Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2018 Nov;6(6):310-314. 10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.310.
Clinical validation of ImmuneCheck IgE for the rapid detection of serum total IgE
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. PARKJW@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute for Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2427490
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.310
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Conventional serum IgE assay was costly, required the skills of expert, and relied heavily on expensive equipment. Quantitative measurement of total IgE using Point of Care Test (POCT) device can be the solution for these limitations. This study evaluated and validated the reproducibility of ImmuneCheck IgE.
METHODS
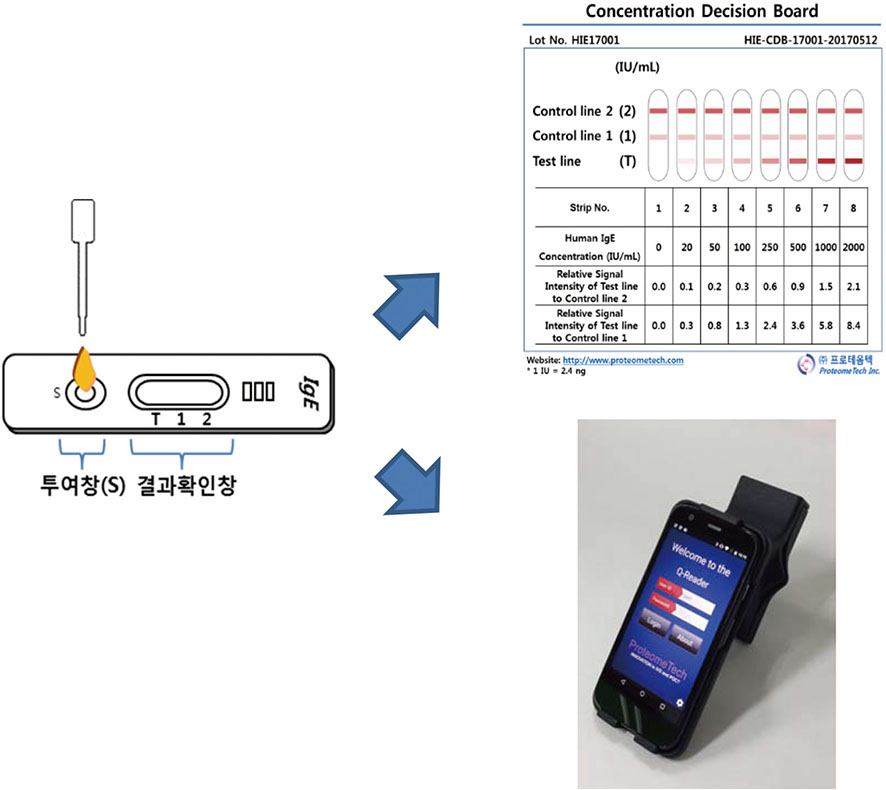
This study included 120 patients of allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, atopic dermatitis, or anaphylaxis . The reliability of POCT ImmuneCheck IgE was evaluated by comparing results from the naked eye and from the Q-Reader. Intratest reproducibility and intertest correlation were analyzed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
RESULTS
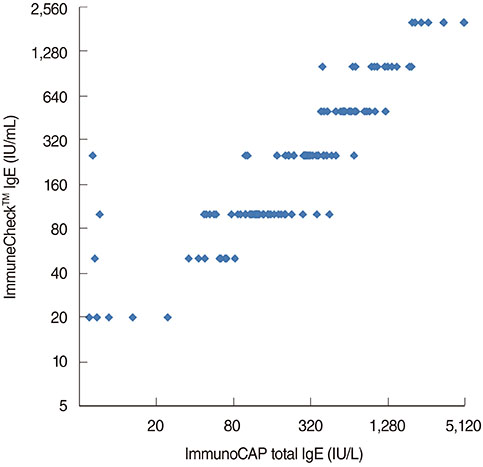
Of the 120 enrolled patients, 51 were males and 69 were females. The ages ranged from 19 to 84 years, with an average age of 51.5 years. The concentration of serum total IgE measured by Phadia ImmunoCAP IgE ranged from 5.95 to 5,000 IU/mL. ICC for Intratest reproducibility of ImmuneCheck IgE by naked eye and by Q-Reader were 0.991 (P < 0.001) and 0.989 (P < 0.001), respectively. In addition, intertest correlation between ImmuneCheck IgE and Phadia ImmunoCAP IgE results of naked eye and Q-Reader were 0.968 (P < 0.001) and 0.948 (P < 0.001), respectively.
CONCLUSION
The ImmuneCheck IgE was reproducible and highly correlated with conventional Phadia ImmunoCAP IgE assay. This result suggests that ImmuneCheck IgE can be a useful tool for rapid and precise detection of total IgE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stone KD, Prussin C, Metcalfe DD. IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:2 Suppl 2. S73–S80.
Article2. Schroeder HW Jr, Cavacini L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:2 Suppl 2. S41–S52.
Article3. Bonilla FA. Pharmacokinetics of immunoglobulin administered via intravenous or subcutaneous routes. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2008; 28:803–819.
Article4. Kelly BT, Grayson MH. Immunoglobulin E, what is it good for. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016; 116:183–187.
Article5. Lawrence MG, Woodfolk JA, Schuyler AJ, Stillman LC, Chapman MD, Platts-Mills TA. Half-life of IgE in serum and skin: consequences for anti-IgE therapy in patients with allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139:422–428.
Article6. Johansson SG. The discovery of immunoglobulin e and its role in allergy. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2014; 100:150–154.
Article7. Sanjuan MA, Sagar D, Kolbeck R. Role of IgE in autoimmunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:1651–1661.
Article8. Huang Y, Yang Z, McGowan J, Huang H, O'Brien RL, Born WK. Regulation of IgE Responses by γδ T Cells. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015; 15:13.
Article9. Park HJ, Kim EJ, Yoon D, Lee JK, Chang WS, Lim YM, et al. Prevalence of self-reported allergic diseases and IgE levels: a 2010 KNHANES analysis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:329–339.
Article10. Greenberger PA, Bush RK, Demain JG, Luong A, Slavin RG, Knutsen AP. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014; 2:703–708.
Article11. Kornmann O, Watz H, Fuhr R, Krug N, Erpenbeck VJ, Kaiser G. Omalizumab in patients with allergic (IgE-mediated) asthma and IgE/bodyweight combinations above those in the initially approved dosing table. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 28:149–153.
Article12. Baker DL, Peng K, Cheu M, Fischer SK. Response to Becher and Strohner comment regarding Baker DL et al. Evaluation of two commercial omalizumab/free IgE immunoassays: implications of use during therapy. CMRO. 2014; 30:913–922.
Article13. Gould HJ, Sutton BJ. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8:205–217.
Article14. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174.
Article15. Nichols JH. Point of care testing. Clin Lab Med. 2007; 27:893–908.
Article16. Price CP. Point of care testing. BMJ. 2001; 322:1285–1288.17. Hirsch J, Wendt T, Kuhly P, Schaffartzik W. Point-of-care testing apparatus. Measurement of coagulation. Anaesthesia. 2001; 56:760–763.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of specific IgE antibody in Clonorchis sinensis infection
- Clinical characteristics of total IgE in pediatric allergic disease
- Assessment of IgE Detecting Methods in Cord and Maternal Serum
- Clinical significance of serum IgE
- The Relationship between Total Serum IgE, Allergen-Specific IgE, and Skin Prick Test in Children with Atopic Asthma