Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2018 Oct;6(2):54-59. 10.14791/btrt.2018.6.e12.
A Retrospective Analysis of the Clinical Outcomes of Leptomeningeal Metastasis in Patients with Solid Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hemato-Oncology, Pusan University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gaspel Hospital, Busan, Korea. byule00@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2423974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2018.6.e12
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) is an uncommon, but devastating complication of advanced cancer and has no standard treatment. Herein, we analyzed the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with solid tumors who were diagnosed with LM.
METHODS
Between January 2007 and December 2017, we retrospectively analyzed the medical records of patients with solid tumors who were diagnosed with LM.
RESULTS
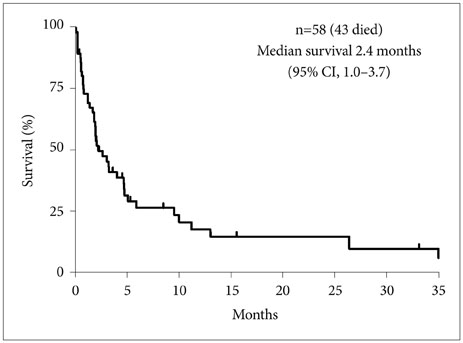
A total of 58 patients were enrolled in this study. The median age of patients was 51 years (range, 27-72 years), and 62.1% had a poor Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) (>2). The common types of primary tumor were breast cancer (39.7%), gastric cancer (25.9%), and non-small cell lung cancer (20.7%). Forty-two patients (72.4%) were diagnosed with LM by MRI of the brain and/or spine and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, 14 were diagnosed by CSF analysis alone, and 2 were diagnosed by MRI alone. Treatments for LM were performed in 53 patients (91.4%), and best supportive care was provided for 5 patients (8.6%). Intrathecal chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and systemic chemotherapy were administered in 43 (74.1%), 17 (29.3%), and 24 (41.4%) patients, respectively. The median overall survival of the entire cohort was 2.4 months (95% confidence interval, 1.0-3.7). In the analysis of prognostic factors for survival, a good ECOG PS (≤2), administration of systemic chemotherapy after LM diagnosis, and a prior history of brain radiation were associated with prolonged survival.
CONCLUSION
Although the prognosis of LM in patients with solid tumors is poor, systemic chemotherapy might improve survival in selected patients with a good PS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Posner JB, Chernik NL. Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol. 1978; 19:579–592.2. Wasserstrom WR, Glass JP, Posner JB. Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors: experience with 90 patients. Cancer. 1982; 49:759–772.
Article3. Pavlidis N. The diagnostic and therapeutic management of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:Suppl 4. iv285–iv291.
Article4. Taillibert S, Laigle-Donadey F, Chodkiewicz C, Sanson M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY. Leptomeningeal metastases from solid malignancy: a review. J Neurooncol. 2005; 75:85–99.
Article5. Herrlinger U, Förschler H, Küker W, et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis: survival and prognostic factors in 155 patients. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 223:167–178.
Article6. Waki F, Ando M, Takashima A, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. J Neurooncol. 2009; 93:205–212.
Article7. Clarke JL, Perez HR, Jacks LM, Panageas KS, Deangelis LM. Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology. 2010; 74:1449–1454.
Article8. Oechsle K, Lange-Brock V, Kruell A, Bokemeyer C, de Wit M. Prognostic factors and treatment options in patients with leptomeningeal metastases of different primary tumors: a retrospective analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010; 136:1729–1735.
Article9. Pentheroudakis G, Pavlidis N. Management of leptomeningeal malignancy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005; 6:1115–1125.
Article10. Chamberlain MC. Combined-modality treatment of leptomeningeal gliomatosis. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52:324–329.
Article11. Du C, Hong R, Shi Y, Yu X, Wang J. Leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors: a single center experience in Chinese patients. J Neurooncol. 2013; 115:285–291.
Article12. Kwon J, Chie EK, Kim K, et al. Impact of multimodality approach for patients with leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1094–1101.
Article13. Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Glantz LK, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in patients with cancer: minimizing false-negative results. Cancer. 1998; 82:733–739.
Article14. Prömmel P, Pilgram-Pastor S, Sitter H, Buhk JH, Strik H. Neoplastic meningitis: how MRI and CSF cytology are influenced by CSF cell count and tumor type. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013; 2013:248072.
Article15. Hyun JW, Jeong IH, Joung A, Cho HJ, Kim SH, Kim HJ. Leptomeningeal metastasis: clinical experience of 519 cases. Eur J Cancer. 2016; 56:107–114.
Article16. Palma JA, Fernandez-Torron R, Esteve-Belloch P, et al. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: prognostic value of clinical, cerebrospinal fluid, and neuroimaging features. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:19–25.
Article17. Brower JV, Saha S, Rosenberg SA, Hullett CR, Ian Robins H. Management of leptomeningeal metastases: prognostic factors and associated outcomes. J Clin Neurosci. 2016; 27:130–137.
Article18. Chamberlain MC, Johnston SK, Glantz MJ. Neoplastic meningitis-related prognostic significance of the Karnofsky performance status. Arch Neurol. 2009; 66:74–78.
Article19. Freilich RJ, Krol G, DeAngelis LM. Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann Neurol. 1995; 38:51–57.
Article20. Boogerd W, van den Bent MJ, Koehler PJ, et al. The relevance of intraventricular chemotherapy for leptomeningeal metastasis in breast cancer: a randomised study. Eur J Cancer. 2004; 40:2726–2733.
Article21. Lee DW, Lee KH, Kim JW, Keam B. Molecular targeted therapies for the treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: current evidence and future directions. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:1074.
Article22. Liao BC, Lee JH, Lin CC, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for non-small-cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Thorac Oncol. 2015; 10:1754–1761.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Breast Cancer with Leptomeningeal Metastasis
- Chest Wall Pain as the Presenting Symptom of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- A Case of Leptomeningeal Metastasis Associated with Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
- Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Level of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Patients with Leptomeningeal Carcinomatous Metastasis
- Malignant Ascites after Subduroperitoneal Shunt in a Patient with Leptomeningeal Metastasis