invest Radiol. 2007; 42:676–683.11. Lee ES, Lee JM, Kim KW, Lee IJ, Han JK, Choi BI. Evaluation of the in vivo efficiency and safety of hepatic radiofrequency ablation using a 15-G Octopus® in pig liver. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:194–201.12. Wang X, Hu Y, Ren M, Lu X, Lu G, He S. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinomas compared with radiofrequency ablation alone: a time-to-event meta-analysis. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:93–102.13. Kim JW, Shin SS, Heo SH, Hong JH, Lim HS, Seon HJ, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: how we do it safely and completely. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:1226–1239.14. Hori T, Nagata K, Hasuike S, Onaga M, Motoda M, Moriuchi A, et al. Risk factors for the local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a single session of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:977–981.15. Stigliano R, Marelli L, Yu D, Davies N, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Seeding following percutaneous diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. What is the risk and the outcome? Seeding risk for percutaneous approach of HCC. Cancer Treat Rev. 2007; 33:437–444.16. Imamura J, Tateishi R, Shiina S, Goto E, Sato T, Ohki T, et al. Neoplastic seeding after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:3057–3062.17. Snoeren N, Jansen MC, Rijken AM, van Hillegersberg R, Slooter G, Klaase J, et al. Assessment of viable tumour tissue attached to needle applicators after local ablation of liver tumours. Dig Surg. 2009; 26:56–62.18. Park SI, Kim IJ, Lee SJ, Shin MW, Shin WS, Chung YE, et al. Angled cool-tip electrode for radiofrequency ablation of small superficial subcapsular tumors in the liver: a feasibility study. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:742–749.19. Seror O, N’Kontchou G, Van Nhieu JT, Rabahi Y, Nahon P, Laurent A, et al. Histopathologic comparison of monopolar versus no-touch multipolar radiofrequency ablation to treat hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014; 25:599–607.20. Wu LW, Chen CY, Liu CJ, Chen MY, Liu PC, Liu PF, et al. Multipolar radiofrequency ablation with non-touch technique for hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3 cm: a preliminary report. Adv Dig Med. 2014; 1:80–85.21. Hocquelet A, Aubé C, Rode A, Cartier V, Sutter O, Manichon AF, et al. Comparison of no-touch multi-bipolar vs. monopolar radiofrequency ablation for small HCC. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:67–74.22. Seror O, N'Kontchou G, Nault JC, Rabahi Y, Nahon P, Ganne-Carrié N, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria: no-touch multibipolar radiofrequency ablation for treatment-long-term results. Radiology. 2016; 280:611–621.23. Lee JM, Kim SH, Han JK, Sohn KL, Choi BI. Ex vivo experiment of saline-enhanced hepatic bipolar radiofrequency ablation with a perfused needle electrode: comparison with conventional monopolar and simultaneous monopolar modes. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2005; 28:338–345.24. Osaki Y, Ikeda K, Izumi N, Yamashita S, Kumada H, Hatta S, et al. Clinical effectiveness of bipolar radiofrequency ablation for small liver cancers. J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:874–883.25. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Woo S, Hwang EJ, Hwang I, Choi W, et al. Switching bipolar hepatic radiofrequency ablation using internally cooled wet electrodes: comparison with consecutive monopolar and switching monopolar modes. Br J Radiol. 2015; 88:20140468.26. Lee FT Jr, Haemmerich D, Wright AS, Mahvi DM, Sampson LA, Webster JG. Multiple probe radiofrequency ablation: pilot study in an animal model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:1437–1442.27. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. Dual switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a separable clustered electrode: comparison with consecutive and switching monopolar modes in ex vivo bovine livers. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:403–411.28. Kim YS, Rhim H, Cho OK, Koh BH, Kim Y. Intrahepatic recurrence after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the pattern and risk factors. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 59:432–441.29. Nakazawa T, Kokubu S, Shibuya A, Ono K, Watanabe M, Hidaka H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation between local tumor progression after ablation and ablative margin. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:480–488.30. Kim YS, Lee WJ, Rhim H, Lim HK, Choi D, Lee JY. The minimal ablative margin of radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma (> 2 and < 5 cm) needed to prevent local tumor progression: 3D quantitative assessment using CT image fusion. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:758–765.31. Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL, Breen DJ, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update. Radiology. 2014; 273:241–260.32. Tulikangas PK, Smith T, Falcone T, Boparai N, Walters MD. Gross and histologic characteristics of laparoscopic injuries with four different energy sources. Fertil Steril. 2001; 75:806–810.33. Martin KE, Moore CM, Tucker R, Fuchshuber P, Robinson T. Quantifying inadvertent thermal bowel injury from the monopolar instrument. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:4776–4784.34. Pillai K, Akhter J, Chua TC, Shehata M, Alzahrani N, Al-Alem I, et al. Heat sink effect on tumor ablation characteristics as observed in monopolar radiofrequency, bipolar radiofrequency, and microwave, using ex vivo calf liver model. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e580.35. Llovet JM, Vilana R, Brú C, Bianchi L, Salmeron JM, Boix L, et al. Increased risk of tumor seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2001; 33:1124–1129.36. Cabibbo G, Craxì A. Needle track seeding following percutaneous procedures for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2009; 1:62–66.37. Kawamura Y, Ikeda K, Fukushima T, Hara T, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, et al. Potential of a no-touch pincer ablation procedure for small hepatocellular carcinoma that uses a multipolar radiofrequency ablation system: an experimental animal study. Hepatol Res. 2014; 44:1234–1240.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Dual-Switching System and a Separable Clustered Electrode: Evaluation of the In Vivo Efficiency
- Dual Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: Comparison with Consecutive and Switching Monopolar Modes in Ex Vivo Bovine Livers
- RE: Should We Use a Monopolar or Bipolar Mode for Performing No-Touch Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Tumors? Clinical Practice Might have Already Resolved the Matter Once and for All
- Ablative Outcomes of Various Energy Modes for No-Touch and Peripheral Tumor-Puncturing Radiofrequency Ablation: An Ex Vivo Simulation Study
- Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using Dual Internally Cooled Wet Electrodes: Experimental Study in Ex Vivo Bovine Liver