Korean J Orthod.
2017 Jul;47(4):256-267. 10.4041/kjod.2017.47.4.256.
Comparison of changes in the transverse dental axis between patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry treated by orthognathic surgery with and without presurgical orthodontic treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, The Institute of Craniofacial Deformity, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. yumichael@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2379558
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2017.47.4.256
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate transverse skeletal and dental changes, including those in the buccolingual dental axis, between patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry after bilateral intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy with and without presurgical orthodontic treatment.
METHODS
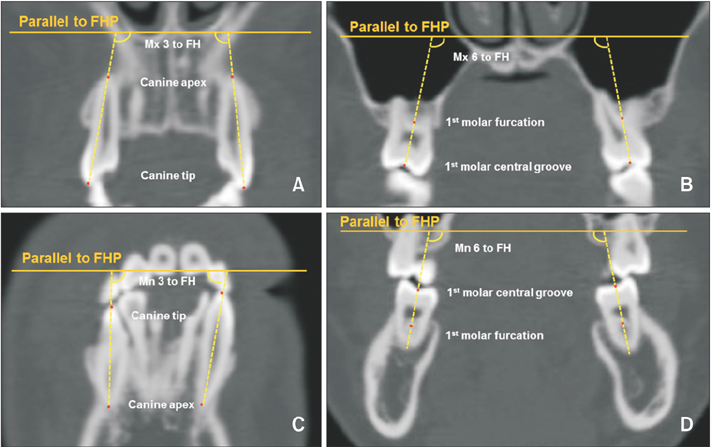
This retrospective study included 29 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry including menton deviation > 4 mm from the midsagittal plane. To evaluate changes in transverse skeletal and dental variables (i.e., buccolingual inclination of the upper and lower canines and first molars), the data for 16 patients who underwent conventional orthognathic surgery (CS) were compared with those for 13 patients who underwent preorthodontic orthognathic surgery (POGS), using three-dimensional computed tomography at initial examination, 1 month before surgery, and at 7 days and 1 year after surgery.
RESULTS
The 1-year postsurgical examination revealed no significant changes in the postoperative transverse dental axis in the CS group. In the POGS group, the upper first molar inclined lingually on both sides (deviated side, −1.8°± 2.8°, p = 0.044; nondeviated side, −3.7°± 3.3°, p = 0.001) and the lower canine inclined lingually on the nondeviated side (4.0°± 5.4°, p = 0.022) during postsurgical orthodontic treatment. There were no significant differences in the skeletal and dental variables between the two groups at 1 year after surgery.
CONCLUSIONS
POGS may be a clinically acceptable alternative to CS as a treatment to achieve stable transverse axes of the dentition in both arches in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jacobs JD, Sinclair PM. Principles of orthodontic mechanics in orthognathic surgery cases. Am J Orthod. 1983; 84:399–407.
Article2. Tompach PC, Wheeler JJ, Fridrich KL. Orthodontic considerations in orthognathic surgery. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1995; 10:97–107.3. Sabri R. Orthodontic objectives in orthognathic surgery: state of the art today. World J Orthod. 2006; 7:177–191.4. Nagasaka H, Sugawara J, Kawamura H, Nanda R. “Surgery first” skeletal Class III correction using the Skeletal Anchorage System. J Clin Orthod. 2009; 43:97–105.5. Villegas C, Uribe F, Sugawara J, Nanda R. Expedited correction of significant dentofacial asymmetry using a “surgery first” approach. J Clin Orthod. 2010; 44:97–103. quiz 105.6. Choi SH, Hwang CJ, Baik HS, Jung YS, Lee KJ. Stability of pre-orthodontic orthognathic surgery using intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy versus conventional treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 74:610–619.
Article7. Ann HR, Jung YS, Lee KJ, Baik HS. Evaluation of stability after pre-orthodontic orthognathic surgery using cone-beam computed tomography: a comparison with conventional treatment. Korean J Orthod. 2016; 46:301–309.
Article8. Min BK, Choi JY, Baek SH. Comparison of treatment duration between conventional three-stage method and surgery-first approach in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion. J Craniofac Surg. 2014; 25:1752–1756.
Article9. Park JK, Choi JY, Yang IH, Baek SH. Patient's satisfaction in skeletal class III cases treated with two-jaw surgery using orthognathic quality of life questionnaire: conventional three-stage method versus surgery-first approach. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26:2086–2093.
Article10. Frost HM. The biology of fracture healing. An overview for clinicians. Part I. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (248):283–293.11. Liou EJ, Chen PH, Wang YC, Yu CC, Huang CS, Chen YR. Surgery-first accelerated orthognathic surgery: postoperative rapid orthodontic tooth movement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69:781–785.
Article12. Ko EW, Lin SC, Chen YR, Huang CS. Skeletal and dental variables related to the stability of orthognathic surgery in skeletal Class III malocclusion with a surgery-first approach. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 71:e215–e223.
Article13. Park KH, Sandor GK, Kim YD. Skeletal stability of surgery-first bimaxillary orthognathic surgery for skeletal class III malocclusion, using standardized criteria. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 45:35–40.
Article14. Rhee CH, Choi YK, Kim YI, Kim SS, Park SB, Son WS. Correlation between skeletal and dental changes after mandibular setback surgery-first orthodontic treatment: Cone-beam computed tomography-generated half-cephalograms. Korean J Orthod. 2015; 45:59–65.
Article15. Wang YC, Ko EW, Huang CS, Chen YR, Takano-Yamamoto T. Comparison of transverse dimensional changes in surgical skeletal Class III patients with and without presurgical orthodontics. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:1807–1812.
Article16. Kim YK, Yun PY, Moon SW, Lee YS, Lee NK. Influence of the changes in arch width on postsurgical relapse after mandibular setback surgery with minimal orthodontics. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72:1820–1831.
Article17. Lee KM, Hwang HS, Cho JH. Comparison of transverse analysis between posteroanterior cephalogram and cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 2014; 84:715–719.
Article18. Ryu HS, An KY, Kang KH. Cone-beam computed tomography based evaluation of rotational patterns of dentofacial structures in skeletal Class III deformity with mandibular asymmetry. Korean J Orthod. 2015; 45:153–163.
Article19. Lee RT. The benefits of post-surgical orthodontic treatment. Br J Orthod. 1994; 21:265–274.
Article20. Vanarsdall RL Jr. Transverse dimension and long-term stability. Semin Orthod. 1999; 5:171–180.
Article21. Choi SH, Kang DY, Cha JY, Jung YS, Yu HS, Park HS, et al. Major factors contributing to anterior and posterior relapse after intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016; 44:413–420.
Article22. Jung HD, Jung YS, Kim SY, Kim DW, Park HS. Postoperative stability following bilateral intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy based on amount of setback. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 51:822–826.
Article23. Park SH, Yu HS, Kim KD, Lee KJ, Baik HS. A proposal for a new analysis of craniofacial morphology by 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006; 129:600.e23–600.e34.
Article24. Hwang HS, Youn IS, Lee KH, Lim HJ. Classification of facial asymmetry by cluster analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007; 132:279.e1–279.e6.
Article25. Baek C, Paeng JY, Lee JS, Hong J. Morphologic evaluation and classification of facial asymmetry using 3-dimensional computed tomography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70:1161–1169.
Article26. Tyan S, Park HS, Janchivdorj M, Han SH, Kim SJ, Ahn HW. Three-dimensional analysis of molar compensation in patients with facial asymmetry and mandibular prognathism. Angle Orthod. 2016; 86:421–430.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A study of the characteristics of craniofacial skeleton on orthognathic surgical cases with skeletal Class III malocclusion
- 2 Phase Treatment Without Preoperative Orthodontics In Skeletal Class III Malocclusion
- Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of transverse dental compensation in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and facial asymmetry
- Combined orthodontic-surgical treatment for Class III patient with midfacial deficiency and mandibular prognathism
- Surgery-first Approach for Facial Asymmetry with Transverse Discrepancy Using Hyrax-type Palatal Expansion Appliance