J Vet Sci.
2018 Sep;19(5):708-715. 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.5.708.
Bee venom stimulation of a lung meridian acupoint reduces inflammation in carrageenan-induced pleurisy: an alternative therapeutic approach for respiratory inflammation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Physiology, BK21 PLUS Program for Creative Veterinary Science Research, Research Institute for Veterinary Science and College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. yhryu@kiom.re.kr
- 2KM Fundamental Research Division, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, Daejeon 34054, Korea. yhryu@kiom.re.kr
- 3Department of Oral Physiology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Korea.
- KMID: 2420941
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.5.708
Abstract
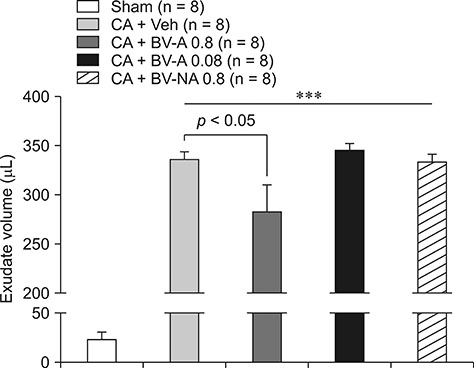
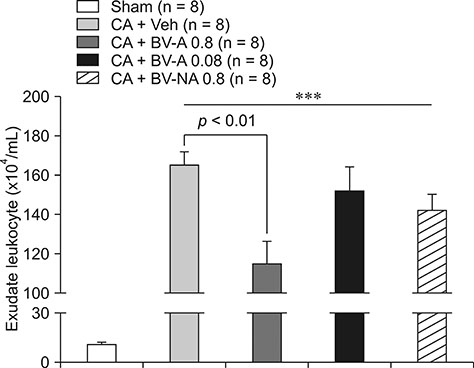
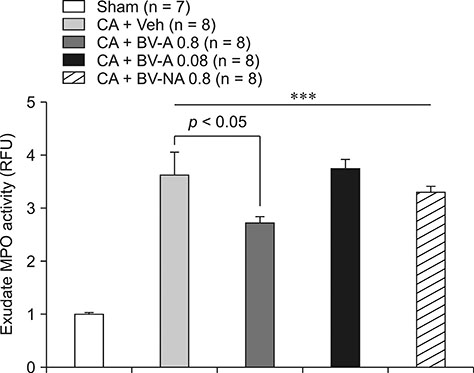
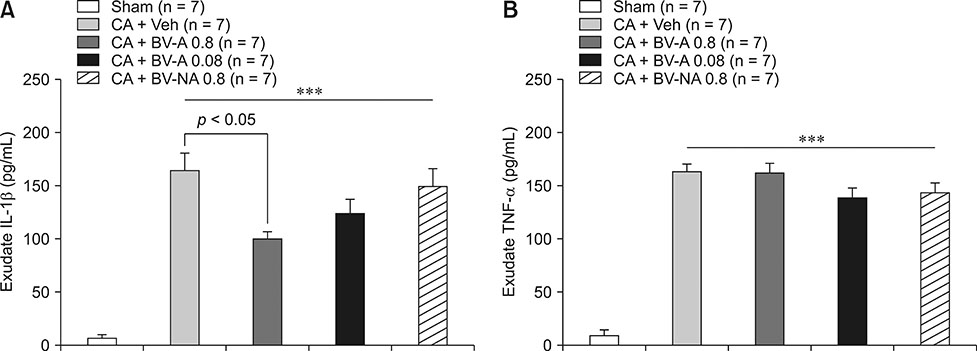
- Respiratory inflammation is a frequent and fatal pathologic state encountered in veterinary medicine. Although diluted bee venom (dBV) has potent anti-inflammatory effects, the clinical use of dBV is limited to several chronic inflammatory diseases. The present study was designed to propose an acupoint dBV treatment as a novel therapeutic strategy for respiratory inflammatory disease. Experimental pleurisy was induced by injection of carrageenan into the left pleural space in mouse. The dBV was injected into a specific lung meridian acupoint (LU-5) or into an arbitrary non-acupoint located near the midline of the back in mouse. The inflammatory responses were evaluated by analyzing inflammatory indicators in pleural exudate. The dBV injection into the LU-5 acupoint significantly suppressed the carrageenan-induced increase of pleural exudate volume, leukocyte accumulation, and myeloperoxidase activity. Moreover, dBV acupoint treatment effectively inhibited the production of interleukin 1 beta, but not tumor necrosis factor alpha in the pleural exudate. On the other hand, dBV treatment at non-acupoint did not inhibit the inflammatory responses in carrageenan-induced pleurisy. The present results demonstrate that dBV stimulation in the LU-5 lung meridian acupoint can produce significant anti-inflammatory effects on carrageenan-induced pleurisy suggesting that dBV acupuncture may be a promising alternative medicine therapy for respiratory inflammatory diseases.
MeSH Terms
-
Acupuncture
Acupuncture Points*
Animals
Bee Venoms*
Bees*
Carrageenan
Complementary Therapies
Exudates and Transudates
Hand
Inflammation*
Interleukin-1beta
Leukocytes
Lung*
Mice
Peroxidase
Pleurisy*
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Veterinary Medicine
Bee Venoms
Carrageenan
Interleukin-1beta
Peroxidase
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Authier FJ, Chazaud B, Plonquet A, Eliezer-Vanerot MC, Poron F, Belec L, Barlovatz-Meimon G, Gherardi RK. Differential expression of the IL-1 system components during in vitro myogenesis: implication of IL-1beta in induction of myogenic cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999; 6:1012–1021.
Article2. Bhattacharyya S, Borthakur A, Anbazhagan AN, Katyal S, Dudeja PK, Tobacman JK. Specific effects of BCL10 Serine mutations on phosphorylations in canonical and noncanonical pathways of NF-κB activation following carrageenan. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011; 301:G475–G486.
Article3. Davies NM, Jamali F. COX-2 selective inhibitors cardiac toxicity: getting to the heart of the matter. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2004; 7:332–336.4. Efthimiou P, Kukar M. Complementary and alternative medicine use in rheumatoid arthritis: proposed mechanism of action and efficacy of commonly used modalities. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:571–586.
Article5. Fuertes G, Laorden ML, Milanés MV. Noradrenergic and dopaminergic activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus after naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal. Neuroendocrinology. 2000; 71:60–67.
Article6. Gruber W, Eber E, Malle-Scheid D, Pfleger A, Weinhandl E, Dorfer L, Zach MS. Laser acupuncture in children and adolescents with exercise induced asthma. Thorax. 2002; 57:222–225.
Article7. Haegens A, Vernooy JH, Heeringa P, Mossman BT, Wouters EF. Myeloperoxidase modulates lung epithelial responses to pro-inflammatory agents. Eur Respir J. 2008; 31:252–260.
Article8. Hajhashemi V, Sadeghi H, Minaiyan M, Movahedian A, Talebi A. Central and peripheral anti-inflammatory effects of maprotiline on carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats. Inflamm Res. 2010; 59:1053–1059.
Article9. Harirforoosh S, Jamali F. Renal adverse effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2009; 8:669–681.
Article10. Kang SS, Pak SC, Choi SH. The effect of whole bee venom on arthritis. Am J Chin Med. 2002; 30:73–80.
Article11. Kang SY, Roh DH, Kim HW, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Blockade of adrenal medulla-derived epinephrine potentiates bee venom-induced antinociception in the mouse formalin test: involvement of peripheral β-adrenoceptors. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013:809062.12. Kim HW, Uh DK, Yoon SY, Roh DH, Kwon YB, Han HJ, Lee HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Low-frequency electroacupuncture suppresses carrageenan-induced paw inflammation in mice via sympathetic post-ganglionic neurons, while high-frequency EA suppression is mediated by the sympathoadrenal medullary axis. Brain Res Bull. 2008; 75:698–705.
Article13. Kolber BJ, Muglia LJ. Defining brain region-specific glucocorticoid action during stress by conditional gene disruption in mice. Brain Res. 2009; 1293:85–90.
Article14. Kwon YB, Ham TW, Kim HW, Roh DH, Yoon SY, Han HJ, Yang IS, Kim KW, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Water soluble fraction (<10 kDa) from bee venom reduces visceral pain behavior through spinal α2-adrenergic activity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005; 80:181–187.
Article15. Kwon YB, Kim HW, Ham TW, Yoon SY, Roh DH, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Yang IS, Lee JH. The anti-inflammatory effect of bee venom stimulation in a mouse air pouch model is mediated by adrenal medullary activity. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003; 15:93–96.
Article16. Kwon YB, Lee HJ, Han HJ, Mar WC, Kang SK, Yoon OB, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. The water-soluble fraction of bee venom produces antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects on rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Life Sci. 2002; 71:191–204.
Article17. Lee JD, Park HJ, Chae Y, Lim S. An overview of bee venom acupuncture in the treatment of arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2005; 2:79–84.
Article18. Lee JH, Kwon YB, Han HJ, Mar WC, Lee HJ, Yang IS, Beitz AJ, Kang SK. Bee venom pretreatment has both an antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effect on carrageenan-induced inflammation. J Vet Med Sci. 2001; 63:251–259.
Article19. Lee MS, Pittler MH, Shin BC, Kong JC, Ernst E. Bee venom acupuncture for musculoskeletal pain: a review. J Pain. 2008; 9:289–297.
Article20. Li L, Yu J, Mu R, Dong S. Clinical effect of electroacupuncture on lung injury patients caused by severe acute pancreatitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017; 2017:3162851.
Article21. Liu XY, Zhou HF, Pan YL, Liang XB, Niu DB, Xue B, Li FQ, He QH, Wang XH, Wang XM. Electro-acupuncture stimulation protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-mediated damage in medial forebrain bundle-transected rats. Exp Neurol. 2004; 189:189–196.
Article22. Loram LC, Fuller A, Fick LG, Cartmell T, Poole S, Mitchell D. Cytokine profiles during carrageenan-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia in rat muscle and hind paw. J Pain. 2007; 8:127–136.
Article23. Malhotra S, Deshmukh SS, Dastidar SG. COX inhibitors for airway inflammation. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012; 16:195–207.
Article24. Menegazzi M, Di Paola R, Mazzon E, Genovese T, Crisafulli C, Dal Bosco M, Zou Z, Suzuki H, Cuzzocrea S. Glycyrrhizin attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced lung injury in mice. Pharmacol Res. 2008; 58:22–31.
Article25. Nestor PJ, Scheltens P, Hodges JR. Advances in the early detection of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 2004; 10:Suppl. S34–S41.
Article26. Nicoletti F, Auci DL, Mangano K, Flores-Riveros J, Villegas S, Frincke JM, Reading CL, Offner H. 5-androstenediol ameliorates pleurisy, septic shock, and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Autoimmune Dis. 2010; 2010:757432.
Article27. Ong CK, Lirk P, Tan CH, Seymour RA. An evidence-based update on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Med Res. 2007; 5:19–34.
Article28. Park HJ, Lee HJ, Choi MS, Son DJ, Song HS, Song MJ, Lee JM, Han SB, Kim Y, Hong JT. JNK pathway is involved in the inhibition of inflammatory target gene expression and NF-kappaB activation by melittin. J Inflamm (Lond). 2008; 5:7.
Article29. Roh DH, Choi SR, Yoon SY, Kang SY, Moon JY, Kwon SG, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Spinal neuronal NOS activation mediates sigma-1 receptor-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity in mice: involvement of PKC-dependent GluN1 phosphorylation. Br J Pharmacol. 2011; 163:1707–1720.
Article30. Saleh TSF, Calixto JB, Medeiros YS. Anti-inflammatory effects of theophylline, cromolyn and salbutamol in a murine model of pleurisy. Br J Pharmacol. 1996; 118:811–819.
Article31. Saleh TSF, Calixto JB, Medeiros YS. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs upon nitrate and myeloperoxidase levels in the mouse pleurisy induced by carrageenan. Peptides. 1999; 20:949–956.
Article32. Son DJ, Lee JW, Lee YH, Song HS, Lee CK, Hong JT. Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 115:246–270.
Article33. U.S. National Institutes of Health. Laboratory animal welfare: public health service policy on humane care and use of laboratory animals by awardee institutions; notice. Fed Regist. 1985; 50:19584–19585.34. Vazquez E, Navarro M, Salazar Y, Crespo G, Bruges G, Osorio C, Tortorici V, Vanegas H, López M. Systemic changes following carrageenan-induced paw inflammation in rats. Inflamm Res. 2015; 64:333–342.
Article35. Wu ZJ, Xu J, Wang J, Gong CP, Cai RL, Hu L. Correlation of electroacupuncture on the heart and lung meridians with dopamine secretion in the hypothalamus of rats in a myocardial ischemia model. Med Acupunct. 2016; 28:331–338.
Article36. Yin CS, Jeong HS, Park HJ, Baik Y, Yoon MH, Choi CB, Koh HG. A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model. Res Vet Sci. 2008; 84:159–165.
Article37. Yoon SY, Kwon YB, Kim HW, Roh DH, Seo HS, Han HJ, Lee HJ, Beitz AJ, Hwang SW, Lee JH. Peripheral bee venom’s anti-inflammatory effect involves activation of the coeruleospinal pathway and sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Neurosci Res. 2007; 59:51–59.
Article38. Yoon SY, Kwon YB, Kim HW, Roh DH, Seo HS, Han HJ, Lee HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Bee venom injection produces a peripheral anti-inflammatory effect by activation of a nitric oxide-dependent spinocoeruleus pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2008; 430:163–168.
Article39. Zimmermann M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain. 1983; 16:109–110.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of bee venom pretreatment of an acupoint on inflammation and hyperalgesia induced by peptidoglycan
- A Case of Steven-Johnson Syndrome after Live Bee Acupuncture (Bong-Chim)
- A Case of Newly Developed Pemphigus Foliaceus and Possible Association with Alternative Bee-Venom Therapy
- Serum sickness reaction with skin involvement induced by bee venom injection therapy
- Foreign Body Granuloma Following Dried Honey Bee Venom (Apitoxin Inj) Injection