Infect Chemother.
2018 Sep;50(3):252-262. 10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.252.
Effectiveness, Safety, and Tolerability of a Switch to Dual Therapy with Dolutegravir Plus Cobicistat-Boosted Darunavir in Treatment-Experienced Patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. ksw2kms@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.252
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Dual regimen with dolutegravir plus cobicistat-boosted darunavir (DTG/DRV/c) is reasonable alternative option for patients with existing resistance and/or intolerance to nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). MATERIAL AND METHODS: All patients who switched to DTG/DRV/c among treatment-experienced patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in a tertiary university hospital were selected. We analyzed the effectiveness, safety, and tolerability based on serial laboratory data and clinical findings. The primary endpoint was defined as the proportion of patients with plasma HIV RNA below 50 copies/mL at week 48 after switch. Secondary endpoints included evaluation of safety and tolerability.
RESULTS
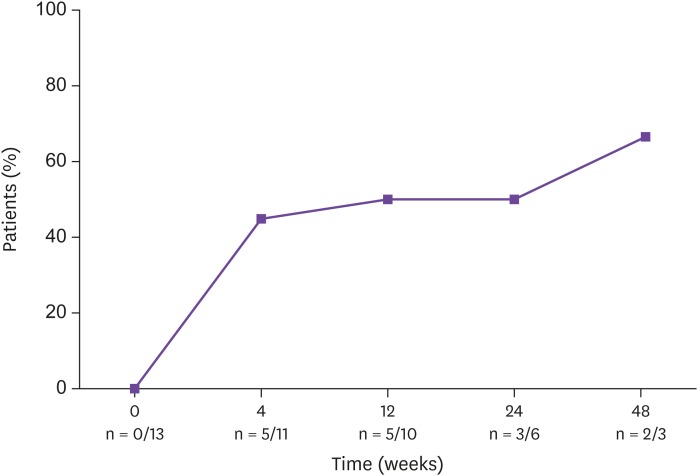
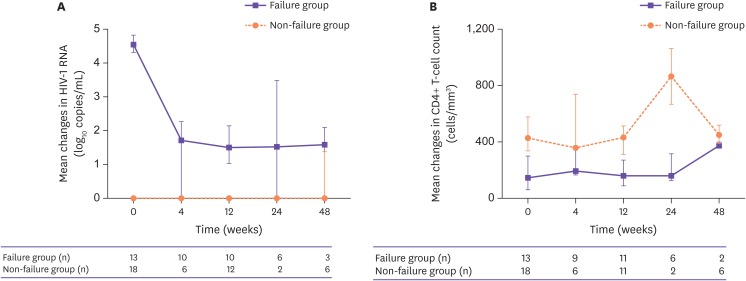
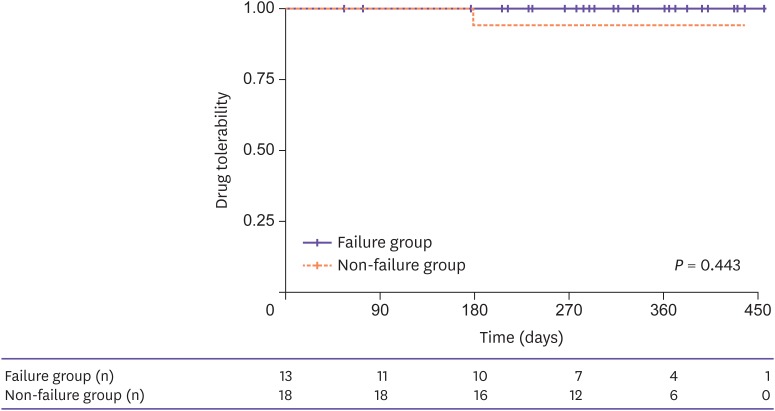
Thirty-one patients were retrospectively analyzed. The main reasons for the change to DTG/DRV/c were treatment failure in 13 patients (41.9%), simplification in 12 patients (38.7%), and adverse drug reaction in 6 patients (19.4%). Among the 13 patients who switched owing to treatment failure, the proportion of patients in whom the viral loads were suppressed to less than 50 copies/mL increased from 0% at baseline to 45% at 4 weeks, 50% at 12 weeks, 50% at 24 weeks, and 66.7% at 48 weeks. HIV virus levels decreased and CD4⺠T cell counts increased during the follow-up period. In non-treatment failure patients (18 patients), the levels of viral suppression and CD4⺠T cells were maintained. There were no significant differences in renal function, liver function, glucose levels, and lipid profile before and after regimen changes. The tolerability was very good: 30 patients (96.8%) tolerated the drugs well and only 1 patient discontinued owing to no improvement in renal insufficiency. Two patients (6.4%) in treatment failure group failed to reach viral suppression.
CONCLUSION
The use of DTG/DRV/c in HIV treatment-experienced patients appears to be a very good regimen for switch therapy that is effective and well tolerated, without significant adverse drug reaction.
MeSH Terms
-
Cell Count
Cobicistat
Darunavir*
Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Follow-Up Studies
Glucose
HIV*
Humans
Humans*
Liver
Plasma
Renal Insufficiency
Retrospective Studies
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
RNA
T-Lymphocytes
Treatment Failure
Viral Load
Cobicistat
Darunavir
Glucose
RNA
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nachega JB, Parienti JJ, Uthman OA, Gross R, Dowdy DW, Sax PE, Gallant JE, Mugavero MJ, Mills EJ, Giordano TP. Lower pill burden and once-daily antiretroviral treatment regimens for HIV infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2014; 58:1297–1307. PMID: 24457345.
Article2. Burgos J, Crespo M, Falcó V, Curran A, Navarro J, Imaz A, Domingo P, Podzamczer D, Mateo MG, Villar S, Van den Eynde E, Ribera E, Pahissa A. Simplification to dual antiretroviral therapy including a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:2479–2486. PMID: 22729925.
Article3. Bierman WF, van Agtmael MA, Nijhuis M, Danner SA, Boucher CA. HIV monotherapy with ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors: a systematic review. AIDS. 2009; 23:279–291. PMID: 19114854.
Article4. Seang S, Schneider L, Nguyen T, Lê MP, Soulie C, Calin R, Caby F, Valantin MA, Tubiana R, Assoumou L, Marcelin AG, Peytavin G, Katlama C. Darunavir/ritonavir monotherapy at a low dose (600/100 mg/day) in HIV-1-infected individuals with suppressed HIV viraemia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017; 73:490–493.5. Spagnuolo V, Galli L, Bigoloni A, Nozza S, Monforte Ad, Antinori A, Di Biagio A, Rusconi S, Guaraldi G, Di Giambenedetto S, Lazzarin A, Castagna A. Atazanavir/ritonavir monotherapy as maintenance strategy in HIV-1 treated subjects with viral suppression: 96-week analysis results of the MODAT study. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014; 17(4 Suppl 3):19806. PMID: 25397550.
Article6. Wijting I, Rokx C, Boucher C, van Kampen J, Pas S, de Vries-Sluijs T, Schurink C, Bax H, Derksen M, Andrinopoulou ER, van der Ende M, van Gorp E, Nouwen J, Verbon A, Bierman W, Rijnders B. Dolutegravir as maintenance monotherapy for HIV (DOMONO): a phase 2, randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet HIV. 2017; 4:e547–e554. PMID: 29107562.
Article7. Yendewa GA, Salata RA. Hot news: ready for HIV dual therapy? - new data from international HIV/AIDS society 2017. AIDS Rev. 2017; 19:167–172.8. Soriano V, Peña JM. A new HIV paradigm: dual antiretroviral regimens as maintenance therapy. AIDS Rev. 2017; 19:113–114.9. Soriano V, Fernandez-Montero JV, Benitez-Gutierrez L, Mendoza C, Arias A, Barreiro P, Peña JM, Labarga P. Dual antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017; 16:923–932. PMID: 28621159.
Article10. Spinner CD, Kummerle T, Krznaric I, Degen O, Schwerdtfeger C, Zink A, Wolf E, Klinker HHF, Boesecke C. Pharmacokinetics of once-daily dolutegravir and ritonavir-boosted darunavir in HIV patients: the DUALIS study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017; 72:2679–2681. PMID: 28859438.
Article11. Borghetti A, Baldin G, Ciccullo A, Gagliardini R, D'Avino A, Mondi A, Ciccarelli N, Lamonica S, Fanti I, Trecarichi E, Fabbiani M, Cauda R, De Luca A, Di Giambenedetto S. Virological control and metabolic improvement in HIV-infected, virologically suppressed patients switching to lamivudine/dolutegravir dual therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016; 71:2359–2361. PMID: 27147306.12. Maggiolo F, Gulminetti R, Pagnucco L, Digaetano M, Benatti S, Valenti D, Callegaro A, Ripamonti D, Mussini C. Lamivudine/dolutegravir dual therapy in HIV-infected, virologically suppressed patients. BMC Infect Dis. 2017; 17:215. PMID: 28302065.
Article13. Capetti AF, Sterrantino G, Cossu MV, Orofino G, Barbarini G, De Socio GV, Di Giambenedetto S, Di Biagio A, Celesia BM, Argenteri B, Rizzardini G. Switch to dolutegravir plus rilpivirine dual therapy in cART-experienced subjects: an observational cohort. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0164753. PMID: 27741309.
Article14. Gantner P, Cuzin L, Allavena C, Cabie A, Pugliese P, Valantin MA, Bani-Sadr F, Joly V, Ferry T, Poizot-Martin I, Garraffo R, Peytavin G, Fafi-Kremer S, Rey D. Dat'AIDS study group. Efficacy and safety of dolutegravir and rilpivirine dual therapy as a simplification strategy: a cohort study. HIV Med. 2017; 18:704–708. PMID: 28444816.
Article15. Revuelta-Herrero JL, Chamorro-de-Vega E, Rodríguez-González CG, Alonso R, Herranz-Alonso A, Sanjurjo-Sáez M. Effectiveness, safety, and costs of a treatment switch to dolutegravir plus rilpivirine dual therapy in treatment-experienced HIV patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2018; 52:11–18. PMID: 28836468.
Article16. Capetti AF, Cossu MV, Paladini L, Rizzardini G. Dolutegravir plus rilpivirine dual therapy in treating HIV-1 infection. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018; 19:65–77. PMID: 29246084.
Article17. Capetti AF, Sterrantino G, Cossu MV, Cenderello G, Cattelan AM, De Socio GV, Rusconi S, Riccardi N, Baldin GM, Cima S, Niero FP, Rizzardini G, Sasset L. Salvage therapy or simplification of salvage regimens with dolutegravir plus ritonavir-boosted darunavir dual therapy in highly cART-experienced subjects: an Italian cohort. Antivir Ther. 2017; 22:257–262. PMID: 27661787.
Article18. Capetti AF, Cossu MV, Orofino G, Sterrantino G, Cenderello G, De Socio GV, Cattelan AM, Soria A, Rusconi S, Riccardi N, Baldin GM, Niero FP, Barbarini G, Rizzardini G. A dual regimen of ritonavir/darunavir plus dolutegravir for rescue or simplification of rescue therapy: 48 weeks' observational data. BMC Infect Dis. 2017; 17:658. PMID: 28964268.
Article19. Zuo Z, Liang S, Sun X, Bussell S, Yan J, Kan W, Leng X, Liao L, Ruan Y, Shao Y, Xing H. Drug resistance and virological failure among HIV-infected patients after a decade of antiretroviral treatment expansion in eight provinces of China. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0166661. PMID: 27997554.
Article20. Kan W, Teng T, Liang S, Ma Y, Tang H, Zuohela T, Sun G, He C, Wall KM, Marconi VC, Liao L, Leng X, Liu P, Ruan Y, Xing H, Shao Y. Predictors of HIV virological failure and drug resistance in Chinese patients after 48 months of antiretroviral treatment, 2008-2012: a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2017; 7:e016012.
Article21. Tsai HC, Chen IT, Wu KS, Tseng YT, Sy CL, Chen JK, Lee SS, Chen YS. High rate of HIV-1 drug resistance in treatment failure patients in Taiwan, 2009-2014. Infect Drug Resist. 2017; 10:343–352. PMID: 29081666.22. Gubavu C, Prazuck T, Niang M, Buret J, Mille C, Guinard J, Avettand-Fenoel V, Hocqueloux L. Dolutegravir-based monotherapy or dual therapy maintains a high proportion of viral suppression even in highly experienced HIV-1-infected patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016; 71:1046–1050. PMID: 26712907.
Article23. Kim MJ, Kim SW, Chang HH, Kim Y, Jin S, Jung H, Park JH, Kim S, Lee JM. Comparison of antiretroviral regimens: adverse effects and tolerability failure that cause regimen switching. Infect Chemother. 2015; 47:231–238. PMID: 26788406.
Article24. Capetti A, Cossu MV, Rizzardini G. Darunavir/cobicistat for the treatment of HIV-1: a new era for compact drugs with high genetic barrier to resistance. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015; 16:2689–2702. PMID: 26612518.
Article25. De La Fuente S, Gutierrez A, Gomez A, Díaz-de Santiago A, Anula Á, Pintos I, Roque F, Sanz J, Ángel-Moreno A. Dual therapy with dolutegravir plus darunavir/cobicistat as salvage therapy regimen. results at 24 weeks. Poster session presented at: International AIDS Society 2017. 2017 July 23-26; France, Paris.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness and Tolerability of Dual Therapy with Dolutegravir Plus Darunavir/ cobicistat in Treatment-Experienced Patients with HIV: A 144-Week Follow-Up
- Safety and Effectiveness of Darunavir in Korean Patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection: A Post-Marketing Observational Study
- Use of Darunavir-Cobicistat as a Treatment Option for Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- Efficacy and Safety of Elvitegravir/Cobicistat/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in Asian Subjects with Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection: A Sub-Analysis of Phase 3 Clinical Trials
- A Korean Post-Marketing Study of Abacavir/Dolutegravir/Lamivudine in Patients with HIV-1