Korean J Pain.
2018 Oct;31(4):253-260. 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.4.253.
Therapeutic alternatives in painful diabetic neuropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pain Clinic, University Hospital Virgen del RocÃo, Seville, Spain. samuelvilarpalomo@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Nursing, Physiotherapy and Podiatry, University of Seville, Seville, Spain.
- 3Department of Nursing, Physiotherapy and Podiatry, University Hospital Cruz Roja, Seville, Spain.
- KMID: 2421516
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2018.31.4.253
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
One of the most frequent problems caused by diabetes is the so called painful diabetic neuropathy. This condition can be treated through numerous types of therapy. The purpose of this study was to analyze, as a meta-analysis, different treatments used to alleviate painful diabetic neuropathy, with the aim of generating results that help making decisions when applying such treatments to tackle this pathology.
METHODS
A search was conducted in the main databases for Health Sciences, such as PUBMED, Web of Science (WOS), and IME biomedicina (Spanish Medical Reports in Biomedicine), to gather randomized controlled trials about treatments used for painful diabetic neuropathy. The analyzed studies were required to meet the inclusion criteria selected, especially those results related to pain intensity.
RESULTS
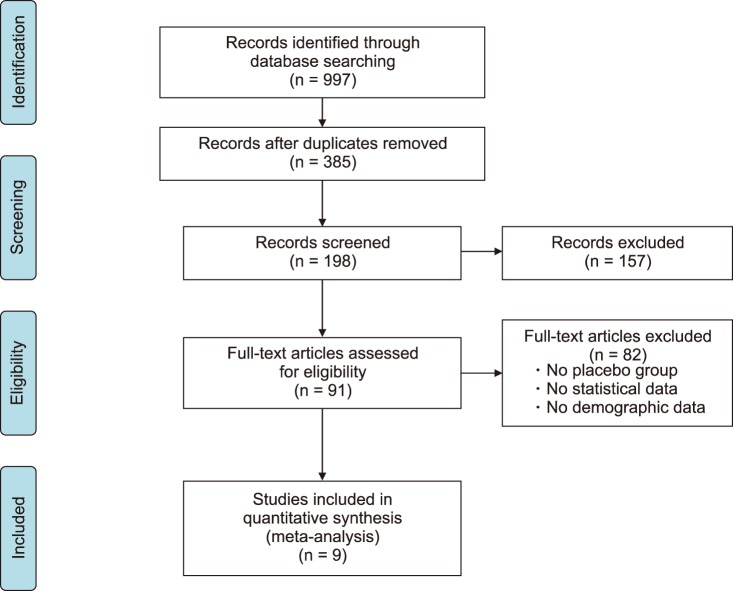
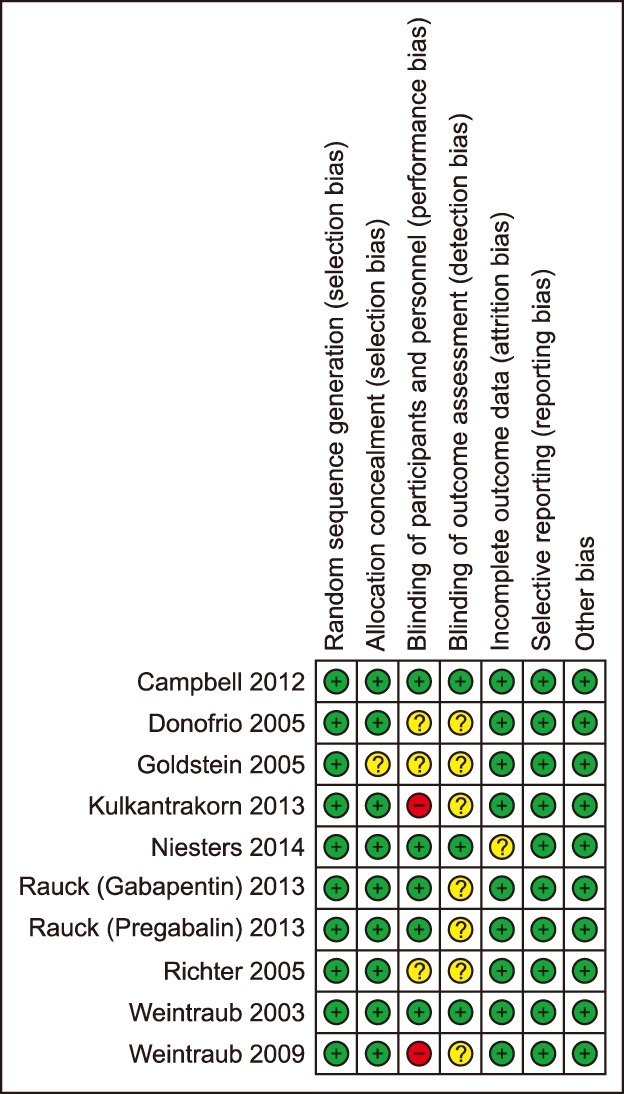
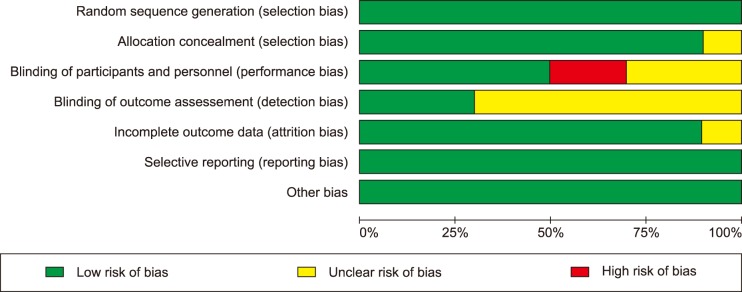
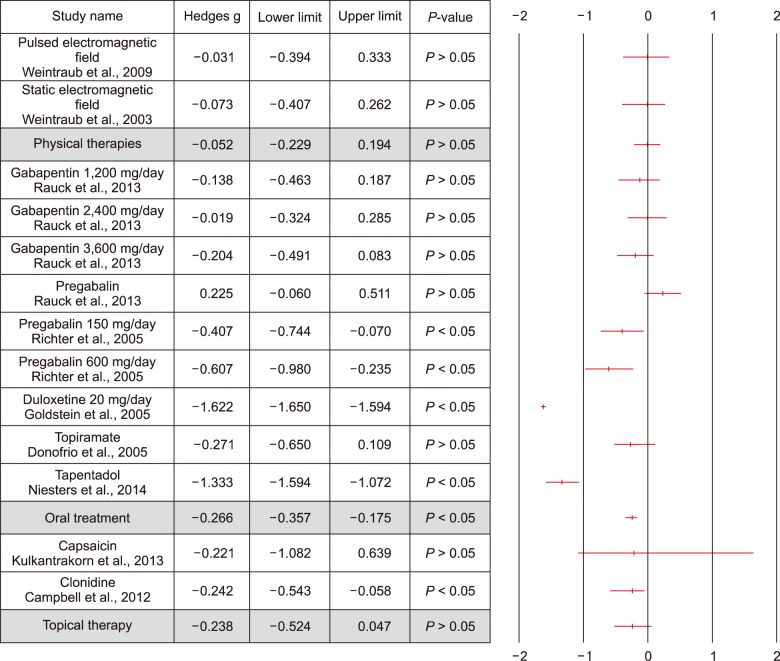
Nine randomized controlled trials were chosen. The meta-analysis shows significant positive effects for those treatments based on tapentadol [g: −1.333, 95% CI (−1.594; −1.072), P < 0.05], duloxetine [g: −1.622, 95 % CI (−1.650; −1.594), P < 0.05], pregabalin [g: −0.607, 95% CI (−0.980; −0.325), P < 0.05], and clonidine [g: −0.242, 95 % CI (−0.543; −0.058), P < 0.05].
CONCLUSIONS
This meta-analysis indicates the effectiveness of the treatments based on duloxetine, gabapentin and pregabalin, as well as other drugs, such as tapentadol and topic clonidine, whose use is better prescribed in more specific situations. The results provided can help increase the knowledge about the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy and also in the making of clinical practice guidelines for healthcare professionals.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Perioperative duloxetine as part of a multimodal analgesia regime reduces postoperative pain in lumbar canal stenosis surgery: a randomized, triple blind, and placebo-controlled trial
Nishith Govil, Kumar Parag, Pankaj Arora, Hariom Khandelwal, Ashutosh Singh, Ruchi
Korean J Pain. 2020;33(1):40-47. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.1.40.
Reference
-
1. Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017; 128:40–50. PMID: 28437734.
Article2. Asociación Española de Enfermería Vascular y Heridas (AEEVH). Guía de práctica clínica: consenso sobre úlceras vasculares y pie diabético. Segunda edición. Seville: Asociación Española de Enfermería Vascular y Heridas;2014. p. 1–90.3. Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:956–962. PMID: 15793206.4. Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpää M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:1113–1123. e67–e88. PMID: 20402746.
Article5. Stein C, Eibel B, Sbruzzi G, Lago PD, Plentz RD. Electrical stimulation and electromagnetic field use in patients with diabetic neuropathy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2013; 17:93–104. PMID: 23778776.
Article6. Schreiber AK, Nones CF, Reis RC, Chichorro JG, Cunha JM. Diabetic neuropathic pain: physiopathology and treatment. World J Diabetes. 2015; 6:432–444. PMID: 25897354.
Article7. Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, Backonja M, Cohen J, Del Toro D, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American academy of neurology, the American association of neuromuscular and electrodiagnostic medicine, and the American academy of physical medicine and rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011; 76:1758–1765. PMID: 21482920.
Article8. Park HJ, Moon DE. Pharmacologic management of chronic pain. Korean J Pain. 2010; 23:99–108. PMID: 20556211.
Article9. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Reprint--preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Phys Ther. 2009; 89:873–880. PMID: 19723669.
Article10. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17:1–12. PMID: 8721797.
Article11. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011; 343:d5928. PMID: 22008217.
Article12. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [Internet]. London: The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. updated March 2011. cited 2018 March 3. Available at http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/.13. Goldstein DJ, Lu Y, Detke MJ, Lee TC, Iyengar S. Duloxetine vs. placebo in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain. 2005; 116:109–118. PMID: 15927394.
Article14. Niesters M, Proto PL, Aarts L, Sarton EY, Drewes AM, Dahan A. Tapentadol potentiates descending pain inhibition in chronic pain patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Br J Anaesth. 2014; 113:148–156. PMID: 24713310.
Article15. Richter RW, Portenoy R, Sharma U, Lamoreaux L, Bockbrader H, Knapp LE. Relief of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy with pregabalin: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Pain. 2005; 6:253–260. PMID: 15820913.
Article16. Campbell CM, Kipnes MS, Stouch BC, Brady KL, Kelly M, Schmidt WK, et al. Randomized control trial of topical clonidine for treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain. 2012; 153:1815–1823. PMID: 22683276.
Article17. Rauck R, Makumi CW, Schwartz S, Graff O, Meno-Tetang G, Bell CF, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain Pract. 2013; 13:485–496. PMID: 23186035.
Article18. Weintraub MI, Herrmann DN, Smith AG, Backonja MM, Cole SP. Pulsed electromagnetic fields to reduce diabetic neuropathic pain and stimulate neuronal repair: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:1102–1109. PMID: 19577022.
Article19. Weintraub MI, Wolfe GI, Barohn RA, Cole SP, Parry GJ, Hayat G, et al. Static magnetic field therapy for symptomatic diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:736–746. PMID: 12736891.
Article20. Donofrio PD, Raskin P, Rosenthal NR, Hewitt DJ, Jordan DM, Xiang J, et al. Safety and effectiveness of topiramate for the management of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in an open-label extension study. Clin Ther. 2005; 27:1420–1431. PMID: 16291415.
Article21. Kulkantrakorn K, Lorsuwansiri C, Meesawatsom P. 0.025% capsaicin gel for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2013; 13:497–503. PMID: 23228119.
Article22. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Neuropathic pain in adults: the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in adults in non-specialist settings. NICE clinical guideline. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence;2013.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of Intractable Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: The Perspective of a Pain Specialist
- Prophylactic efficacy of probiotics on travelers' diarrhea: an adaptive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Design and Conduct of Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
- Clinical spectrum and diagnosis of diabetic neuropathies
- Meta-Analysis and Quality Assessment of Randomized Controlled Trials