J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Oct;79(4):227-232. 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.4.227.
Bronchogenic Cyst in an Intradiaphragmatic Location: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. gnlee@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2421226
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.4.227
Abstract
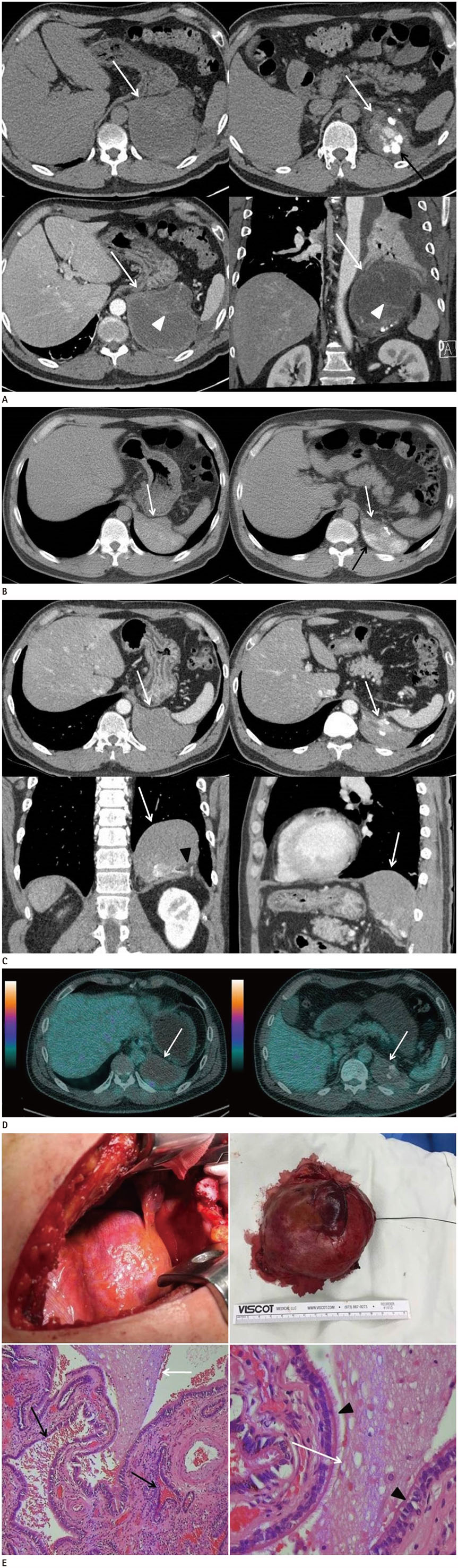
- Bronchogenic cysts are congenital lesions usually observed in the mediastinum, near the tracheal carina and middle mediastinum. Herein, we present an exceedingly rare case of intradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst with an infectious complication in a 52-year-old man. Chest CT and three-dimensional volume rendered reconstructed images revealed an oval, cystic mass with multiple nodular calcifications, centered in the left diaphragm crus. CT facilitated documentation of the healing process of this rare entity, revealing decrease in size and increase in internal density.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mubang R, Brady JJ, Mao M, Burfeind W, Puc M. Intradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cysts: case report and systematic review. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016; 11:79.
Article2. McAdams HP, Kirejczyk WM, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, Matsumoto S. Bronchogenic cyst: imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 2000; 217:441–446.
Article3. Liou CH, Hsu HH, Hsueh CJ, Juan CJ, Chen CY. Imaging findings of intradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst: a case report. J Formos Med Assoc. 2001; 100:712–714.4. Subramanian S, Chandra T, Whitehouse J, Suchi M, Arca M, Maheshwari M. Bronchogenic cyst in the intradiaphragmatic location. WMJ. 2013; 112:262–264.5. Mustafa KOÇ, Hasan DEMİR. Intradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst: a very rare diaphragmatic mass: case report. Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci. 2015; 35:125–128.
Article