Korean J Orthod.
2018 Nov;48(6):357-366. 10.4041/kjod.2018.48.6.357.
Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of transverse dental compensation in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. sangkim@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2427773
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2018.48.6.357
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to analyze the transverse dental compensation in reference to the maxillary and mandibular basal bones using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and evaluate the correlations between transverse dental compensation and skeletal asymmetry variables in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry.
METHODS
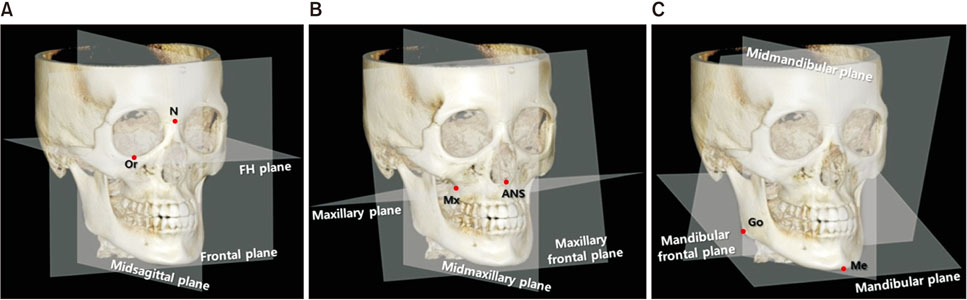
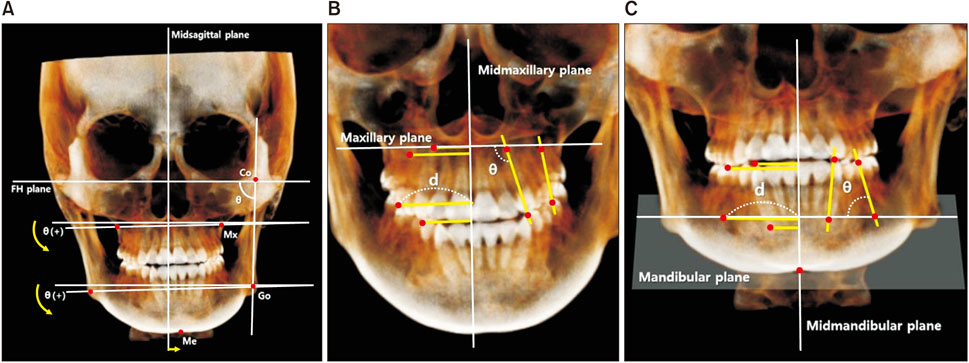
Thirty patients with skeletal Class I (control group; 15 men, 15 women) and 30 patients with skeletal Class III with menton deviation (asymmetry group; 16 men, 14 women) were included. Skeletal and dental measurements were acquired from reconstructed CBCT images using OnDemand3D 1.0 software. All measurements were compared between groups and between the deviated and nondeviated sides of the asymmetry group. Correlation coefficients for the association between skeletal and dental measurements were calculated.
RESULTS
Differences in the ramus inclination (p < 0.001), maxillary canine and first molar inclinations (p < 0.001), and distances from the canine and first molar cusp tips to the midmaxillary or midmandibular planes (p < 0.01) between the right and left sides were significantly greater in the asymmetry group than in the control group. In the asymmetry group, the ramus inclination difference (p < 0.05) and mandibular canting (p < 0.05) were correlated with the amount of menton deviation. In addition, dental measurements were positively correlated with the amount of menton deviation (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Transverse dental compensation was correlated with the maxillary and mandibular asymmetry patterns. These results would be helpful in understanding the pattern of transverse dental compensation and planning surgical procedure for patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Severt TR, Proffit WR. The prevalence of facial asymmetry in the dentofacial deformities population at the University of North Carolina. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1997; 12:171–176.2. Haraguchi S, Takada K, Yasuda Y. Facial asymmetry in subjects with skeletal Class III deformity. Angle Orthod. 2002; 72:28–35.3. Chew MT. Spectrum and management of dentofacial deformities in a multiethnic Asian population. Angle Orthod. 2006; 76:806–809.4. Piao Y, Kim SJ, Yu HS, Cha JY, Baik HS. Five-year investigation of a large orthodontic patient population at a dental hospital in South Korea. Korean J Orthod. 2016; 46:137–145.
Article5. Rhodes G, Proffitt F, Grady JM, Sumich A. Facial symmetry and the perception of beauty. Psychon Bull Rev. 1998; 5:659–669.
Article6. Bailey LJ, Haltiwanger LH, Blakey GH, Proffit WR. Who seeks surgical-orthodontic treatment: a current review. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 2001; 16:280–292.7. Vig PS, Hewitt AB. Asymmetry of the human facial skeleton. Angle Orthod. 1975; 45:125–129.8. Worms FW, Isaacson RJ, Speidel TM. Surgical orthodontic treatment planning: profile analysis and mandibular surgery. Angle Orthod. 1976; 46:1–25.9. Woods MG, Swift JQ, Markowitz NR. Clinical implications of advances in orthognathic surgery. J Clin Orthod. 1989; 23:420–429.10. Sekiya T, Nakamura Y, Oikawa T, Ishii H, Hirashita A, Seto K. Elimination of transverse dental compensation is critical for treatment of patients with severe facial asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010; 137:552–562.
Article11. Kim DW, Son WS. The relationship between facial asymmetry and maxillary dental arch shape. Korean J Orthod. 1997; 27:445–456.12. Kusayama M, Motohashi N, Kuroda T. Relationship between transverse dental anomalies and skeletal asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003; 123:329–337.
Article13. Major PW, Johnson DE, Hesse KL, Glover KE. Landmark identification error in posterior anterior cephalometrics. Angle Orthod. 1994; 64:447–454.14. Major PW, Johnson DE, Hesse KL, Glover KE. Effect of head orientation on posterior anterior cephalometric landmark identification. Angle Orthod. 1996; 66:51–60.15. Park SB, Park JH, Jung YH, Jo BH, Kim YI. Correlation between menton deviation and dental compensation in facial asymmetry using cone-beam CT. Korean J Orthod. 2009; 39:300–309.
Article16. Song HK, Son WS, Park SB, Kim SS, Lim YI. The assessment of dentoalveolar compensation in facial asymmetry individuals: integration of cone beam CT and laser scanned dental cast images. Korean J Orthod. 2010; 40:373–382.
Article17. Ahn J, Kim SJ, Lee JY, Chung CJ, Kim KH. Transverse dental compensation in relation to sagittal and transverse skeletal discrepancies in skeletal Class III patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2017; 151:148–156.
Article18. Tyan S, Park HS, Janchivdorj M, Han SH, Kim SJ, Ahn HW. Three-dimensional analysis of molar compensation in patients with facial asymmetry and mandibular prognathism. Angle Orthod. 2016; 86:421–430.
Article19. Baek C, Paeng JY, Lee JS, Hong J. Morphologic evaluation and classification of facial asymmetry using 3-dimensional computed tomography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70:1161–1169.
Article20. Kim KA, Lee JW, Park JH, Kim BH, Ahn HW, Kim SJ. Targeted presurgical decompensation in patients with yaw-dependent facial asymmetry. Korean J Orthod. 2017; 47:195–206.
Article21. Park SH, Yu HS, Kim KD, Lee KJ, Baik HS. A proposal for a new analysis of craniofacial morphology by 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006; 129:600.e23–600.e34.
Article22. Ryu HS, An KY, Kang KH. Cone-beam computed tomography based evaluation of rotational patterns of dentofacial structures in skeletal Class III deformity with mandibular asymmetry. Korean J Orthod. 2015; 45:153–163.
Article23. Baumgaertel S, Palomo JM, Palomo L, Hans MG. Reliability and accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography dental measurements. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009; 136:19–25. discussion 25-8.
Article24. Damstra J, Fourie Z, Ren Y. Evaluation and comparison of postero-anterior cephalograms and cone-beam computed tomography images for the detection of mandibular asymmetry. Eur J Orthod. 2013; 35:45–50.
Article25. Hwang HS, Hwang CH, Lee KH, Kang BC. Maxillofacial 3-dimensional image analysis for the diagnosis of facial asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006; 130:779–785.
Article26. Bayome M, Park JH, Kook YA. New three-dimensional cephalometric analyses among adults with a skeletal Class I pattern and normal occlusion. Korean J Orthod. 2013; 43:62–73.
Article27. Chebib FS, Chamma AM. Indices of craniofacial asymmetry. Angle Orthod. 1981; 51:214–226.28. Choi KY. Analysis of facial asymmetry. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2015; 16:1–10.
Article29. Garcia-Figueroa MA, Raboud DW, Lam EW, Heo G, Major PW. Effect of buccolingual root angulation on the mesiodistal angulation shown on panoramic radiographs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008; 134:93–99.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of changes in the transverse dental axis between patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry treated by orthognathic surgery with and without presurgical orthodontic treatment
- Differences in positions of cone-beam computed tomography landmarks in patients with skeletal Class III facial asymmetry according to midsagittal planes
- The relationship between posterior dental compensation and skeletal discrepancy in class III malocclusion
- Posterior dental compensation and occlusal function in adults with different sagittal skeletal malocclusions
- Three-dimensional analysis of dental decompensation for skeletal Class III malocclusion on the basis of vertical skeletal patterns obtained using cone-beam computed tomography