Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2018 Sep;26(3):103-110. 10.12793/tcp.2018.26.3.103.
Microbe-derived extracellular vesicles as a smart drug delivery system
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of MD Healthcare Inc., Seoul 03923, Republic of Korea. ykkim@mdhc.kr
- KMID: 2420291
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2018.26.3.103
Abstract
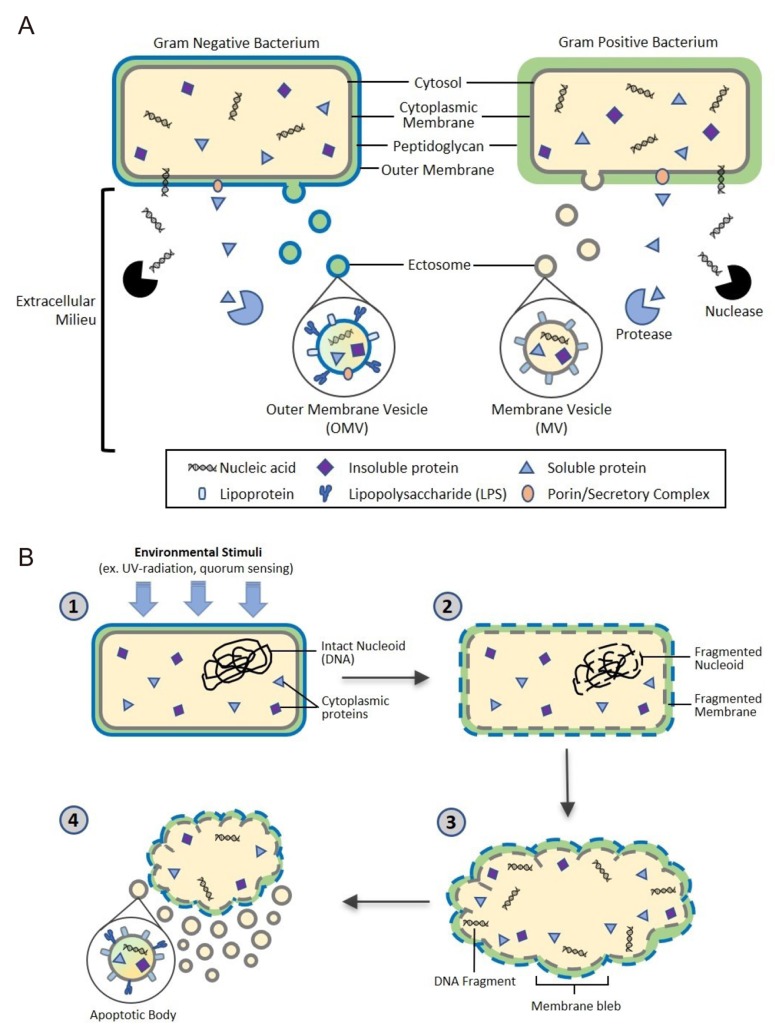
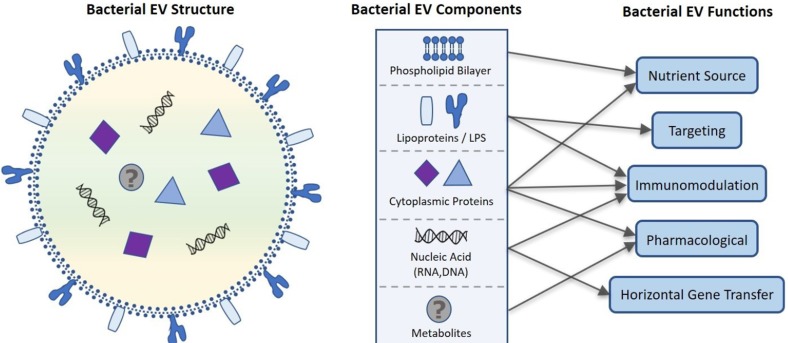
- The human microbiome is known to play an essential role in influencing host health. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have also been reported to act on a variety of signaling pathways, distally transport cellular components such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acid, and have immunomodulatory effects. Here we shall review the current understanding of the intersectionality of the human microbiome and EVs in the emerging field of microbiota-derived EVs and their pharmacological potential. Microbes secrete several classes of EVs: outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), membrane vesicles (MVs), and apoptotic bodies. EV biogenesis is unique to each cell and regulated by sophisticated signaling pathways. EVs are primarily composed of lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and recent evidence suggests they may also carry metabolites. These components interact with host cells and control various cellular processes by transferring their constituents. The pharmacological potential of microbiomederived EVs as vaccine candidates, biomarkers, and a smart drug delivery system is a promising area of future research. Therefore, it is necessary to elucidate in detail the mechanisms of microbiome-derived EV action in host health in a multi-disciplinary manner.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. H Rashed M, Bayraktar E, K Helal G, Abd-Ellah MF, Amero P, Chavez-Reyes A, et al. Exosomes: From Garbage Bins to Promising Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18:E538. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18030538. PMID: 28257101.2. Deatherage BL, Cookson BT. Membrane vesicle release in bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea: a conserved yet underappreciated aspect of microbial life. Infect Immun. 2012; 80:1948–1957. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.06014-11. PMID: 22409932.
Article3. Zaborowski MP, Balaj L, Breakefield XO, Lai CP. Extracellular vesicles: Composition, biological relevance, and methods of study. Bioscience. 2015; 65:783–797. PMID: 26955082.
Article4. McConnell MJ. Extracellular vesicles and immune modulation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2018; 96:681–682.
Article5. Lederberg J, Mccray AT. “Ome Sweet'Omics--A Genealogical Treasury of Words”. The Scientist. 2001; 8.6. Young VB. The role of the microbiome in human health and disease: an introduction for clinicians. BMJ. 2017; 356:j831. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.j831. PMID: 28298355.
Article7. Takiishi T, Fenero CIM, Câmara NOS. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers. 2017; 5:e1373208. PMID: 28956703.
Article8. Rowland I, Gibson G, Heinken A, Scott K, Swann J, Thiele I, et al. Gut microbiota functions: metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur J Nutr. 2018; 57:1–24. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-017-1445-8.
Article9. Lee EY, Choi DY, Kim DK, Kim JW, Park JO, Kim S, et al. Gram-positive bacteria produce membrane vesicles: proteomics-based characterization of Staphylococcus aureus-derived membrane vesicles. Proteomics. 2009; 9:5425–5436. DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200900338. PMID: 19834908.10. Peeters SH, de Jonge MI. For the greater good: Programmed cell death in bacterial communities. Microbiol Res. 2018; 207:161–169. DOI: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.11.016. PMID: 29458850.
Article11. National Human Genome Research Institute. An Overview of the Human Genome Project. Accessed 03 Oct 2018. https://www.genome.gov/12011238/an-overview-of-thehuman-genome-project/.12. Hillier LW, Coulson A, Murray JI, Bao Z, Sulston JE, Waterston RH. Genomics in C. elegans: so many genes, such a little worm. Genome Res. 2005; 15:1651–1660. PMID: 16339362.13. Lloyd-Price J, Mahurkar A, Rahnavard G, Crabtree J, Orvis J, Hall AB, et al. Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded Human Microbiome Project. Nature. 2017; 550:61–66. DOI: 10.1038/nature23889. PMID: 28953883.
Article14. Gilbert JA, Blaser MJ, Caporaso JG, Jansson JK, Lynch SV, Knight R. Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nature Med. 2018; 24:392–400. PMID: 29634682.
Article15. Wang B, Yao M, Lv L, Ling Z, Li L. The Human Microbiota in Health and Disease. Engineering. 2017; 3:71–82.
Article16. Carabotti M, Scirocco A, Maselli MA, Severi C. The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol. 2015; 28:203–209. PMID: 25830558.17. Huang YJ, Marsland BJ, Bunyavanich S, O'Mahony L, Leung DY, Muraro A, et al. The microbiome in allergic disease: Current understanding and future opportunities-2017 PRACTALL document of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology and the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139:1099–1110. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.02.007. PMID: 28257972.18. Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013; 32:623–642. DOI: 10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9. PMID: 23709120.
Article19. Cocucci E, Meldolesi J. Ectosome and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015; 6:364–372.20. Kulp A, Kuehn MJ. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010; 64:163–184. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.micro.091208.073413. PMID: 20825345.
Article21. McBroom AJ, Kuehn MJ. Release of outer membrane vesicles by Gramnegative bacteria is a novel envelope stress response. Mol Microbiol. 2007; 63:545–558. PMID: 17163978.
Article22. Akers JC, Gonda D, Kim R, Carter BS, Chen CC. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J Neurooncol. 2013; 113:1–11. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-013-1084-8. PMID: 23456661.
Article23. Rivera J, Cordero RJ, Nakouzi AS, Frases S, Nicola A, Casadevall A. Bacillus anthracis produces membrane-derived vesicles containing biologically active toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:19002–19007. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1008843107. PMID: 20956325.
Article24. Brown L, Wolf JM, Prados-Rosales R, Casadevall A. Through the wall: extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015; 13:620–630. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro3480. PMID: 26324094.
Article25. Allocati N, Masulli M, Di Ilio C, De Laurenzi V. Die for the community: an overview of programmed cell death in bacteria. Cell Death Dis. 2015; 6:e1609. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.570. PMID: 25611384.
Article26. Abels ER, Breakefield XO. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA cargo selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016; 36:301–312. DOI: 10.1007/s10571-016-0366-z. PMID: 27053351.
Article27. Hanson PI, Cashikar A. Multivesicular body morphogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2012; 28:337–362. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154152. PMID: 22831642.
Article28. Colombo M, Raposo G, Théry C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014; 30:255–289. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326. PMID: 25288114.
Article29. Williams RL, Urbé S. The emerging shape of the ESCRT machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 8:355–368. PMID: 17450176.
Article30. Ghossoub R, Lembo F, Rubio A, Gaillard CB, Bouchet J, Vitale N, et al. Syntenin-ALIX exosome biogenesis and budding into multivesicular bodies are controlled by ARF6 and PLD2. Nat Commun. 2014; 5:3477. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4477. PMID: 24637612.
Article31. van Niel G, Charrin S, Simoes S, Romao M, Rochin L, Saftig P, et al. The tetraspanin CD63 regulates ESCRT-independent and dependent endosomal sorting during melanogenesis. Dev Cell. 2011; 21:708–721. PMID: 21962903.32. Lee EY, Choi DS, Kim KP, Gho YS. Proteomics in gram-negative bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018; 27:535–555. DOI: 10.1002/mas.20175.
Article33. Poste G, Papahadjopoulos D. Lipid vesicles as carriers for introducing materials into cultured cells: influence of vesicle lipid composition on mechanism(s) of vesicle incorporation into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976; 73:1603–1607. PMID: 818640.
Article34. Papahadjopoulos D, Poste G, Schaeffer BE, Vail WJ. Membrane fusion and molecular segregation in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974; 352:10–28. PMID: 4859411.
Article35. Papahadjopoulos D, Mayhew E, Poste G, Smith S, Vail WJ. Incorporation of lipid vesicles by mammalian cells provides a potential method for modifying cell behaviour. Nature. 1974; 252:163–166. PMID: 4371572.
Article36. Poste G, Papahadjopoulos D, Vail WJ. Lipid vesicles as carriers for introducing biologically active materials into cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976; 14:33–71. PMID: 794631.37. Casal JI, Rueda P, Hurtado A. Parvovirus-like particles as vaccine vectors. Methods. 1999; 19:174–186. PMID: 10525454.
Article38. Parmar MM, Edwards K, Madden TD. Incorporation of bacterial membrane proteins into liposomes: factors influencing protein reconstitution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999; 1421:77–90. PMID: 10561473.
Article39. Gho YS, Kim OY, Jang SC, Yoon CM, Kim YK. Method for treating and diagnosing cancer by using cell-derived microvesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1788:2150–2159. PMID: 19695218.40. Raetz CR, Whitfield C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002; 71:635–700. PMID: 12045108.
Article41. Kooijmans SA, Vader P, van Dommelen SM, van Solinge WW, Schiffelers RM. Exosome mimetics: a novel class of drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012; 7:1525–1541. DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S29661. PMID: 22619510.42. Baldeschwieler JD. Phospholipid vesicle targeting using synthetic glycolipid and other determinants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985; 446:349–367. PMID: 3860161.
Article43. Bussian RW, Wriston JC Jr. Influence of incorporated cerebrosides on the interaction of liposomes with HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977; 471:336. PMID: 921985.
Article44. Juliano RL. Drug delivery systems: characteristics and biomedical applications. USA: Oxford University Press;1980. p. 189–236.45. Mauk MR, Gamble RC, Baldeschwieler JD. Vesicle targeting: timed release and specificity for leukocytes in mice by subcutaneous injection. Science. 1980; 207:309–311. PMID: 7350660.
Article46. Mauk MR, Gamble RC, Baldeschwieler JD. Targeting of lipid vesicles: specificity of carbohydrate receptor analogues for leukocytes in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980; 77:4430–4434. PMID: 6933495.
Article47. Weinstein JN. Liposomes as “targeted” drug carriers: a physical chemical perspective. Pure Appl Chem. 1981; 53:2241–2254.
Article48. Choi DS, Kim DK, Choi SJ, Lee J, Choi JP, Rho S, et al. Proteomic analysis of outer membrane vesicles derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proteomics. 2011; 11:3424–3429. PMID: 21751344.
Article49. Chuanchuen R, Narasaki CT, Schweizer HP. The MexJK efflux pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires OprM for antibiotic efflux but not for efflux of triclosan. J Bacteriol. 2002; 184:5036–5044. PMID: 12193619.50. Zapun A, Contreras-Martel C, Vernet T. Penicillin-binding proteins and β-lactam resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008; 32:361–385. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00095.x. PMID: 18248419.
Article51. Storey DG, Ujack EE, Rabin HR, Mitchell I. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR Transcription correlates with the transcription of lasA, lasB, and toxA in chronic lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1998; 66:2521–2528. PMID: 9596711.52. Ashwell G, Morell AG. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974; 41:99–128. PMID: 4609051.
Article53. Achord DT, Brot FE, Sly WS. Inhibition of the rat clearance system for agalacto-orosomucoid by yeast mannans and by mannose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977; 77:409–415. PMID: 329842.
Article54. Stahl PD, Rodman JS, Miller MJ, Schlesinger PH. Evidence for receptormediated binding of glycoproteins, glycoconjugates, and lysosomal glycosidases by alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978; 75:1399–1403. PMID: 274729.
Article55. Hong SW, Choi EB, Min TK, Kim JH, Kim MH, Jeon SG, et al. An important role of α-hemolysin in extracellular vesicles on the development of atopic dermatitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e100499. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100499. PMID: 24992681.
Article56. Otto M. Basis of virulence in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010; 64:143–162. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134309. PMID: 20825344.
Article57. Walev I, Martin E, Jonas D, Mohamadzadeh M, Müller-Klieser W, Kunz L, et al. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin kills human keratinocytes by permeabilizing the plasma membrane for monovalent ions. Infect Immun. 1993; 61:4972–4979. PMID: 8225571.
Article58. Wichmann K, Uter W, Weiss J, Breuer K, Heratizadeh A, Mai U, et al. Isolation of α-toxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus from the skin of highly sensitized adult patients with severe atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:300–305. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09229.x. PMID: 19438853.59. Tsatsaronis JA, Franch-Arroyo S, Resch U, Charpentier E. Extracellular vesicle RNA: A universal mediator of microbial communication. Trends Microbiol. 2018; 26:401–410. DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.02.009. PMID: 29548832.
Article60. Bitto NJ, Chapman R, Pidot S, Costin A, Lo C, Choi J, et al. Bacteria membrane vesicles transport their DNA cargo into host cells. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:7072. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07288-4. PMID: 28765539.
Article61. Lambertz U, Oviedo Ovando ME, Vasconcelos EJ, Unrau PJ, Myler PJ, Reiner NE. Small RNAs derived from tRNAs and rRNAs are highly enriched in exosomes from both old and new world Leishmania providing evidence for conserved exosomal RNA Packaging. BMC Genomics. 2015; 16:151. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1260-7. PMID: 25764986.
Article62. Blenkiron C, Simonov D, Muthukaruppan A, Tsai P, Dauros P, Green S, et al. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli releases extracellular vesicles that are associated with RNA. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0160440. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160440. PMID: 27500956.63. Sjöström AE, Sandblad L, Uhlin BE, Wai SN. Membrane vesicle-mediated release of bacterial RNA. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:15329. DOI: 10.1038/srep15329. PMID: 26483327.
Article64. Choi EB, Hong SW, Kim DK, Jeon SG, Kim KR, Cho SH, et al. Decreased diversity of nasal microbiota and their secreted extracellular vesicles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis based on a metagenomic analysis. Allergy. 2014; 69:517–526. PMID: 24611950.
Article65. Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Sato TA, Ochiya T. Extracellular vesicles as trans-genomic agents: Emerging roles in disease and evolution. Cancer Sci. 2017; 108:824–830. DOI: 10.1111/cas.13222. PMID: 28256033.
Article66. Eigenbrod T, Dalpke AH. Bacterial RNA: An underestimated stimulus for innate immune responses. J Immunol. 2015; 195:411–418. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500530. PMID: 26138638.
Article67. Choi SJ, Kim MH, Jeon J, Kim OY, Choi Y, Seo J, et al. Active immunization with extracellular vesicles derived from Staphylococcus aureus effectively protects against Staphylococcal lung infections, mainly via Th1 Cell-mediated immunity. PLoS ONE. 2015; 10:e0136021. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136021. PMID: 26333035.68. Iraci N, Gaude E, Leonardi T, Costa ASH, Cossetti C, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, et al. Extracellular vesicles are independent metabolic units with asparaginase activity. Nat Chem Biol. 2017; 13:951–955. DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2422. PMID: 28671681.
Article69. Garcia NA, Moncayo-Arlandi J, Sepulveda P, Diez-Juan A. Cardiomyocyte exosomes regulate glycolytic flux in endothelium by direct transfer of GLUT transporters and glycolytic enzymes. Cardiovasc Res. 2016; 109:397–408. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvv260. PMID: 26609058.
Article70. Cohen LJ, Esterhazy D, Kim SH, Lemetre C, Aguilar RR, Gordon EA, et al. Commensal bacteria make GPCR ligands that mimic human signalling molecules. Nature. 2017; 549:48–53. DOI: 10.1038/nature23874. PMID: 28854168.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracellular Vesicles and Immune System in Ageing and Immune Diseases
- Potential of Gut Microbe-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Differentiate Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients from Healthy Controls
- Trends in Developing Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics
- Extracellular Vesicles of Neutrophils
- Extracellular Vesicles in Psychiatry Research in the Context of RDoC Criteria