Korean J Radiol.
2014 Apr;15(2):235-244. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.2.235.
Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Dual-Switching System and a Separable Clustered Electrode: Evaluation of the In Vivo Efficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea. jmsh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 1705578
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.2.235
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine the in vivo efficiency of monopolar radiofrequency ablation (RFA) using a dual-switching (DS) system and a separable clustered (SC) electrode to create coagulation in swine liver.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
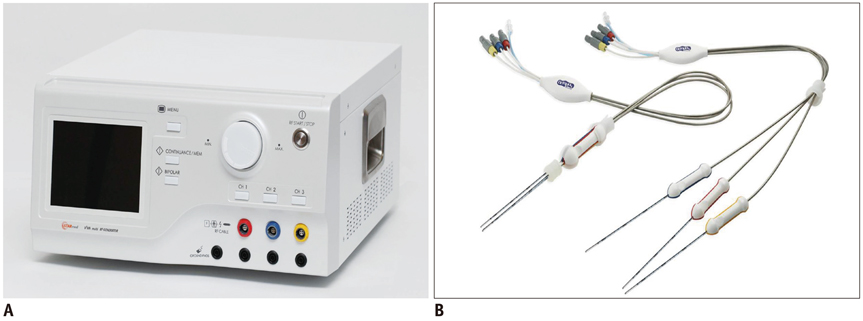
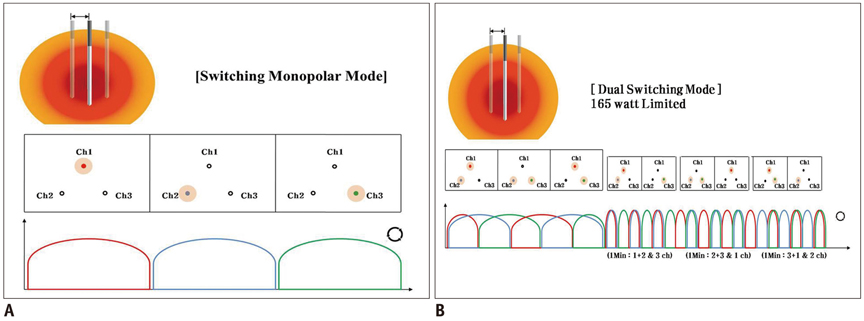
Thirty-three ablation zones were created in nine pigs using a DS system and an SC electrode in the switching monopolar mode. The pigs were divided into two groups for two experiments: 1) preliminary experiments (n = 3) to identify the optimal inter-electrode distances (IEDs) for dual-switching monopolar (DSM)-RFA, and 2) main experiments (n = 6) to compare the in vivo efficiency of DSM-RFA with that of a single-switching monopolar (SSM)-RFA. RF energy was alternatively applied to one of the three electrodes (SSM-RFA) or concurrently applied to a pair of electrodes (DSM-RFA) for 12 minutes in in vivo porcine livers. The delivered RFA energy and the shapes and dimensions of the coagulation areas were compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
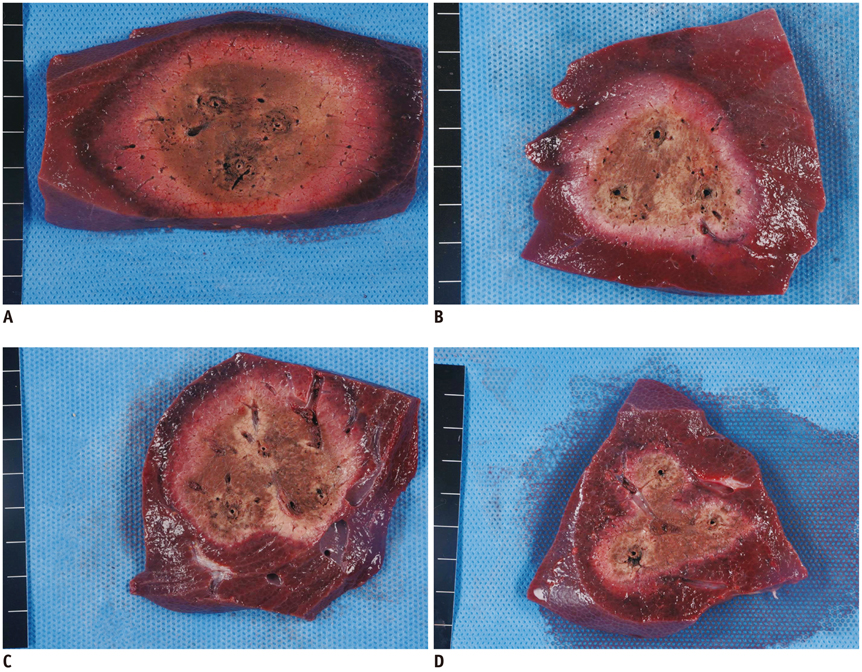
No pig died during RFA. The ideal IEDs for creating round or oval coagulation area using the DSM-RFA were 2.0 and 2.5 cm. DSM-RFA allowed more efficient RF energy delivery than SSM-RFA at the given time (23.0 +/- 4.0 kcal vs. 16.92 +/- 2.0 kcal, respectively; p = 0.0005). DSM-RFA created a significantly larger coagulation volume than SSM-RFA (40.4 +/- 16.4 cm3 vs. 20.8 +/- 10.7 cm3; p < 0.001). Both groups showed similar circularity of the ablation zones (p = 0.29).
CONCLUSION
Dual-switching monopolar-radiofrequency ablation using an SC electrode is feasible and can create larger ablation zones than SSM-RFA as it allows more RF energy delivery at a given time.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma
Jung Wook Seo
J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58(6):542-547. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.6.542.
Reference
-
1. Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Pina MC, Cioni D. Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:547–556.2. Lencioni R. Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010; 52:762–773.3. Cho YK, Kim JK, Kim MY, Rhim H, Han JK. Systematic review of randomized trials for hepatocellular carcinoma treated with percutaneous ablation therapies. Hepatology. 2009; 49:453–459.4. Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012; 379:1245–1255.5. Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008; 47:82–89.6. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943.7. Peng ZW, Lin XJ, Zhang YJ, Liang HH, Guo RP, Shi M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas 2 cm or smaller: a retrospective comparative study. Radiology. 2012; 262:1022–1033.8. Kuvshinoff BW, Ota DM. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: influence of technique and tumor size. Surgery. 2002; 132:605–611. discussion 611-612.9. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Ierace T, Solbiati L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology. 2000; 214:761–768.10. Waki K, Aikata H, Katamura Y, Kawaoka T, Takaki S, Hiramatsu A, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma: results and prognostic factors on long-term follow up. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:597–604.11. Solmi L, Nigro G, Roda E. Therapeutic effectiveness of echo-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy with a LeVeen needle electrode in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:1098–1104.12. Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, Fujishima T, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:122–130.13. Mazzaferro V, Battiston C, Perrone S, Pulvirenti A, Regalia E, Romito R, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients awaiting liver transplantation: a prospective study. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:900–909.14. Lopez PM, Villanueva A, Llovet JM. Systematic review: evidence-based management of hepatocellular carcinoma--an updated analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23:1535–1547.15. Pompili M, Saviano A, de Matthaeis N, Cucchetti A, Ardito F, Federico B, et al. Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3 cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:89–97.16. Dodd GD 3rd, Frank MS, Aribandi M, Chopra S, Chintapalli KN. Radiofrequency thermal ablation: computer analysis of the size of the thermal injury created by overlapping ablations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 177:777–782.17. Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K, Zou MW, Solbiati L, Liu JB, et al. Large liver tumors: protocol for radiofrequency ablation and its clinical application in 110 patients--mathematic model, overlapping mode, and electrode placement process. Radiology. 2004; 232:260–271.18. Mulier S, Miao Y, Mulier P, Dupas B, Pereira P, De Baere T, et al. Electrodes and multiple electrode systems for radio frequency ablation: a proposal for updated terminology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006; 574:57–73.19. Ni Y, Mulier S, Miao Y, Michel L, Marchal G. A review of the general aspects of radiofrequency ablation. Abdom Imaging. 2005; 30:381–400.20. Lee J, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Lee JY, Kim SH, Lee JE, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with multiple electrodes for medium-sized hepatocellular carcinomas. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:34–43.21. Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Haemmerich D, Brace CL, Fine JP, Frey TM, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation creates confluent areas of necrosis: in vivo porcine liver results. Radiology. 2006; 241:116–124.22. Frericks BB, Ritz JP, Roggan A, Wolf KJ, Albrecht T. Multipolar radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: initial experience. Radiology. 2005; 237:1056–1062.23. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim HC, Choi YH, Kim SH, Choi JY, et al. Switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation technique using multiple, internally cooled electrodes and a multichannel generator: ex vivo and in vivo pilot study. Invest Radiol. 2007; 42:163–171.24. Woo S, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Joo I, Kim SH, Lee JY, et al. Small- and medium-sized hepatocellular carcinomas: monopolar radiofrequency ablation with a multiple-electrode switching system-mid-term results. Radiology. 2013; 268:589–600.25. Lee ES, Lee JM, Kim WS, Choi SH, Joo I, Kim M, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablations using Octopus® electrodes in an in vivo porcine liver model. Br J Radiol. 2012; 85:e609–e615.26. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. Dual switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a separable clustered electrode: comparison with consecutive and switching monopolar modes in ex vivo bovine livers. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:403–411.27. Lee FT Jr, Haemmerich D, Wright AS, Mahvi DM, Sampson LA, Webster JG. Multiple probe radiofrequency ablation: pilot study in an animal model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:1437–1442.28. Lee ES, Lee JM, Kim KW, Lee IJ, Han JK, Choi BI. Evaluation of the in vivo efficiency and safety of hepatic radiofrequency ablation using a 15-G Octopus® in pig liver. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:194–201.29. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, Choi SH, An SK, Han CJ, et al. Bipolar radiofrequency ablation using wet-cooled electrodes: an in vitro experimental study in bovine liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:391–397.30. Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Frey TM, Mukherjee R, Winter TC 3rd, Lee FT Jr, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation: comparison with a conventional cluster electrode in an in vivo porcine kidney model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007; 18:1005–1010.31. Lee JD, Lee JM, Kim SW, Kim CS, Mun WS. MR imaging-histopathologic correlation of radiofrequency thermal ablation lesion in a rabbit liver model: observation during acute and chronic stages. Korean J Radiol. 2001; 2:151–158.32. Lee JM, Han JK, Lee JY, Kim SH, Choi JY, Lee MW, et al. Hepatic radiofrequency ablation using multiple probes: ex vivo and in vivo comparative studies of monopolar versus multipolar modes. Korean J Radiol. 2006; 7:106–117.33. Lee JM, Han JK, Chang JM, Chung SY, Kim SH, Lee JY, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of the porcine liver in vivo: increased coagulation with an internally cooled perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol. 2006; 13:343–352.34. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, Shin KS, Lee JY, Park HS, et al. Comparison of wet radiofrequency ablation with dry radiofrequency ablation and radiofrequency ablation using hypertonic saline preinjection: ex vivo bovine liver. Korean J Radiol. 2004; 5:258–265.35. Appelbaum L, Sosna J, Pearson R, Perez S, Nissenbaum Y, Mertyna P, et al. Algorithm optimization for multitined radiofrequency ablation: comparative study in ex vivo and in vivo bovine liver. Radiology. 2010; 254:430–440.36. Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Haemmerich D, Brace CL, Fine JP, Frey TM, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation: simultaneous production of separate zones of coagulation in an in vivo porcine liver model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:1727–1735.37. Baldwin K, Katz SC, Rubin A, Somasundar P. Bipolar radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: technical experience and interval follow-up in 22 patients with 33 ablations. J Surg Oncol. 2012; 106:905–910.38. Clasen S, Rempp H, Schmidt D, Schraml C, Hoffmann R, Claussen CD, et al. Multipolar radiofrequency ablation using internally cooled electrodes in ex vivo bovine liver: correlation between volume of coagulation and amount of applied energy. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:111–113.39. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim HC, Kim SH, Kim KW, Joo SM, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablation of in vivo porcine liver: comparative studies of consecutive monopolar, switching monopolar versus multipolar modes. Invest Radiol. 2007; 42:676–683.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dual Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: Comparison with Consecutive and Switching Monopolar Modes in Ex Vivo Bovine Livers
- Percutaneous Dual-Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: A Preliminary Study
- Ablative Outcomes of Various Energy Modes for No-Touch and Peripheral Tumor-Puncturing Radiofrequency Ablation: An Ex Vivo Simulation Study
- Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinomas: A Randomized Controlled Trial of a DualSwitching Monopolar Mode Versus a Single-Switching Monopolar Mode
- Evaluation of the In Vivo Efficiency and Safety of Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation Using a 15-G Octopus(R) in Pig Liver