Korean J Adult Nurs.
2015 Dec;27(6):684-694. 10.7475/kjan.2015.27.6.684.
A Structural Equation Model of Fall Prevention Behavior among Community-dwelling Older Adults with Osteoarthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Cheongju University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. songry@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2221722
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.6.684
Abstract
- PURPOSE
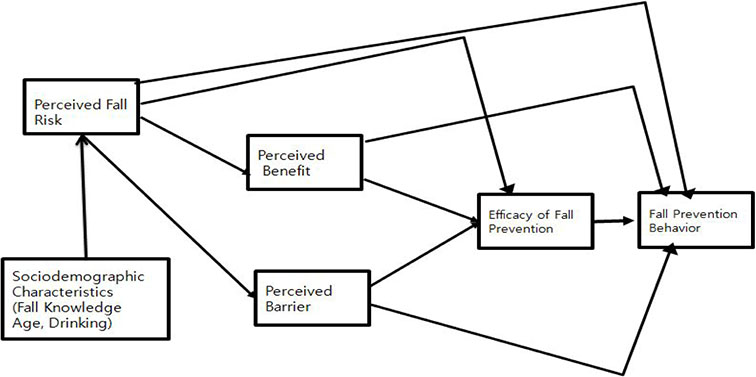
The purpose of this study was to explain fall prevention behaviors of community-dwelling elderly with osteoarthritis based on the Health Belief Model.
METHODS
A total of 200 older adults with osteoarthritis residing in community was recruited from July 10 to August 30, 2013. The direct and indirect effects of perceived fall risk, perceived benefits and barriers, and self efficacy of fall prevention were examined on fall prevention behaviors. Data were collected with structured questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS/WIN 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program.
RESULTS
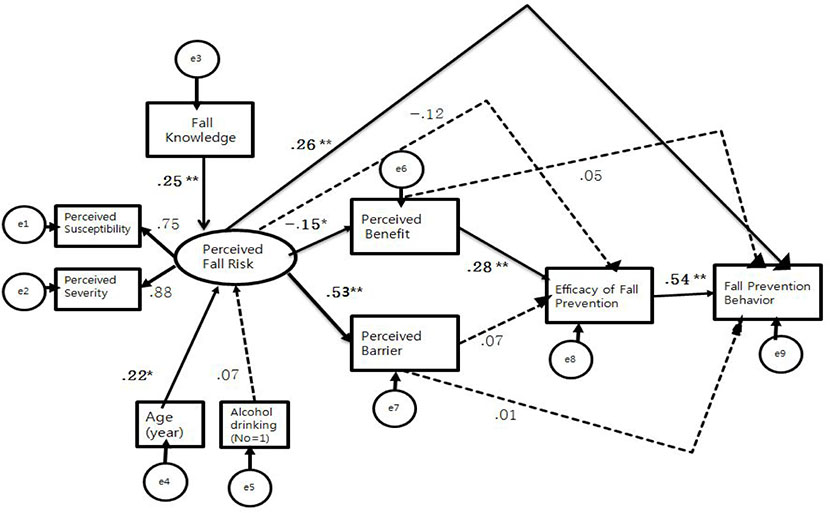
The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data based on the model fit indices. Among socio-demographic variables, age and fall knowledge showed significant direct effects on fall prevention behaviors. The constructed model explained 34.2% of the variance of fall prevention behaviors, including perceived fall risk and efficacy of fall prevention behaviors as significant predictors.
CONCLUSION
The findings revealed the need to develop an effective nursing intervention to promote fall prevention behaviors of community-dwelling elderly with osteoarthritis by focusing on perceived fall risk and efficacy of fall prevention behaviors. Knowledge about fall can also be increased by an age-based education program.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jang IS, Kim SM. A study on risk factors of injuries from fall experienced by home-staying elders in a provincial area. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2006; 8(2):107–116.2. Sturnieks DL, Tiedemann A, Chapman K, Munro B, Murray SM, Lord SR. Physiological risk factors for falls in older people with lower limb arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 2004; 31:2272–2279.3. Kannus P, Sievanen H, Palvanen M, Jarvinen T, Parkkari J. Prevention of falls and consequent injuries in elderly people. Lancet. 2005; 366(26):1885–1893. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67604-0.
Article4. Deandrea S, Lucenteforte E, Bravi F, Foschi R, La Vecchia C, Negri E. Risk factors for falls in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology. 2010; 21(5):658–668. DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181e89905.5. Todd C, Skelton D. What are the main risk factors for falls amongst older people and what are the most effective intervention to prevent these falls? Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe(Health Evidence Network report);2004. cited 2014 December 5. Available from: http://www.euro.who.int/document/E82552.pdf.6. Braun BL. Knowledge and perception of fall-related risk factors and fall-reduction techniques among communitydwelling elderly individuals. Physical Therapy. 1998; 78:1262–1276.
Article7. Stevens JA, Noonan RK, Rubenstein LZ. Older adult fall prevention: perceptions, beliefs, and behaviors. American Journal of Life style Medicine. 2010; 4(1):16–20. DOI: 10.1177/1559827609348350.
Article8. Yardley L, Bishop FL, Beyer N, Hauer K, Kempen GI, Piot-Ziegler C, et al. Older people's views of falls-prevention interventions in six European countries. Gerontologist. 2006; 46(5):650–660. DOI: 10.1093/geront/46.5.650.
Article9. Bunn F, Dickinson A, Barnett-Page E, Mcinnes E, Horton K. A systematic review of older people's perceptions of facilitators and barriers to participation in falls-prevention interventions. Ageing and Society. 2008; 28(4):449–472. DOI: 10.1017/S0144686X07006861.
Article10. Kim YH. Relations among fall efficacy, perception of fall risk and fall prevention behavior in the frail elderly at home. Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society. 2013; 14(7):3383–3389. DOI: 10.5762/KAIS.2013.14.7.3383.
Article11. Shin KR, Shin SJ, Kim JS, Kim JY. The effects of fall prevention program on knowledge, self-efficacy, and preventive activity related to fall, and depression of low-income elderly women. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005; 35(1):104–112.
Article12. Hyeon IS, Park MH, Park KM, Kim CN. The effects of a fall prevention program on the low-income elderly at risk of falls. Journal of Korean Academy Community Health Nursing. 2010; 21(2):200–209.
Article13. Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K. Health behavior and health education: theory, research, and practice. Australia: John Wiley & Sons;2008.14. Rosenstock IM, Strecher VJ, Becker MH. Social learning theory and the health belief model. Health Education & Behavior. 1988; 15(2):175–183.
Article15. Lee SH. Prediction model on osteoporosis prevention behavior in middle aged women. [dissertation]. Seoul: Korea University;2006.16. Jang HJ, Ahn SH. A predictive model of fall prevention behaviors in postmenopausal Women. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2014; 44(5):525–533. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.525.
Article17. Kim NS, Lee KE. Factors affecting cancer preventive behavior in middle-aged people. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2014; 21(1):29–38. DOI: 10.7739/jkafn.2014.21.1.29.
Article18. Kang JS, Kang HS, Yun EK, Choi HR. Factors influencing health behavior compliance of patients with metabolic syndrome. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2012; 24(2):191–199. DOI: 10.7475/kjan.2012.24.2.191.
Article19. Bae BY. Structural equation modeling with Amos 19: Principles and Practice. Seoul: Chunglam;2011.20. Hong CM. Development of a knowledge scale of fall risk factors for community-dwelling older adults. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2012; 24(3):244–252. DOI: 10.7475/kjan.2012.24.3.244.
Article21. Champion VL. Instrument development for health belief model constructs. Advances in Nursing Science. 1984; 6(3):73–85.
Article22. Moon JS. A study of instrument development for health belief of Korean adults. [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;1990.23. Clemson L, Cumming RG, Heard R. The development of an assessment to evaluate behavioral factors associated with falling. The American journal of occupational therapy. 2003; 57(4):380–388. DOI: 10.5014/ajot.57.4.380.
Article24. Finch JF, West SG. The investigation of personality structure: statistical models. Journal of Research in Personality. 1997; 31(4):439–485. DOI: 10.1006/jrpe.1997.2194.
Article25. Moon ES, Lee ES. The relationship between knowledge, health beliefs, and prevention behaviors of osteoporotic fracture in patients receiving osteoporosis treatment. Korean Society of Women Health Nursing. 2010; 16(2):147–156. DOI: 10.4069/kjwhn.2010.16.2.147.
Article26. Blalock SJ, DeVellis RF, Giorgino KB, DeVellis BM, Gold DT, Dooley MA, et al. Osteoporosis prevention in premenopausal women: using a stage model approach to examine the predictors of behavior. Health Psychology. 1996; 15(2):84.
Article27. Tinetti ME, Richman D, Powell L. Falls efficacy as a measure of fear of falling. Journal of gerontology. 1990; 45(6):239–243. DOI: 10.1093/geronj/45.6.P239.
Article28. Kwon MS. Relations among knowledge, fear and efficacy of falling the community dwelling elderly. Journal of Korean Academy Community Health Nursing. 2010; 21(2):139–147.29. Kim MH, Kim MS. A study on the relationships between knowledge about osteoporosis and cognitive factors in middle-aged women. Korean Society of Women Health Nursing. 2005; 11(1):52–57.
Article30. Shon YH. Predictive model for health promotion behavior of Korean patients on hemodialysis. [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2001.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of a Fall Prevention Program on Physical Fitness, Fall Efficacy and Fall Prevention Behavior among Community-dwelling Older Adults
- Development of a Knowledge Scale of Fall Risk Factors for Community-dwelling Older Adults
- Development of a fall prediction model for community-dwelling older adults in South Korea using machine learning: a secondary data analysis
- Fall Risk Home Environment and Fall Experiences among Community-Dwelling Older People
- The Association of Family and Friend Networks with Appetite: Structural Equation Modeling of the Indirect Effects of Depression among Community-Dwelling Older Adults