J Breast Cancer.
2018 Sep;21(3):288-296. 10.4048/jbc.2018.21.e34.
High RNA-binding Motif Protein 3 Expression Is Associated with Improved Clinical Outcomes in Invasive Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. pathol72@gmail.com
- 3Institute for Cancer Research, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2421369
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2018.21.e34
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Expression of RNA-binding motif protein 3 (RBM3) is induced by hypoxia and hypothermia. Recently, high expression of RBM3 was reported to be associated with a good prognosis in colon cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and malignant melanoma. Studies on RBM3 in invasive breast carcinoma (IBC), however, are limited.
METHODS
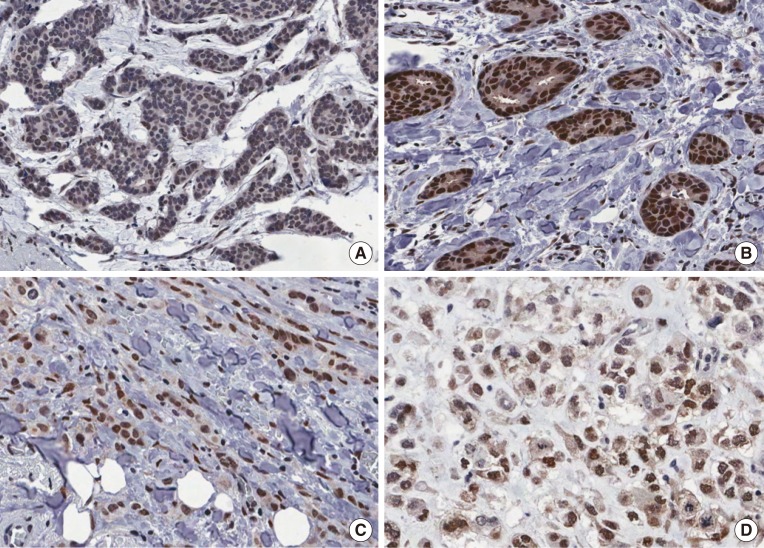
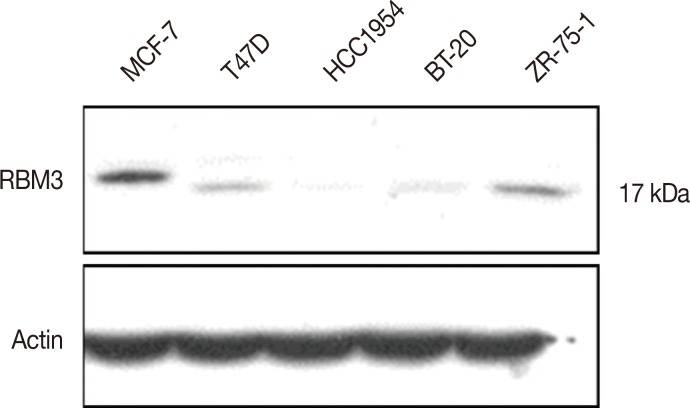
RBM3 expression was examined using a tissue microarray from 361 patients with IBC. Immunohistochemistry was performed for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and Ki-67 to compare the expression of these markers. For scoring of RBM3 expression, NF (nuclear staining fraction)×NI (nuclear staining intensity) was used. The RBM3 expression score was considered indicative of either low (≤4) or high (>4) expression. Western blot analysis was performed on breast cancer cell lines to evaluate RBM3 expression.
RESULTS
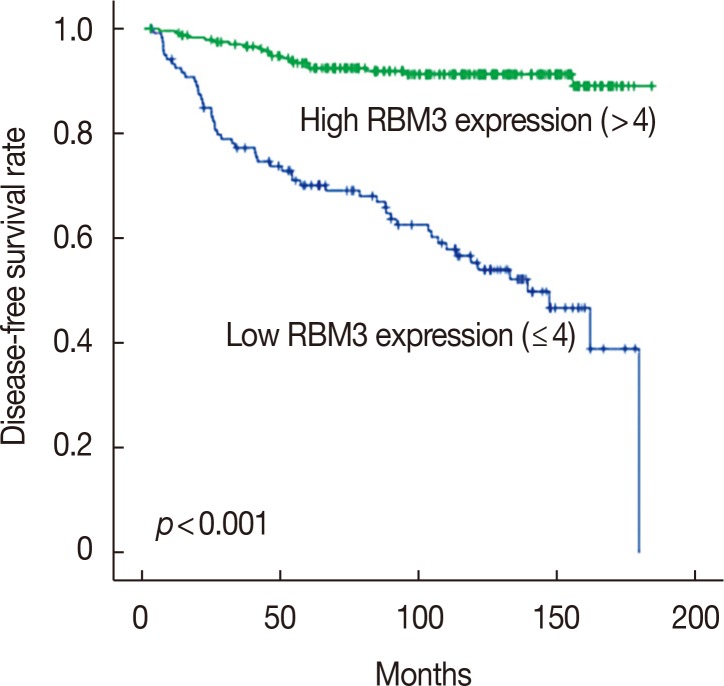
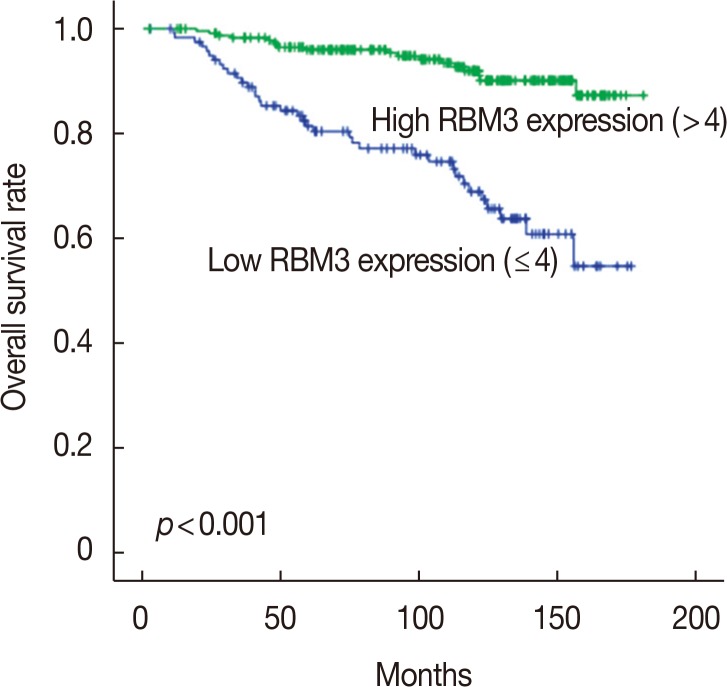
Of the total 361 samples, 240 (66.5%) exhibited high RBM3 expression. High RBM3 expression was significantly associated with positivity for ER (p < 0.001), PR (p < 0.001), T stage (p < 0.001), histologic grade (p < 0.001), and % Ki-67 staining (p=0.004). Multivariate analysis revealed that high RBM3 expression was closely associated with prolonged disease-free survival (DFS) (p < 0.001) and overall survival (OS) (p < 0.001). Western blot analysis revealed reduced RBM3 expression in HCC1954 (HER2-enriched) and BT-20 (basal-like) cells with an aggressive phenotype.
CONCLUSION
High nuclear RBM3 expression is strongly associated with a prolonged DFS and OS. Furthermore, RBM3 expression is closely associated with good prognostic markers such as ER and PR in IBC. High nuclear RBM3 expression is, therefore, a critical biomarker of favorable clinical outcomes in IBC.
MeSH Terms
-
Anoxia
Blotting, Western
Breast Neoplasms*
Breast*
Cell Line
Colonic Neoplasms
Disease-Free Survival
Estrogens
Humans
Hypothermia
Immunohistochemistry
Melanoma
Multivariate Analysis
Ovarian Neoplasms
Phenotype
Prognosis
Prostatic Neoplasms
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Receptors, Progesterone
RNA-Binding Proteins
Estrogens
RNA-Binding Proteins
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Receptors, Progesterone
Figure
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108. PMID: 25651787.
Article2. Oh CM, Won YJ, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Cho H, Lee JK, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2013. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:436–450. PMID: 26987395.
Article3. Prat A, Perou CM. Deconstructing the molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2011; 5:5–23. PMID: 21147047.
Article4. Eroles P, Bosch A, Pérez-Fidalgo JA, Lluch A. Molecular biology in breast cancer: intrinsic subtypes and signaling pathways. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012; 38:698–707. PMID: 22178455.
Article5. Diaz LK, Cryns VL, Symmans WF, Sneige N. Triple negative breast carcinoma and the basal phenotype: from expression profiling to clinical practice. Adv Anat Pathol. 2007; 14:419–430. PMID: 18049131.
Article6. Rakha EA, Ellis IO. Triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer: review. Pathology. 2009; 41:40–47. PMID: 19089739.
Article7. Derry JM, Kerns JA, Francke U. RBM3, a novel human gene in Xp11.23 with a putative RNA-binding domain. Hum Mol Genet. 1995; 4:2307–2311. PMID: 8634703.
Article8. Danno S, Nishiyama H, Higashitsuji H, Yokoi H, Xue JH, Itoh K, et al. Increased transcript level of RBM3, a member of the glycine-rich RNA-binding protein family, in human cells in response to cold stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997; 236:804–807. PMID: 9245737.
Article9. Sutherland LC, Rintala-Maki ND, White RD, Morin CD. RNA binding motif (RBM) proteins: a novel family of apoptosis modulators? J Cell Biochem. 2005; 94:5–24. PMID: 15514923.
Article10. Martínez-Arribas F, Agudo D, Pollán M, Gómez-Esquer F, Díaz-Gil G, Lucas R, et al. Positive correlation between the expression of X-chromosome RBM genes (RBMX, RBM3, RBM10) and the proapoptotic Bax gene in human breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2006; 97:1275–1282. PMID: 16552754.11. Uhlén M, Björling E, Agaton C, Szigyarto CA, Amini B, Andersen E, et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005; 4:1920–1932. PMID: 16127175.
Article12. Jögi A, Brennan DJ, Rydén L, Magnusson K, Fernö M, Stål O, et al. Nuclear expression of the RNA-binding protein RBM3 is associated with an improved clinical outcome in breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 2009; 22:1564–1574. PMID: 19734850.
Article13. Ehlén A, Brennan DJ, Nodin B, O’Connor DP, Eberhard J, Alvarado-Kristensson M, et al. Expression of the RNA-binding protein RBM3 is associated with a favourable prognosis and cisplatin sensitivity in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Transl Med. 2010; 8:78. PMID: 20727170.
Article14. Jonsson L, Gaber A, Ulmert D, Uhlén M, Bjartell A, Jirström K. High RBM3 expression in prostate cancer independently predicts a reduced risk of biochemical recurrence and disease progression. Diagn Pathol. 2011; 6:91. PMID: 21955582.
Article15. Florianova L, Xu B, Traboulsi S, Elmansi H, Tanguay S, Aprikian A, et al. Evaluation of RNA-binding motif protein 3 expression in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: an immunohistochemical study. World J Surg Oncol. 2015; 13:317. PMID: 26577765.
Article16. Jang HH, Lee HN, Kim SY, Hong S, Lee WS. Expression of RNA-binding motif protein 3 (RBM3) and cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) is associated with improved clinical outcome in patients with colon cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017; 37:1779–1785. PMID: 28373441.17. Edge SB. American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC cancer staging handbook: from the AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer;2010.18. Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer (unabridged version). Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010; 134:e48–e72. PMID: 20586616.19. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3997–4013. PMID: 24101045.
Article20. Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ, et al. Strategies for subtypes: dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011; 22:1736–1747. PMID: 21709140.21. Burd CG, Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994; 265:615–621. PMID: 8036511.
Article22. Pilotte J, Dupont-Versteegden EE, Vanderklish PW. Widespread regulation of miRNA biogenesis at the Dicer step by the cold-inducible RNA-binding protein, RBM3. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e28446. PMID: 22145045.
Article23. Grupp K, Wilking J, Prien K, Hube-Magg C, Sirma H, Simon R, et al. High RNA-binding motif protein 3 expression is an independent prognostic marker in operated prostate cancer and tightly linked to ERG activation and PTEN deletions. Eur J Cancer. 2014; 50:852–861. PMID: 24380696.
Article24. Boman K, Segersten U, Ahlgren G, Eberhard J, Uhlén M, Jirström K, et al. Decreased expression of RNA-binding motif protein 3 correlates with tumour progression and poor prognosis in urothelial bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2013; 13:17. PMID: 23565664.
Article25. Ehlén Å, Nodin B, Rexhepaj E, Brändstedt J, Uhlén M, Alvarado-Kristensson M, et al. RBM3-regulated genes promote DNA integrity and affect clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer. Transl Oncol. 2011; 4:212–221. PMID: 21804916.
Article26. Al-Astal HI, Massad M, AlMatar M, Ekal H. Cellular functions of RNA-binding motif protein 3 (RBM3): clues in hypothermia, cancer biology and apoptosis. Protein Pept Lett. 2016; 23:828–835. PMID: 27364162.27. Wellmann S, Truss M, Bruder E, Tornillo L, Zelmer A, Seeger K, et al. The RNA-binding protein RBM3 is required for cell proliferation and protects against serum deprivation-induced cell death. Pediatr Res. 2010; 67:35–41. PMID: 19770690.
Article28. Jonsson L, Bergman J, Nodin B, Manjer J, Pontén F, Uhlén M, et al. Low RBM3 protein expression correlates with tumour progression and poor prognosis in malignant melanoma: an analysis of 215 cases from the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study. J Transl Med. 2011; 9:114. PMID: 21777469.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- RNA Regulation in Neurologic Disease and Cancer
- Overexpression of the Bmi-1 Oncoprotein correlates with Axillary Lymph Node Metastases in Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer
- The Expression of High Mobility Group I (Y) Proteins in Human Breast Cancer
- Expression and Clinical Significance of Angiopoietin-2 and its Receptor Tie-2 in Invasive Breast Cancer
- The Characterization of CpG Methylation of ERalpha and ERbeta Gene in the Breast Cancer