Korean J Radiol.
2013 Apr;14(2):194-201. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.194.
Evaluation of the In Vivo Efficiency and Safety of Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation Using a 15-G Octopus(R) in Pig Liver
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. jmsh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 3National Cancer Center, Seoul 410-769, Korea.
- KMID: 1482777
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.194
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine in vivo efficacy of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in porcine liver by using 15-gauge Octopus(R) (15-G Octopus(R)) electrodes to create a large coagulation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
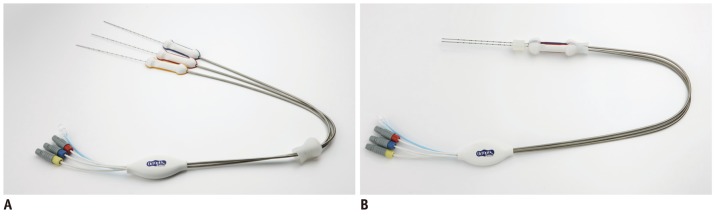
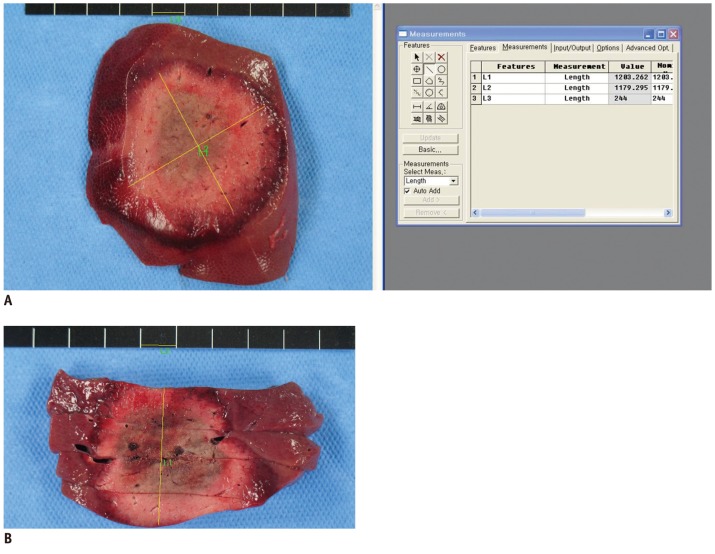
A total of 18 coagulations were created by using a 180-W generator and 15-G Octopus(R) electrodes during laparotomy, performed in 14 pigs. Coagulation necrosis was created in the pig livers by the use of one of three RFA protocols: 1) group A, monopolar RFA using a 15-G Octopus(R) electrode with a 5-mm inter-electrode distance (n = 4); 2) group B, monopolar RFA using a 15-G Octopus(R) electrode with a 10-mm inter-electrode distance (n = 6); and 3) group C, switching monopolar RFA using two 15-G Octopus(R) electrodes (n = 8). The energy efficiency, shape, maximum and minimum diameters (Dmx and Dmi), and the volume of the coagulation volume were measured in each group. The Summary statistics were obtained and Mann-Whitney test was were performed.
RESULTS
The mean ablated volume of each group was 49.23 cm3 in A, 64.11 cm3 in B, and 72.35 cm3 in C. The mean Dmx and Dmi values were 5.68 cm and 4.58 cm in A and 5.97 cm and 4.97 cm in B, respectively. In group C, the mean diameters of Dmx and Dmi were 6.80 cm and 5.11 cm, respectively. The mean ratios of Dmi/Dmx were 1.25, 1.20, and 1.35 in groups A, B, and C, respectively. There was one animal death during the RFA procedure, the cause of which could not be subsequently determined. However, there were no other significant, procedure-related complications during the seven-hour-delayed CT scans.
CONCLUSION
RFA procedures using 15-G Octopus(R) electrodes are useful and safe for creating a large ablation in a single electrode model as well as in the multiple electrodes model.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Decadt B, Siriwardena AK. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours: systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2004; 5:550–560. PMID: 15337485.
Article2. Salhab M, Canelo R. An overview of evidence-based management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Ther. 2011; 7:463–475. PMID: 22269411.
Article3. Shiina S, Tateishi R, Arano T, Uchino K, Enooku K, Nakagawa H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:569–577. quiz 578. PMID: 22158026.
Article4. Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, Ellis LM, Granchi J, Vallone P, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients. Ann Surg. 1999; 230:1–8. PMID: 10400029.5. Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC, Hsu CW, Chen YC. Radiofrequency ablation improves prognosis compared with ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma < or = 4 cm. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:1714–1723. PMID: 15578509.6. Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, Fujishima T, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:122–130. PMID: 16012942.
Article7. Lencioni RA, Allgaier HP, Cioni D, Olschewski M, Deibert P, Crocetti L, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology. 2003; 228:235–240. PMID: 12759473.
Article8. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR. Radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol. 1996; 3:636–644. PMID: 8796727.9. Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, Di Stasi M, Quaretti P, Rago M, et al. Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170:1015–1022. PMID: 9530052.
Article10. Miao Y, Ni Y, Yu J, Zhang H, Baert A, Marchal G. An ex vivo study on radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion size by using an "expandable-wet" electrode. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:1841–1847. PMID: 11511912.
Article11. Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Hahn PF, Cosman E, Conrad JE, Fogle R, et al. Large-volume tissue ablation with radio frequency by using a clustered, internally cooled electrode technique: laboratory and clinical experience in liver metastases. Radiology. 1998; 209:371–379. PMID: 9807561.
Article12. Lee JM, Han JK, Lee JY, Kim SH, Choi JY, Lee MW, et al. Hepatic radiofrequency ablation using multiple probes: ex vivo and in vivo comparative studies of monopolar versus multipolar modes. Korean J Radiol. 2006; 7:106–117. PMID: 16799271.
Article13. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim HC, Choi YH, Kim SH, Choi JY, et al. Switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation technique using multiple, internally cooled electrodes and a multichannel generator: ex vivo and in vivo pilot study. Invest Radiol. 2007; 42:163–171. PMID: 17287646.14. Lee JM, Han JK, Chang JM, Chung SY, Kim SH, Lee JY, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of the porcine liver in vivo: increased coagulation with an internally cooled perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol. 2006; 13:343–352. PMID: 16488847.
Article15. Lee ES, Lee JM, Kim WS, Choi SH, Joo I, Kim M, et al. Multiple-electrode radiofrequency ablations using Octopus® electrodes in an in vivo porcine liver model. Br J Radiol. 2012; 85:e609–e615. PMID: 22422385.16. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Dawson SL, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR, Rosenthal DI. Tissue ablation with radiofrequency: effect of probe size, gauge, duration, and temperature on lesion volume. Acad Radiol. 1995; 2:399–404. PMID: 9419582.17. McGhana JP, Dodd GD 3rd. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:3–16. PMID: 11133529.18. Rhim H. Complications of radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Imaging. 2005; 30:409–418. PMID: 15688113.
Article19. Lubienski A, Bitsch RG, Lubienski K, Kauffmann G, Duex M. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA): development of a flow model for bovine livers for extensive bench testing. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006; 29:1068–1072. PMID: 16845558.
Article20. Kim SW, Rhim H, Park M, Kim H, Kim YS, Choi D, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas adjacent to the gallbladder with internally cooled electrodes: assessment of safety and therapeutic efficacy. Korean J Radiol. 2009; 10:366–376. PMID: 19568465.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Cysts: Case Report
- Radiofrequency Ablation with Epinephrine Injection: In Vivo Study in Normal Pig Livers
- Comparison of Ablation Performance between Octopus Multipurpose Electrode and Conventional Octopus Electrode
- New Radiofrequency Device to Reduce Bleeding after Core Needle Biopsy: Experimental Study in a Porcine Liver Model
- Dual Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: Comparison with Consecutive and Switching Monopolar Modes in Ex Vivo Bovine Livers