J Bone Metab.
2018 Aug;25(3):187-193. 10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.187.
Association between Sarcopenia, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Chronic Disease in Korean Elderly
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Yeonsung University, Anyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. byundw@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2419847
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.187
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
It is a very important social issue for Korea to have a healthy old age as an aged society. Aging causes a lot of physical changes, especially sarcopenia. Sarcopenia is defined as a persistent decrease in skeletal muscle and muscle strength. Sarcopenic obesity is a phenomenon in which fat is replaced instead of muscle. The purpose of this study was to examine the prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in Korean elderly and to analyze the relationship with chronic disease.
METHODS
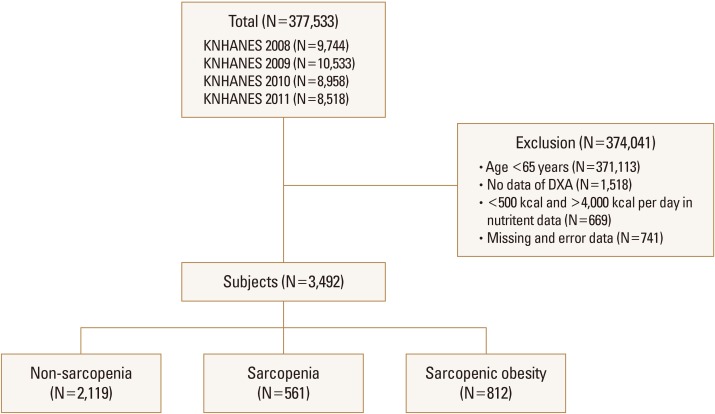
Data from the 2008 to 2011 the Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey were used. A total of 3,492 patients were classified into 3 groups (non-sarcopenia, sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity), and general, anthropometry, health behavior, nutrient intake and chronic disease status were compared by the statistical analysis.
RESULTS
The rate of moderate exercise was significantly lower in the sarcopenia and sarcopenic-obesity group than in the non-sarcopenia group (P=0.007). The sarcopenic obesity group had significantly higher energy (P=0.005), protein (P=0.046) and fat (P=0.001) intake than the sarcopenic group. The sarcopenic-obesity group had the highest ratio of diabetes (P=0.023) and dyslipidemia (P=0.004) in the 3 groups. Compared with the non-sarcopenia group, in the sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity groups, the odds ratios (ORs) of diabetes was increased by 1.24 and 2.16 while the ORs of dyslipidemia was increased by 1.12 and 1.50, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Regular exercise and adequate nutrient intake (energy, protein and fat) are essential for the prevention of sarcopenia in Korean elderly, and management of chronic disease in sarcopenic obesity elderly is important.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effect of CCL11 on
In Vitro Myogenesis and Its Clinical Relevance for Sarcopenia in Older Adults
Da Ae Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Jeoung Hee Kim, Seungjoo Lee, Eunju Lee, Il-Young Jang, Hee-Won Jung, Jin Hoon Park, Beom-Jun Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):455-465. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.942.Application of body composition zones in boys with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Minhye Choi, Seonhwa Lee, Sun Hwan Bae, Sochung Chung
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;24(4):243-247. doi: 10.6065/apem.2019.24.4.243.
Reference
-
1. Laviano A, Gori C, Rianda S. Sarcopenia and nutrition. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2014; 71:101–136. PMID: 24484940.
Article2. Urano T, Inoue S. Recent genetic discoveries in osteoporosis, sarcopenia and obesity. Endocr J. 2015; 62:475–484. PMID: 25866211.3. Janssen I, Shepard DS, Katzmarzyk PT, et al. The healthcare costs of sarcopenia in the United States. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004; 52:80–85. PMID: 14687319.
Article4. Atkins JL, Whincup PH, Morris RW, et al. Sarcopenic obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: a population-based cohort study of older men. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014; 62:253–260. PMID: 24428349.
Article5. Montero-Fernández N, Serra-Rexach JA. Role of exercise on sarcopenia in the elderly. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2013; 49:131–143. PMID: 23575207.6. Lucassen EA, de Mutsert R, le Cessie S, et al. Poor sleep quality and later sleep timing are risk factors for osteopenia and sarcopenia in middle-aged men and women: the NEO study. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0176685. PMID: 28459884.
Article7. Steffl M, Bohannon RW, Petr M, et al. Relation between cigarette smoking and sarcopenia: meta-analysis. Physiol Res. 2015; 64:419–426. PMID: 25536323.
Article8. Sanders KM, Scott D, Ebeling PR. Vitamin D deficiency and its role in muscle-bone interactions in the elderly. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014; 12:74–81. PMID: 24488588.
Article9. Ryu M, Jo J, Lee Y, et al. Association of physical activity with sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling older adults: the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Age Ageing. 2013; 42:734–740. PMID: 23761456.
Article10. Lutz CT, Quinn LS. Sarcopenia, obesity, and natural killer cell immune senescence in aging: altered cytokine levels as a common mechanism. Aging (Albany NY). 2012; 4:535–546. PMID: 22935594.
Article11. Kim JH, Cho JJ, Park YS. Relationship between sarcopenic obesity and cardiovascular disease risk as estimated by the Framingham risk score. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:264–271. PMID: 25729248.
Article12. Gao L, Jiang J, Yang M, et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia and associated factors in Chinese community-dwelling elderly: comparison between rural and urban areas. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015; 16:1003.e1–1003.e6.
Article13. Zembroń-Łacny A, Dziubek W, Rogowski Ł, et al. Sarcopenia: monitoring, molecular mechanisms, and physical intervention. Physiol Res. 2014; 63:683–691. PMID: 25157651.
Article14. Denison HJ, Cooper C, Sayer AA, et al. Prevention and optimal management of sarcopenia: a review of combined exercise and nutrition interventions to improve muscle outcomes in older people. Clin Interv Aging. 2015; 10:859–869. PMID: 25999704.15. Beasley JM, Shikany JM, Thomson CA. The role of dietary protein intake in the prevention of sarcopenia of aging. Nutr Clin Pract. 2013; 28:684–690. PMID: 24163319.
Article16. Kang SY, Lim GE, Kim YK, et al. Association between sarcopenic obesity and metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women: a cross-sectional study based on the Korean national health and nutritional examination surveys from 2008 to 2011. J Bone Metab. 2017; 24:9–14. PMID: 28326296.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity
- Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity
- Prevalence of Sarcopenic Obesity in Various Comorbidities, Diagnostic Markers, and Therapeutic Approaches: A Review
- Health-related quality of life in older Koreans: a HINT-8-based cross-sectional analysis of obesity, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity using the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sarcopenic obesity can be negatively associated with active physical activity and adequate intake of some nutrients in Korean elderly: Findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2008–2011)