J Korean Acad Nurs.
2018 Oct;48(5):588-600. 10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.588.
A Structural Model on the Nursing Competencies of Nursing Simulation Learners
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Andong Science College, Andong, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Konkuk University GLOCAL Campus, Chungju, Korea. esji@kku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2424365
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.588
Abstract
- PURPOSE
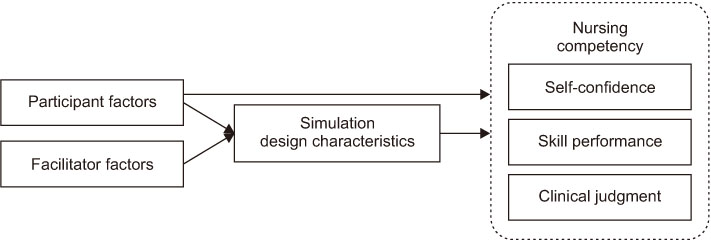
The purpose of this study was to test a model of nursing competencies of nursing simulation learners. The conceptual model was based on the theory of Jeffries's simulaton theory.
METHODS
Data collection was conducted in October 2017 for 310 students from two nursing universities in Kyungbuk area for 20 days. Data analysis methods were covariance structure analysis using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 22.0 statistical programs.
RESULTS
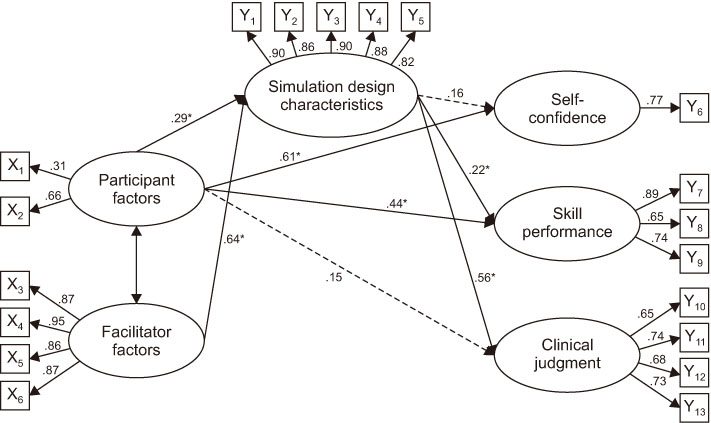
The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were comparative fit index=.97, normed fit index=.94, Tucker-Lewis Index=.97, root mean square error of approximation=.44, and standardized root mean square residual=.04. Teacher factors were directly related to simulation design characteristics, and it was confirmed that the curriculum, classroom operation and teaching method of the instructors were important factors. Learner factors were found to have a direct effect on nursing competence, self-confidence, and clinical performance that belong to nursing capacity. In particular, the results of this study indicate that the simulation design characteristics have a partial mediating effect on learner factors and clinical performance, and a complete mediating effect on learner factors and clinical judgment ability.
CONCLUSION
In order to improve the learner's clinical performance and clinical judgment ability, it is necessary to conduct practical training through nursing simulation besides preparing the learner and the educator.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Comparative Study on Learning Outcomes according to the Integration Sequences of S-PBL in Nursing Students: Randomized Crossover Design
So Young Yun, Ja Yun Choi
J Korean Acad Nurs. 2019;49(1):92-103. doi: 10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.92.Does a preterm labor-assessment algorithm improve preterm labor-related knowledge, clinical practice confidence, and educational satisfaction?: a quasi-experimental study
Hee-Young Choi, Jeung-Im Kim
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2023;29(3):219-228. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2023.08.17.
Reference
-
1. Hyun MS, Yoo MS, Song MS, Park J. Development of the nursing practice capacity scale for evaluating achievement of nursing education objectives. J Korean Acad Soc Home Care Nurs. 2015; 22(2):246–255.2. Rideuot E, Barbara C. The problem-based learning model of nursing education. In : Rideuot E, editor. Transforming Nursing Education Through Problem-Based Learning. Sudbury (MA): Jones and Bartlett Publishers;2001. p. 21–49.3. Lim KC. Planning and applying simulation-based practice for the achievement of program outcomes in nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2015; 21(3):393–405. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2015.21.3.393.
Article4. Arthur C, Kable A, Levett-Jones T, Tracy LJ. Human patient simulation manikins and information communication technology use in Australian schools of nursing: A cross-sectional survey. Clin Simul Nurs. 2011; 7(6):e219–e227. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2010.03.002.
Article5. O'Shea KL. Staff development nursing secrets. Philadelphia (PA): Hanley & Belfus;2002. p. 1–27.6. Lee CM, So HS, Kim YK, Kim JE, An MJ. The effects of high fidelity simulation-based education on clinical competence and confidence in nursing students: A systematic review. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2014; 14(10):850–861. DOI: 10.5392/JKCA.2014.14.10.850.
Article7. Lim KC. Simulation-based clinical judgment and performance ability for tracheal suction in nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2017; 23(3):330–340. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2017.23.3.330.
Article8. Hur HK, Song HY. Effects of simulation-based clinical reasoning education and evaluation of perceived education practices and simulation design characteristics by students nurses. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2015; 15(3):206–218. DOI: 10.5392/JKCA.2015.15.03.206.
Article9. Jeffries PR. A framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating simulations used as teaching strategies in nursing. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2005; 26(2):96–103.10. Ironside PM, Jeffries PR, Martin A. Fostering patient safety competencies using multiple-patient simulation experiences. Nurs Outlook. 2009; 57(6):332–337. DOI: 10.1016/j.outlook.2009.07.010.
Article11. Jansen DA, Johnson N, Larson G, Berry C, Brenner GH. Nursing faculty perceptions of obstacles to utilizing manikin-based simulations and proposed solutions. Clin Simul Nurs. 2009; 5(1):e9–e16. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2008.09.004.
Article12. Mills J, Field J, Cant R. The place of knowledge and evidence in the context of Australian general practice nursing. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2009; 6(4):219–228. DOI: 10.1111/j.1741-6787.2009.00163.x.
Article13. O'Donnell JM, Decker S, Howard V, Levett-Jones T, Miller CW. NLN/Jeffries simulation framework state of the science project: Simulation learning outcomes. Clin Simul Nurs. 2014; 10(7):373–382. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2014.06.004.14. Gates MG, Parr MB, Hughen JE. Enhancing nursing knowledge using high-fidelity simulation. J Nurs Educ. 2012; 51(1):9–15. DOI: 10.3928/01484834-20111116-01.
Article15. Arries E. Practice standards for quality clinical decision-making in nursing. Curationis. 2006; 29(1):62–72. DOI: 10.4102/curationis.v29i1.1052.
Article16. Shin KR, Hwang JW, Shin SJ. Concept analysis on the clinical critical thinking ability in nursing. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2008; 20(5):707–718.17. Jung MS, Kwon HJ. A structural equation model on core competencies of nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2015; 21(2):256–265. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2015.21.2.256.
Article18. International Nursing Association for Clinical Simulation and Learning (INACSL). INACSL standards of best practice: SimulationSM simulation design. Clin Simul Nurs. 2016; 12:Suppl. S5–S12. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2016.09.005.19. National League for Nursing (NLN). 2006 a guide to state approved schools of nursing. Washington DC: NLN;c2006. cited 2017 Nov 16. Available from: http://www.nln.org/docs/default-source/professional-development-programs/nln-instrument_simulation-design-scale.pdf?sfvrsn=0.20. Kim YH, Jang KS. Effect of a simulation-based education on cardio-pulmonary emergency care knowledge, clinical performance ability and problem solving process in new nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(2):245–255. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.245.
Article21. Lee WH, Kim JJ, Yoo JS, Hur HK, Kim KS, Lim SM. Development of clinical performance measurement tools for nursing students. J Yonsei Coll Nurs. 1990; 13:17–29.22. Lejonqvist GB, Eriksson K, Meretoja R. Evidence of clinical competence. Scand J Caring Sci. 2012; 26(2):340–348. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2011.00939.x.
Article23. Yang JJ. The effects of a simulation-based education on the knowledge and clinical competence for nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012; 18(1):14–24. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2012.18.1.014.24. Keller JM. Strategies for stimulating the motivation to learn. Perform Improv. 1987; 26(8):1–7. DOI: 10.1002/pfi.4160260802.
Article25. Foronda C, Liu S, Bauman EB. Evaluation of simulation in undergraduate nurse education: An integrative review. Clin Simul Nurs. 2013; 9(10):e409–e416. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2012.11.003.
Article26. Ha EH, Song HS. The effects of structured self-debriefing using on the clinical competency, self-efficacy, and educational satisfaction in nursing students after simulation. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2015; 21(4):445–454. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2015.21.4.445.
Article27. Baillie L, Joan C. Students' and facilitators' perceptions of simulation in practice learning. Nurse Educ Pract. 2009; 9(5):297–306. DOI: 10.1016/j.nepr.2008.08.007.
Article28. Jöreskog KG, Sörbom D. LISREL 7: A guide to the program and applications. 2nd ed. Chicago (IL): SPSS;1989. p. 1–11.29. Bae BR. Structural equation modeling with Amos 24. Seoul: Chenngram Books;2017. p. 76–309.30. Reeve MM. Development of an instrument to measure effectiveness of clinical instructors. J Nurs Educ. 1994; 33(1):15–20.
Article31. Choi MS. A Study on the relationship between teaching effectiveness of clinical nursing education and clinical performance in nursing students [master's thesis]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2005. 1–68.32. Lynn MR. Determination and quantification of content validity. Nurs Res. 1986; 35(6):382–386. DOI: 10.1097/00006199-198611000-00017.
Article33. Yoo JH. Factors influencing nursing students' flow experience and clinical competency in simulation-based education: Based on Jeffries's simulation model [master's thesis]. Seoul: Sungshin University;2016. 1–71.34. Schwirian PM. Evaluating the performance of nurses: A multi-dimensional approach. Nurs Res. 1978; 27(6):347–351.35. Shim KK, Shin H. The reliability and validity of the lasater clinical judgement rubric in Korean nursing students [master's thesis]. Seoul: Kyunghee University;2012. 1–64.36. Lasater K. High-fidelity simulation and the development of clinical judgment: Students' experiences. J Nurs Educ. 2007; 46(6):269–276.
Article37. Kim EJ, Lee NJ. Significance test of mediation effect by bootstrapping method. Korean J Meas Eval Phys Educ Sport Sci. 2013; 15(3):15–25.38. Shim CS, Park MK, Kim JH. Effects of simulation-based delivery education regarding to obstetric clinical practice before and after of nursing students. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2014; 18(1):125–133.39. Kim JH, Park IH, Shin SJ. Systematic review of Korean studies on simulation within nursing education. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2013; 19(3):307–319. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2013.19.3.307.
Article40. Lee SJ, Park YM, Noh SM. The effects of simulation training with hybrid model for nursing students on nursing performance ability and self confidence. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2013; 25(2):170–182. DOI: 10.7475/kjan.2013.25.2.170.
Article41. Flynn K. The use of standardized patients to minimize anxiety in undergraduate nursing students in the clinical setting [master's thesis]. St Paul (MN): St. Catherine University;2012. 1–25.42. Song MR, Kim EM, Yu SJ. Aanalysis on the competency of nursing students' basic nursing skills. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2012; 12(6):390–401. DOI: 10.5392/JKCA.2012.12.06.390.
Article43. Kim SG. Effects of a simulation-based high-risk neonatal care education on learning satisfaction, class participation, learning motivation and clinical competency in nursing students. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2015; 16(10):6807–6815. DOI: 10.5762/KAIS.2015.16.10.6807.
Article44. McCormick K. The effect of learning styles, critical thinking disposition, and critical thinking on clinical judgment in senior baccalaureate nursing students during human patient simulation [dissertation]. Baton Rouge (LA): Southern University and A&M College;2014. 1–124.45. Suh YO, Ahn YH, Park KS. Content analysis of experience of nursing students in clinical judgment during nursing practicum. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2009; 21(2):245–256.46. Kang SH. Relationships between major satisfaction and career decision efficacy and career attitude maturity of engineering college students. J Fish Mar Sci Educ. 2010; 22(2):151–164.47. Kim DH, Lee YJ, Hwang MS, Park JH, Kim HS, Cha HG. Effects of a simulation-based integrated clinical practice program (SICPP) on the problem solving process, clinical competence and critical thinking in a nursing student. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012; 18(3):499–509. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2012.18.3.499.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Concept Analysis of 'Facilitator' in Simulation Nursing Education
- A Structural Equation Model on Core Competencies of Nursing Students
- Nursing Students' Experiences of Virtual and Hybrid Simulation in Gerontological Nursing: A Mixed-Methods Study
- Improving clinical reasoning competency and communication skills using virtual simulation-based learning focused on a pathophysiological approach in Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- Effectiveness of the Infectious Disease (COVID-19) Simulation Module Program on Nursing Students: Disaster Nursing Scenarios