Yonsei Med J.
2017 Mar;58(2):395-400. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.395.
Filaggrin Mutation in Korean Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimsc@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Dermatology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan.
- KMID: 2427129
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.395
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, relapsing eczematous inflammatory skin disease. Mutations in the filaggrin gene (FLG) are major predisposing factors for AD. Ethnic differences exist between Asian and European populations in the frequency and spectrum of FLG mutations. Moreover, a distinct set of FLG mutations has been reported in Asian populations. The aim of this study was to examine the spectrum of FLG mutations in Koreans with AD. We also investigated the association of FLG mutations and clinical features of AD and compared the Korean FLG landscape with that of other East Asian countries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventy Korean patients with AD were enrolled in this study. Fourteen FLG mutations previously detected in Korean, Japanese, and Chinese patients were screened by genotyping.
RESULTS
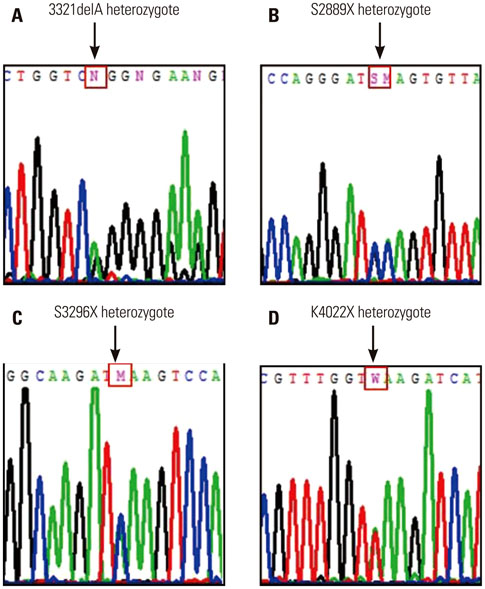
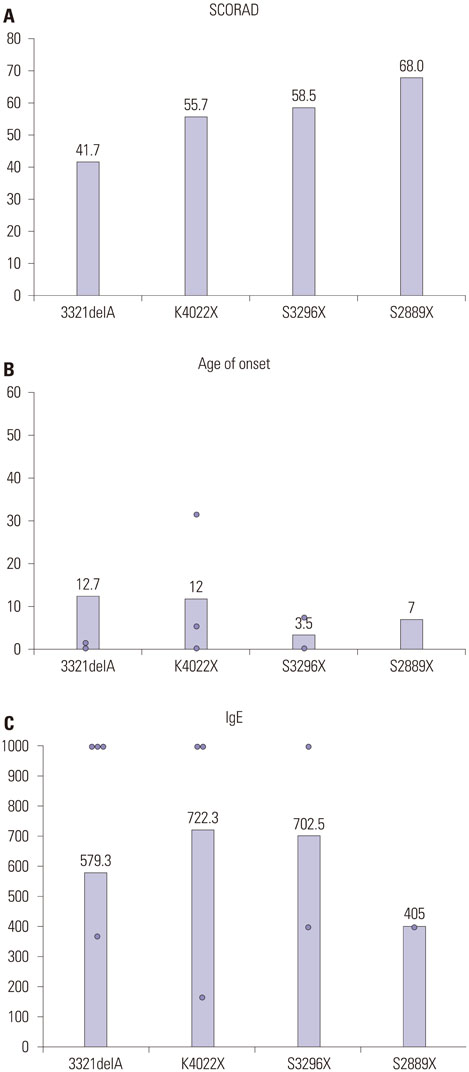
Four FLG null mutations (3321delA, K4022X, S3296X, and S2889X) were identified in eleven patients (15.7%). The most commonly detected mutations in Korean patients with AD were 3321delA (n=6, 9.1%) and K4022X (n=3, 4.5%). FLG mutations were significantly associated with elevated IgE (≥200 KIU/L and/or MAST-CLA >3+, p=0.005), palmar hyperlinearity (p<0.001), and a family history of allergic disease (p=0.021).
CONCLUSION
This study expanded our understanding of the landscape of FLG mutations in Koreans and revealed an association between FLG mutations and AD phenotype.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/genetics
Dermatitis, Atopic/ethnology/*genetics
Ethnic Groups
European Continental Ancestry Group
Female
Genetic Predisposition to Disease
Genotype
Humans
Hypersensitivity/genetics
Ichthyosis Vulgaris
Intermediate Filament Proteins/*genetics
Male
*Mutation
Phenotype
Recurrence
Republic of Korea
Intermediate Filament Proteins
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Variations in Early-Onset Atopic Dermatitis Patients
Beom Jun Kim, Hye-young Wang, Hyeyoung Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Soo-Jong Hong, Eung Ho Choi
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(3):286-293. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.286.
Reference
-
1. Sandilands A, Sutherland C, Irvine AD, McLean WH. Filaggrin in the frontline: role in skin barrier function and disease. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122(Pt 9):1285–1294.
Article2. Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:1483–1494.
Article3. Williams H, Flohr C. How epidemiology has challenged 3 prevailing concepts about atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:209–213.
Article4. Kubo A, Nagao K, Amagai M. Epidermal barrier dysfunction and cutaneous sensitization in atopic diseases. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:440–447.
Article5. Irvine AD, McLean WH, Leung DY. Filaggrin mutations associated with skin and allergic diseases. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:1315–1327.
Article6. Akiyama M. FLG mutations in ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic eczema: spectrum of mutations and population genetics. Br J Dermatol. 2010; 162:472–477.
Article7. Dale BA. Purification and characterization of a basic protein from the stratum corneum of mammalian epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977; 491:193–204.
Article8. Thyssen JP, Godoy-Gijon E, Elias PM. Ichthyosis vulgaris: the filaggrin mutation disease. Br J Dermatol. 2013; 168:1155–1166.
Article9. Smith FJ, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Sandilands A, Campbell LE, Zhao Y, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding filaggrin cause ichthyosis vulgaris. Nat Genet. 2006; 38:337–342.
Article10. Palmer CN, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Zhao Y, Liao H, Lee SP, et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet. 2006; 38:441–446.
Article11. Kim EJ, Jeong MS, Li K, Park MK, Lee MK, Yoon Y, et al. Genetic polymorphism of FLG in Korean ichthyosis vulgaris patients. Ann Dermatol. 2011; 23:170–176.
Article12. Ohguchi Y, Nomura T, Suzuki S, Mizuno O, Nomura Y, Nemoto-Hasebe I, et al. A new filaggrin gene mutation in a Korean patient with ichthyosis vulgaris. Eur J Dermatol. 2014; 24:491–493.
Article13. Yu HS, Kang MJ, Jung YH, Kim HY, Seo JH, Kim YJ, et al. Mutations in the filaggrin are predisposing factor in Korean children with atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:211–215.
Article14. Park J, Jekarl DW, Kim Y, Kim J, Kim M, Park YM. Novel FLG null mutations in Korean patients with atopic dermatitis and comparison of the mutational spectra in Asian populations. J Dermatol. 2015; 42:867–873.
Article15. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1980; 92:44–47.16. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: the SCORAD index. Consensus Report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology. 1993; 186:23–31.17. Fölster-Holst R, Pape M, Buss YL, Christophers E, Weichenthal M. Low prevalence of the intrinsic form of atopic dermatitis among adult patients. Allergy. 2006; 61:629–632.
Article18. Shin JW, Jin SP, Lee JH, Cho S. Analysis of MAST-CLA results as a diagnostic tool in allergic skin diseases. Ann Dermatol. 2010; 22:35–40.
Article19. Sandilands A, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Hull PR, O’Regan GM, Clayton TH, Watson RM, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the gene encoding filaggrin uncovers prevalent and rare mutations in ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic eczema. Nat Genet. 2007; 39:650–654.
Article20. Nomura T, Sandilands A, Akiyama M, Liao H, Evans AT, Sakai K, et al. Unique mutations in the filaggrin gene in Japanese patients with ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:434–440.
Article21. Nomura T, Akiyama M, Sandilands A, Nemoto-Hasebe I, Sakai K, Nagasaki A, et al. Prevalent and rare mutations in the gene encoding filaggrin in Japanese patients with ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009; 129:1302–1305.
Article22. Osawa R, Konno S, Akiyama M, Nemoto-Hasebe I, Nomura T, Nomura Y, et al. Japanese-specific filaggrin gene mutations in Japanese patients suffering from atopic eczema and asthma. J Invest Dermatol. 2010; 130:2834–2836.
Article23. Li M, Liu Q, Liu J, Cheng R, Zhang H, Xue H, et al. Mutations analysis in filaggrin gene in northern China patients with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013; 27:169–174.
Article24. Zhang H, Guo Y, Wang W, Shi M, Chen X, Yao Z. Mutations in the filaggrin gene in Han Chinese patients with atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2011; 66:420–427.
Article25. Hsu CK, Akiyama M, Nemoto-Hasebe I, Nomura T, Sandilands A, Chao SC, et al. Analysis of Taiwanese ichthyosis vulgaris families further demonstrates differences in FLG mutations between European and Asian populations. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:448–451.
Article26. Chen H, Common JE, Haines RL, Balakrishnan A, Brown SJ, Goh CS, et al. Wide spectrum of filaggrin-null mutations in atopic dermatitis highlights differences between Singaporean Chinese and European populations. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165:106–114.
Article27. Thyssen JP, Kezic S. Causes of epidermal filaggrin reduction and their role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 134:792–799.
Article28. Enomoto H, Hirata K, Otsuka K, Kawai T, Takahashi T, Hirota T, et al. Filaggrin null mutations are associated with atopic dermatitis and elevated levels of IgE in the Japanese population: a family and case-control study. J Hum Genet. 2008; 53:615–621.
Article29. Weidinger S, Rodríguez E, Stahl C, Wagenpfeil S, Klopp N, Illig T, et al. Filaggrin mutations strongly predispose to early-onset and extrinsic atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2007; 127:724–726.
Article30. Rupnik H, Rijavec M, Korošec P. Filaggrin loss-of-function mutations are not associated with atopic dermatitis that develops in late childhood or adulthood. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 172:455–461.
Article31. Meng L, Wang L, Tang H, Tang X, Jiang X, Zhao J, et al. Filaggrin gene mutation c.3321delA is associated with various clinical features of atopic dermatitis in the Chinese Han population. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e98235.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Analysis of the Filaggrin Gene Polymorphism in Korean Atopic Dermatitis Patients
- Characteristic Clinical Features of Korean Atopic Dermatitis Patients with Interleukin-17 Receptor A Gene Mutation
- Comparison of Clinical Features according to FLG Mutation in Korean Atopic Dermatitis Patients
- Atopic dermatitis and skin barrier dysfunction
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability