J Korean Acad Nurs.
2016 Oct;46(5):630-641. 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.630.
A Prediction Model of Drug Misuse Behaviors in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Hanil University & Presbyterian Theological Seminary, Wanju, Korea. shhong7004@hanmail.net
- 2College of Nursing, Chonbuk National Universty, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2424636
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.630
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was designed to construct a model which explains drug misuse behaviors in community-dwelling older adults.
METHODS
The design of this research is a cross-sectional study using structure equation modeling. The hypothetical model consisted of two types of variables: the exogenous variables of health status, cognitive ability, and negative emotion, and the endogenous variables of number of drugs, and drug misuse behaviors. The data collection was conducted from September 2 to September 21, 2013 through self-report questionnaires. Participants were 320 community-dwelling adults over the age of 65 living in J city. Data were analyzed with SPSS 21.0 program and Amos 18.0 program.
RESULTS
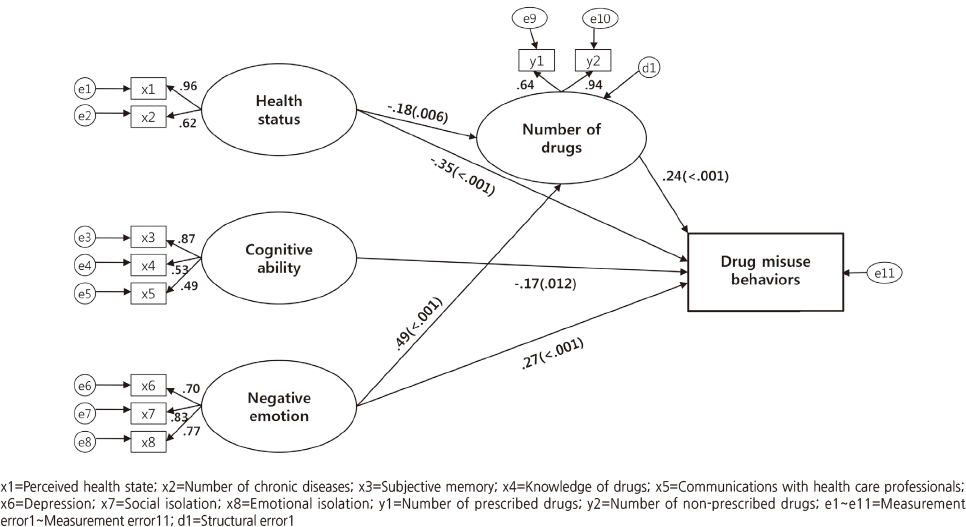
The results of the model fitness analysis were satisfied. The predictor variables for the hypothetical model explained 62.3% of variance regarding drug misuse behaviors. Drug misuse behaviors were directly affected by health status, cognitive ability, negative emotion and number of drugs and indirectly affected by health status, and negative emotion through number of drugs.
CONCLUSION
These findings indicate factors that should be used in developing effective nursing interventions for safe and proper drug use and the prevention of drug misuse behaviors in community-dwelling older adults.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Statistics Korea. Elderly statistics 2013 [Internet]. Daejeon: Author;2013. cited 2013 September 30. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/1/index.board?bmode=read&bSeq=&aSeq=308688&pageNo=1&rowNum=10&navCount=10&currPg=&sTarget=title&sTxt=0.2. Chung KH, Oh YH, Lee YK, Son CG, Park BM, Lee SY, et al. Report No.: Policy Report 2012-04. A survey of Korean older persons. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korean Institute of Health and Social Welfare;2012.3. Park M. Drug use in the elderly. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2008; 15(2):195–205.4. Jang SM, Park CM, Bae GR, Lee HJ, Kim HS. Report No.: Research Report 2010-13. Analysis of the factors related to the pharmaceutical expenditure of the National Health Insurance. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2011.5. Barat I, Andreasen F, Damsgaard EM. The consumption of drugs by 75-year-old individuals living in their own homes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2000; 56(6-7):501–509. DOI: 10.1007/s002280000157.6. Lee DY. Development and evaluation of preventive education program for medication misuse of the community dwelling elderly [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2002. 1–123.7. Jang IS. A study on the status of drug use in elders in KyongBuk province. J Korean Gerontol Nurs. 2007; 9(1):40–50.8. Pellegrino AN, Martin MT, Tilton JJ, Touchette DR. Medication therapy management services: Definitions and outcomes. Drugs. 2009; 69(4):393–406.9. Schonfeld L, King-Kallimanis BL, Duchene DM, Etheridge RL, Herrera JR, Barry KL, et al. Screening and brief intervention for substance misuse among older adults: The Florida BRITE project. Am J Public Health. 2010; 100(1):108–114. DOI: 10.2105/ajph.2008.149534.10. Heo YH. A study on drug awareness information, usage and misusage on elderly inpatients of veterans hospital. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2013; 14(9):4326–4334. DOI: 10.5762/KAIS.2013.14.9.4326.11. Lee JK. Factors associated with drug misuse behaviors among polypharmacy elderly. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2011; 23(6):554–563.12. Lee JH, Park M. The effects of an education program for safe drug use in the rural elderly. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2007; 37(3):295–304.13. Rhoades H, Wenzel SL. Correlates of prescription drug misuse among heterosexually active homeless men. Subst Abus. 2013; 34(2):143–149. DOI: 10.1080/08897077.2012.726960.14. Lin HY, Liao CC, Cheng SH, Wang PC, Hsueh YS. Association of potentially inappropriate medication use with adverse outcomes in ambulatory elderly patients with chronic diseases: Experience in a Taiwanese medical setting. Drugs Aging. 2008; 25(1):49–59. DOI: 10.2165/00002512-200825010-00006.15. Sergi G, De Rui M, Sarti S, Manzato E. Polypharmacy in the elderly: Can comprehensive geriatric assessment reduce inappropriate medication use? Drugs Aging. 2011; 28(7):509–518. DOI: 10.2165/11592010-000000000-00000.16. Murray RB, Huelskoetter MMW, O'Driscoll DL. The nursing process in later maturity. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall;1980. p. 1–630.17. Jamison RN, Edwards RR. Risk factor assessment for problematic use of opioids for chronic pain. Clin Neuropsychol. 2013; 27(1):60–80. DOI: 10.1080/13854046.2012.715204.18. Tsai R, Noone M, Johnson B, Pradeep VG, Verghese J. Potentially inappropriate medication use in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: Results from the Kerala Einstein study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012; 60(7):1369–1370. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04012.x.19. Deitz DK, Cook RF, Hendrickson A. Preventing prescription drug misuse: Field test of the SmartRx web program. Subst Use Misuse. 2011; 46(5):678–686. DOI: 10.3109/10826084.2010.528124.20. Keshishian F, Colodny N, Boone RT. Physician-patient and pharmacist-patient communication: Geriatrics' perceptions and opinions. Patient Educ Couns. 2008; 71(2):265–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2008.01.004.21. Martel MO, Dolman AJ, Edwards RR, Jamison RN, Wasan AD. The association between negative affect and prescription opioid misuse in patients with chronic pain: The mediating role of opioid craving. J Pain. 2014; 15(1):90–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.09.014.22. Harugeri A, Joseph J, Parthasarathi G, Ramesh M, Guido S. Potentially inappropriate medication use in elderly patients: A study of prevalence and predictors in two teaching hospitals. J Postgrad Med. 2010; 56(3):186–191. DOI: 10.4103/0022-3859.68642.23. Jyrkkä J, Enlund H, Korhonen MJ, Sulkava R, Hartikainen S. Patterns of drug use and factors associated with polypharmacy and excessive polypharmacy in elderly persons: Results of the Kuopio 75+ study: A cross-sectional analysis. Drugs Aging. 2009; 26(6):493–503. DOI: 10.2165/00002512-200926060-00006.24. Lee HS, Lim JH. Structural equation modeling with AMOS 20.0. Seoul: JipHyunJae Publishing Co.;2013. p. 1–319.25. Lawton MP, Moss M, Fulcomer M, Kleban MH. A research and service oriented multilevel assessment instrument. J Gerontol. 1982; 37(1):91–99. DOI: 10.1093/geronj/37.1.91.26. Troyer AK, Rich JB. Psychometric properties of a new metamemory questionnaire for older adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2002; 57(1):P19–P27. DOI: 10.1093/geronb/57.1.P19.27. Chin JH. Clinical subtypes and psychological characteristics of subjective memory complaints in older adults [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2011. p. 1–108.28. Hogan DB, Kwan M. Patient sheet: Tips for avoiding problems with polypharmacy. CMAJ. 2006; 175(8):876. DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.060888.29. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, Lum O, Huang V, Adey M, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res. 1982; 17(1):37–49. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3956(82)90033-4.30. Vincenzi H, Grabosky F. Measuring the emotional/social aspects of loneliness and isolation. J Soc Behav Pers. 1987; 2(2):257–270.31. Cha SE, Han GH, Lee JH. Relationship between self-rated health and physical · mental · social health: Differences among three aged group. J Korea Gerontol Soc. 2002; 22(1):173–190.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Structural Equation Model of Fall Prevention Behavior among Community-dwelling Older Adults with Osteoarthritis
- Development of a fall prediction model for community-dwelling older adults in South Korea using machine learning: a secondary data analysis
- Drug Use in the Elderly
- Linear Association between Frailty as Assessed by the Kihon Checklist and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study
- Health Literacy, Cancer Knowledge, and Cancer Preventive Behaviors among Rural Older Adults